|
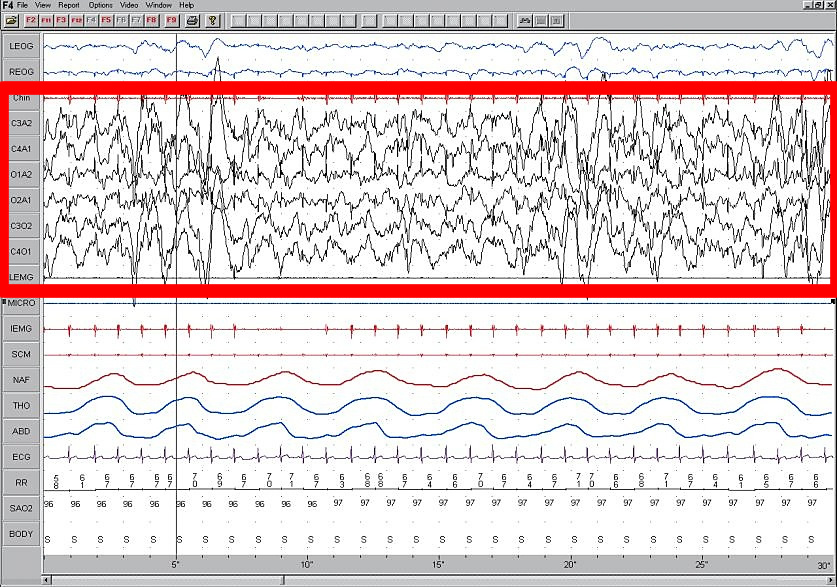
Sensorimotor Rhythm
The sensorimotor rhythm (SMR) is a brain wave. It is an oscillatory idle rhythm of synchronized electric brain activity. It appears in spindles in recordings of EEG, MEG, and ECoG over the sensorimotor cortex. For most individuals, the frequency of the SMR is in the range of 7 to 11 Hz. Meaning The meaning of SMR is not fully understood. Phenomenologically, a person is producing a stronger SMR amplitude when the corresponding sensorimotor areas are idle, e.g. during states of immobility. SMR typically decreases in amplitude when the corresponding sensory or motor areas are activated, e.g. during motor tasks and even during motor imagery. Conceptually, SMR is sometimes mixed up with alpha waves of occipital origin, the strongest source of neural signals in the EEG. One reason might be, that without appropriate spatial filtering the SMR is very difficult to detect because it is usually flooded by the stronger occipital alpha waves. The feline SMR has been noted as bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eeg SMR
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The bio signals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex and allocortex. It is typically non-invasive, with the EEG electrodes placed along the scalp (commonly called "scalp EEG") using the International 10–20 system, or variations of it. Electrocorticography, involving surgical placement of electrodes, is sometimes called "intracranial EEG". Clinical interpretation of EEG recordings is most often performed by visual inspection of the tracing or quantitative EEG analysis. Voltage fluctuations measured by the EEG bio amplifier and electrodes allow the evaluation of normal brain activity. As the electrical activity monitored by EEG originates in neurons in the underlying brain tissue, the recordings made by the electrodes on the surface of the scalp vary in accordance with their orienta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurofeedback
Neurofeedback is a form of biofeedback that uses electrical potentials in the brain to reinforce desired brain states through operant conditioning. This process is non-invasive neurotherapy and typically collects brain activity data using electroencephalography (EEG). Several neurofeedback protocols exist, with potential additional benefit from use of quantitative electroencephalography (QEEG) or functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to localize and personalize treatment. Related technologies include Functional near-infrared spectroscopy, functional near-infrared spectroscopy-mediated (fNIRS) neurofeedback, hemoencephalography biofeedback (HEG), and fMRI biofeedback. Neurofeedback is FDA-cleared for PTSD treatment, and training for ADHD and major depressive disorder shows promising results. It has been shown to trigger positive behavioral outcomes, such as relieving symptoms related to psychiatric disorders or improving specific cognitive functions in healthy participants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motor Control
Motor control is the regulation of movements in organisms that possess a nervous system. Motor control includes conscious voluntary movements, subconscious muscle memory and involuntary reflexes, as well as instinctual taxes. To control movement, the nervous system must integrate multimodal sensory information (both from the external world as well as proprioception) and elicit the necessary signals to recruit muscles to carry out a goal. This pathway spans many disciplines, including multisensory integration, signal processing, coordination, biomechanics, and cognition, and the computational challenges are often discussed under the term sensorimotor control. Successful motor control is crucial to interacting with the world to carry out goals as well as for posture, balance, and stability. Some researchers (mostly neuroscientists studying movement, such as Daniel Wolpert and Randy Flanagan) argue that motor control is the reason brains exist at all. Neural control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electroencephalography
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignal, bio signals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex and allocortex. It is typically non-invasive, with the EEG electrodes placed along the scalp (commonly called "scalp EEG") using the 10–20 system (EEG), International 10–20 system, or variations of it. Electrocorticography, involving surgical placement of electrodes, is sometimes called Electrocorticography, "intracranial EEG". Clinical interpretation of EEG recordings is most often performed by visual inspection of the tracing or quantitative EEG, quantitative EEG analysis. Voltage fluctuations measured by the EEG bioamplifier, bio amplifier and electrodes allow the evaluation of normal Brain activity and meditation, brain activity. As the electrical activity monitored by EEG originates in neurons in the underlying Huma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Wave
A gamma wave or gamma rhythm is a pattern of neural oscillation in humans with a frequency between 30 and 100 Hz, the 40 Hz point being of particular interest. Gamma waves with frequencies between 30 and 70 hertz may be classified as low gamma, and those between 70 and 150 hertz as high gamma. Gamma rhythms are correlated with large-scale brain network activity and cognitive phenomena such as working memory, attention, and perceptual grouping, and can be increased in amplitude via meditation or neurostimulation. Altered gamma activity has been observed in many mood and cognitive disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, epilepsy, and schizophrenia. Discovery Gamma waves can be detected by electroencephalography or magnetoencephalography. One of the earliest reports of gamma wave activity was recorded from the visual cortex of awake monkeys. Subsequently, significant research activity has concentrated on gamma activity in visual cortex. Gamma activity has also been detect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Wave
Beta waves, or beta rhythm, are neural oscillations (brainwaves) in the brain with a frequency range of between 12.5 and 30 Hz (12.5 to 30 cycles per second). Several different rhythms coexist, with some being inhibitory and others excitory in function. Beta waves can be split into three sections: Low Beta Waves (12.5–16 Hz, "Beta 1"); Beta Waves (16.5–20 Hz, "Beta 2"); and High Beta Waves (20.5–28 Hz, "Beta 3"). Beta states are the states associated with normal waking consciousness. History Beta waves were discovered and named by the German psychiatrist Hans Berger, who invented electroencephalography (EEG) in 1924, as a method of recording electrical brain activity from the human scalp. Berger termed the larger amplitude, slower frequency waves that appeared over the posterior scalp when the subject's eye were closed alpha waves. The smaller amplitude, faster frequency waves that replaced alpha waves when the subject opened their eye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mu Wave
The sensorimotor mu rhythm, also known as mu wave, comb or wicket rhythms or arciform rhythms, are synchronized patterns of electrical activity involving large numbers of neurons, probably of the pyramidal type, Motor cortex, in the part of the brain that controls voluntary movement. These patterns as measured by electroencephalography (EEG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), or electrocorticography (ECoG), repeat at a frequency of 7.5–12.5 (and primarily 9–11) Hertz, Hz, and are most prominent when the body is physically at rest. Unlike the alpha wave, which occurs at a similar frequency over the resting visual cortex at the back of the scalp, the mu rhythm is found over the motor cortex, in a band approximately from ear to ear. People suppress mu rhythms when they perform motor actions or, with practice, when they visualize performing motor actions. This suppression is called wikt:desynchronization, desynchronization of the wave because EEG wave forms are caused by large numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Wave
Alpha waves, or the alpha rhythm, are neural oscillations in the frequency range of 8–12 Hz likely originating from the synchronous and coherent ( in phase or constructive) neocortical neuronal electrical activity possibly involving thalamic pacemaker cells. Historically, they are also called "Berger's waves" after Hans Berger, who first described them when he invented the EEG in 1924. Alpha waves are one type of brain waves detected by electrophysiological methods, e.g., electroencephalography (EEG) or magnetoencephalography (MEG), and can be quantified using power spectra and time-frequency representations of power like quantitative electroencephalography (qEEG). They are predominantly recorded over parieto-occipital brain and were the earliest brain rhythm recorded in humans. Alpha waves can be observed during relaxed wakefulness, especially when there is no mental activity. During the eyes-closed condition, alpha waves are prominent at parietal locations. Atte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theta Wave
Theta waves generate the theta rhythm, a neural oscillation in the brain that underlies various aspects of cognition and behavior, including learning, memory, and spatial navigation in many animals. It can be recorded using various electrophysiological methods, such as electroencephalogram (EEG), recorded either from inside the brain or from electrodes attached to the scalp. At least two types of theta rhythm have been described. The hippocampal theta rhythm is a strong oscillation that can be observed in the hippocampus and other brain structures in numerous species of mammals including rodents, rabbits, dogs, cats, and marsupials. ''"Cortical theta rhythms"'' are low-frequency components of scalp EEG, usually recorded from humans. Theta rhythms can be quantified using quantitative electroencephalography (qEEG) using freely available toolboxes, such as, EEGLAB or the Neurophysiological Biomarker Toolbox (NBT). In rats, theta wave rhythmicity is easily observed in the hipp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta Wave
Delta waves are high amplitude neural oscillations with a frequency between 0.5 and 4 hertz. Delta waves, like other brain waves, can be recorded with electroencephalography (EEG) and are usually associated with the deep stage 3 of NREM sleep, also known as slow-wave sleep (SWS), and aid in characterizing the depth of sleep. Suppression of delta waves leads to inability of body rejuvenation, brain revitalization and poor sleep. Background and history "Delta waves" were first described in the 1930s by W. Grey Walter, who improved upon Hans Berger's electroencephalograph machine (EEG) to detect alpha and delta waves. Delta waves can be quantified using quantitative electroencephalography. Classification and features Delta waves, like all brain waves, can be detected by electroencephalography (EEG). Delta waves were originally defined as having a frequency between 1 and 4 Hz, although more recent classifications put the boundaries at between 0.5 and 2 Hz. They ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klaus-Robert Müller
Klaus-Robert Müller (born 1964 in Karlsruhe, West Germany) is a German computer scientist and physicist, most noted for his work in machine learning and brain–computer interfaces. Career Klaus-Robert Müller received his Diplom in mathematical physics and PhD in theoretical computer science from the University of Karlsruhe. Following his Ph.D. he went to Berlin as a postdoctoral fellow at GMD (German National Research Center for Computer Science) Berlin (now part of Fraunhofer Institute for Open Communication Systems), where he started building up the Intelligent Data Analysis (IDA) group. From 1994 to 1995 he was a research fellow at Shun'ichi Amari's lab at the University of Tokyo. 1999 Müller became an associate professor for neuroinformatics at the University of Potsdam, transitioning to the full professorship for Neural Networks and Time Series Analysis in 2003. Since 2006 he holds the chair for Machine Learning at Technische Universität Berlin. Since 2012 he holds a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain–computer Interface
A brain–computer interface (BCI), sometimes called a brain–machine interface (BMI), is a direct communication link between the brain's electrical activity and an external device, most commonly a computer or robotic limb. BCIs are often directed at researching, Brain mapping, mapping, assisting, Augmented cognition, augmenting, or repairing human Cognitive skill, cognitive or Sensory-motor coupling, sensory-motor functions. They are often conceptualized as a human–machine interface that skips the intermediary of moving body parts (e.g. hands or feet). BCI implementations range from non-invasive (EEG, Magnetoencephalography, MEG, MRI) and partially invasive (ECoG and endovascular) to invasive (microelectrode array), based on how physically close electrodes are to brain tissue. Research on BCIs began in the 1970s by Jacques Vidal at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) under a grant from the National Science Foundation, followed by a contract from the Defense Adva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |