|
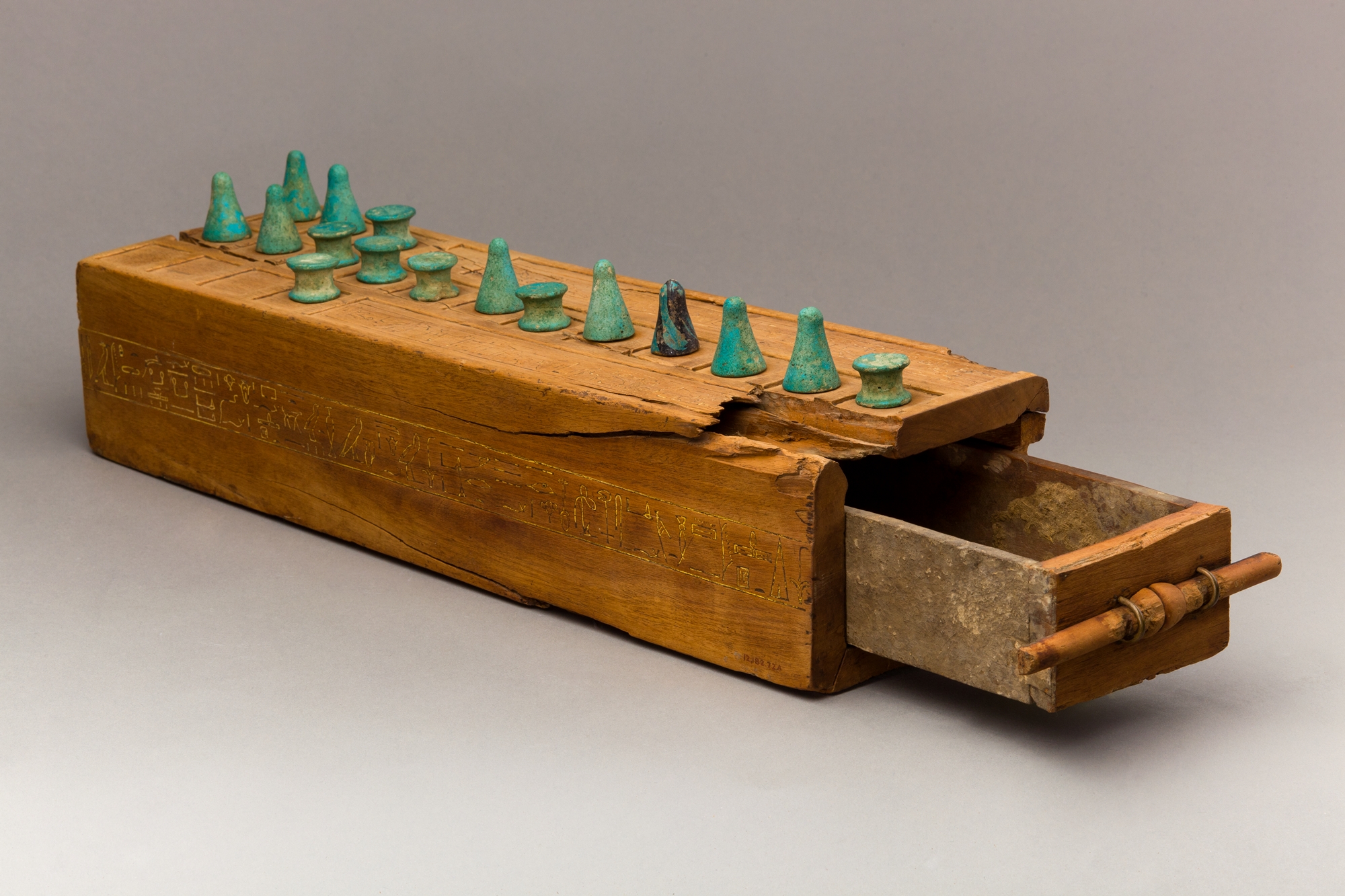
Senet
Senet or senat ( egy, znt, translation=passing; cf. Coptic ⲥⲓⲛⲉ /sinə/ "passing, afternoon") is a board game from ancient Egypt. The earliest representation of senet is dated to E from the Mastaba of Hesy-Re, while similar boards and hieroglyphic signs are found even earlier. The game fell out of use following the Roman period, and its original rules are the subject of conjecture. History Fragmentary boards that could be senet have been found in First Dynasty burials in Egypt, E. The first unequivocal painting of this ancient game is from the Third Dynasty The Third Dynasty of ancient Egypt (Dynasty III) is the first dynasty of the Old Kingdom. Other dynasties of the Old Kingdom include the Fourth, Fifth and Sixth. The capital during the period of the Old Kingdom was at Memphis. Overview Af ... tomb of Hesy (c. 2686–2613 BCE). People are depicted playing senet in a painting in the tomb of Rashepes, as well as from other tombs of the Fifth and Sixth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Board Game
Board games are tabletop games that typically use . These pieces are moved or placed on a pre-marked board (playing surface) and often include elements of table, card, role-playing, and miniatures games as well. Many board games feature a competition between two or more players. To show a few examples: in checkers (British English name 'draughts'), a player wins by capturing all opposing pieces, while Eurogames often end with a calculation of final scores. ''Pandemic'' is a cooperative game where players all win or lose as a team, and peg solitaire is a puzzle for one person. There are many varieties of board games. Their representation of real-life situations can range from having no inherent theme, such as checkers, to having a specific theme and narrative, such as '' Cluedo''. Rules can range from the very simple, such as in snakes and ladders; to deeply complex, as in '' Advanced Squad Leader''. Play components now often include custom figures or shaped counters, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastaba Of Hesy-Re
The Mastaba of Hesy-re is an ancient Egyptian tomb complex in the great necropolis of Saqqara in Egypt. It is the final resting place of the high official Hesy-re, who served in office during the Third Dynasty under King Djoser (Netjerikhet). His large mastaba is renowned for its well-preserved wall paintings and relief panels made from imported Lebanese cedar, which are today considered masterpieces of Old Kingdom wood carving. The mastaba itself is the earliest example of a painted tomb from the Old Kingdom and the only known example from the Third Dynasty. The tomb was excavated by the Egyptologists Auguste Mariette and James Edward Quibell. Discovery and excavation The mastaba of Hesy-re was originally excavated in 1861 by Auguste Mariette and Jacques de Morgan. Mariette quickly discovered the famous niched gallery with its wooden panels and had these valuable artefacts brought to the Egyptian Museum in Cairo. He found the grave shafts empty. In his journal, Mari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tel Arad
Tel Arad ( he, תל ערד), in Arabic Tell 'Arad (تل عراد), is an archaeological tell, or mound, located west of the Dead Sea, about west of the modern Israeli city of Arad in an area surrounded by mountain ridges which is known as the Arad Plain. The site is divided into a lower city and an upper section on a hill. The lower Canaanite settlement and the upper Israelite citadel are now part of the Tel Arad National Park, which has begun projects to restore the walls of the upper and lower sites. Proposed identification It was first identified in modern literature in 1841 by Edward Robinson in his ''Biblical Researches in Palestine'', on account of the similarity of the Arabic place name, Tell 'Arad, with the ''Harad'' in the Book of Joshua. See also Tell Arad in Robinson'name list/ref> Archaeology The upper and lower areas of Tel Arad were excavated during 18 seasons by Ruth Amiran and Yohanan Aharoni between 1962 and 1984.An additional 8 seasons were done on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
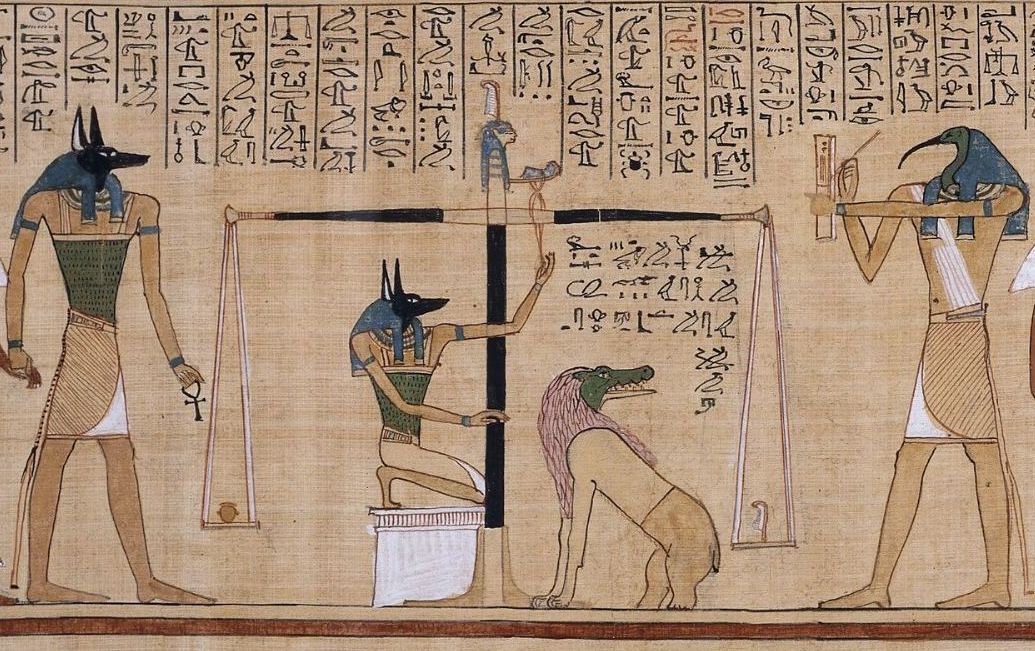
Ancient Egyptian Concept Of The Soul
The ancient Egyptians believed that a soul ( kꜣ and bꜣ; Egypt. pron. ka/ba) was made up of many parts. In addition to these components of the soul, there was the human body (called the ''ḥꜥ'', occasionally a plural '' ḥꜥw'', meaning approximately "sum of bodily parts"). According to ancient Egyptian creation myths, the god Atum created the world out of chaos, utilizing his own magic ( ḥkꜣ). Because the earth was created with magic, Egyptians believed that the world was imbued with magic and so was every living thing upon it. When humans were created, that magic took the form of the soul, an eternal force which resided in and with every human. The concept of the soul and the parts which encompass it has varied from the Old Kingdom to the New Kingdom, at times changing from one dynasty to another, from five parts to more. Most ancient Egyptian funerary texts reference numerous parts of the soul: Collectively, these spirits of a dead person were called the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of The Dead
The ''Book of the Dead'' ( egy, 𓂋𓏤𓈒𓈒𓈒𓏌𓏤𓉐𓂋𓏏𓂻𓅓𓉔𓂋𓅱𓇳𓏤, ''rw n(y)w prt m hrw(w)'') is an ancient Egyptian funerary text generally written on papyrus and used from the beginning of the New Kingdom (around 1550 BCE) to around 50 BCE. The original Egyptian name for the text, transliterated ''rw nw prt m hrw'', is translated as ''Book of Coming Forth by Day'' or ''Book of Emerging Forth into the Light''. "Book" is the closest term to describe the loose collection of texts consisting of a number of magic spells intended to assist a dead person's journey through the '' Duat'', or underworld, and into the afterlife and written by many priests over a period of about 1,000 years. Karl Richard Lepsius introduced for these texts the German name ''Todtenbuch'' (modern spelling ''Totenbuch''), translated to English as Book of the Dead. The ''Book of the Dead'', which was placed in the coffin or burial chamber of the deceased, was part of a tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosicrucian Egyptian Museum
The Rosicrucian Egyptian Museum (REM) is devoted to ancient Egypt, located at Rosicrucian Park in the Rose Garden neighborhood of San Jose, California, United States. It was founded by the Ancient Mystical Order Rosae Crucis (AMORC). The Rosicrucian Order continues to support and expand the museum and its educational and scientific activities. The museum holds the largest collection of ancient Egyptian antiquities in the Western United States,Rachael MyrowWhat Is the Rosicrucian Egyptian Museum and Why Is It in San Jose? ''Kqed.org'', 13 July 2017 and is located next to the Rosicrucian headquarters. History The founder of AMORC, Harvey Spencer Lewis, was a collector of various artifacts with mystical symbolism, some of them from the East. His very first artifact was a small Sekhmet statue. In 1921 he contributed financially to the archaeological excavations at Tel el Amarna (Akhetaten, the capital city of the 18th dynasty pharaoh Akhenaten) of the Egypt Explorations Society of B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Kingdom Of Egypt
The New Kingdom, also referred to as the Egyptian Empire, is the period in ancient Egyptian history between the sixteenth century BC and the eleventh century BC, covering the Eighteenth, Nineteenth, and Twentieth dynasties of Egypt. Radiocarbon dating places the beginning of the New Kingdom between 1570 BC and 1544 BC. The New Kingdom followed the Second Intermediate Period and was succeeded by the Third Intermediate Period. It was Egypt's most prosperous time and marked the peak of its power. The concept of a "New Kingdom" as one of three "golden ages" was coined in 1845 by German Egyptologist Baron von Bunsen, and its definition would evolve significantly throughout the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. The later part of this period, under the Nineteenth and Twentieth dynasties (1292–1069 BC), is also known as the ''Ramesside period''. It is named after the eleven pharaohs who took the name Ramesses, after Ramesses I, the founder of the Nineteenth Dynasty. Possib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levant
The Levant () is an approximation, approximate historical geography, historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is equivalent to a stretch of land bordering the Mediterranean in South-western Asia,Gasiorowski, Mark (2016). ''The Government and Politics of the Middle East and North Africa''. }, ), meaning "the eastern place, where the Sun rises". In the 13th and 14th centuries, the term ''levante'' was used for Italian maritime commerce in the Eastern Mediterranean, including Greece, Anatolia, Syria (region), Syria-Palestine, and Egypt, that is, the lands east of Republic of Venice, Venice. Eventually the term was restricted to the Muslim countries of Syria-Palestine and Egypt. In 1581, England set up the Levant Company to monopolize commerce with the Ottoman Empire. The name ''Levant States'' was used to refer to the Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaming Board Inscribed For Amenhotep III With Separate Sliding Drawer, Ca
Gaming may refer to: Games and sports The act of playing games, as in: * Legalized gambling, playing games of chance for money, often referred to in law as "gaming" * Playing a role-playing game, in which players assume fictional roles * Playing a tabletop game, any game played on a flat surface * Playing a video game, an electronic game with a video interface ** Esports, competing in eSports ** Video game culture Other uses *Gaming, Austria, an Austrian market town and municipality * Gaming the system, manipulating a system's rules to achieve a desired outcome See also * Gamble (other) * Game (other) * Gamer A gamer is a proactive hobbyist who plays interactive games, especially video games, tabletop role-playing games, and skill-based card games, and who plays for usually long periods of time. Some gamers are competitive, meaning they routinely ..., a person who plays games, especially video games * History of games * Online gaming (disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byblos
Byblos ( ; gr, Βύβλος), also known as Jbeil or Jubayl ( ar, جُبَيْل, Jubayl, locally ; phn, 𐤂𐤁𐤋, , probably ), is a city in the Keserwan-Jbeil Governorate of Lebanon. It is believed to have been first occupied between 8800 and 7000BC and continuously inhabited since 5000BC, making it one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. During its history, Byblos was part of numerous civilizations, including Egyptian, Phoenician, Assyrian, Persian, Hellenistic, Roman, Fatimid, Genoese, Mamluk and Ottoman. The city is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. It was in ancient Byblos that the Phoenician alphabet, likely the ancestor of the Greek, Latin and all other Western alphabets, was developed. Etymology Byblos appears as ''Kebny'' in Egyptian hieroglyphic records going back to the 4th-dynasty pharaoh Sneferu (BC) and as () in the Akkadian cuneiform Amarna letters to the 18th-dynasty pharaohs and IV. In the 1stmillenniumBC, its nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Kingdom Of Egypt
In ancient Egyptian history, the Old Kingdom is the period spanning c. 2700–2200 BC. It is also known as the "Age of the Pyramids" or the "Age of the Pyramid Builders", as it encompasses the reigns of the great pyramid-builders of the Fourth Dynasty, such as King Sneferu, who perfected the art of pyramid-building, and the kings Khufu, Khafre and Menkaure, who constructed the pyramids at Giza. Egypt attained its first sustained peak of civilization during the Old Kingdom, the first of three so-called "Kingdom" periods (followed by the Middle Kingdom and New Kingdom), which mark the high points of civilization in the lower Nile Valley. The concept of an "Old Kingdom" as one of three "golden ages" was coined in 1845 by the German Egyptologist Baron von Bunsen, and its definition would evolve significantly throughout the 19th and the 20th centuries. Not only was the last king of the Early Dynastic Period related to the first two kings of the Old Kingdom, but the "capital" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.png)

