|
Semi-peripheral
In world-systems theory, semi-periphery countries are the industrializing, mostly capitalist countries that are positioned between the periphery and the core countries. Semi-periphery countries have organizational characteristics of both core countries and periphery countries and are often geographically located between core and peripheral regions as well as between two or more competing core regions.Chase-Dunn and Thomas D. Hall.''The Seedbed of Change''.Chapter 5 of C. Semi-periphery regions play a major role in mediating economic, political, and social activities that link core and peripheral areas. These regions allow for the possibility of innovative technology, reforms in social and organizational structure, and dominance over peripheral nations. These changes can lead to a semi-periphery country being promoted to a core nation. Semi-periphery is, however, more than a description, as it also serves as a position within the world hierarchy in which social and economic chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Core Countries
In world-systems theory, core countries or the imperial core are the Industrialization, industrialized Capitalism, capitalist and/or Imperialism, imperialist countries. Core countries control and benefit the most resources from the global market. They are usually recognized as Countries by nominal GDP, wealthy states with a wide variety of resources and are in a favorable location compared to other states. They have strong state institutions, a powerful military, and powerful global political alliances. In the 20th-21st centuries they consist of Australia, New Zealand, Canada, Western Europe, Western European countries, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States. The population of the core countries is on average by far the Countries by nominal GDP, wealthiest of the world, with the List of countries by life expectancy, highest life expectancy, List of countries by literacy rate, literacy rate, Education Index, best education and List of countries by social welfare spending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World-systems Theory
World-systems theory (also known as world-systems analysis or the world-systems perspective)Immanuel Wallerstein, (2004), "World-systems Analysis." In ''World System History'', ed. George Modelski, in ''Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems'' (EOLSS), Developed under the Auspices of the UNESCO, Eolss Publishers, Oxford, UK is a multidisciplinary approach to world history and social change which emphasizes the world-system (and not nation states) as the primary (but not exclusive) unit of social analysis. World-systems theorists argue that their theory explains the rise and fall of states, income inequality, social unrest, and imperialism. The "world-system" refers to the inter-regional and transnational division of labor, which divides the world into core countries, semi-periphery countries, and periphery countries. Core countries have higher-skill, capital-intensive industries, and the rest of the world has low-skill, labor-intensive industries and extraction of raw mate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periphery Countries
In world-systems theory, periphery countries are those that are less developed than the semi-periphery and core countries. These countries usually receive a disproportionately small share of global wealth. They have weak state institutions and are dependent on—and, according to some, exploited by— more developed countries. These countries are usually behind because of obstacles such as lack of technology, unstable government, and poor education and health systems. In some instances, the exploitation of periphery countries' agriculture, cheap labor, and natural resources aid core countries in remaining dominant. This is best described by dependency theory,Thomas Shannon. An Introduction to the World-System Perspective. 1996. which is one theory on how globalization can affect the world and the countries in it. It is, however, possible for periphery countries to rise out of their status and move into semi-periphery or core status. This can be done by doing things such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Core Countries
In world-systems theory, core countries or the imperial core are the Industrialization, industrialized Capitalism, capitalist and/or Imperialism, imperialist countries. Core countries control and benefit the most resources from the global market. They are usually recognized as Countries by nominal GDP, wealthy states with a wide variety of resources and are in a favorable location compared to other states. They have strong state institutions, a powerful military, and powerful global political alliances. In the 20th-21st centuries they consist of Australia, New Zealand, Canada, Western Europe, Western European countries, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States. The population of the core countries is on average by far the Countries by nominal GDP, wealthiest of the world, with the List of countries by life expectancy, highest life expectancy, List of countries by literacy rate, literacy rate, Education Index, best education and List of countries by social welfare spending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periphery Countries
In world-systems theory, periphery countries are those that are less developed than the semi-periphery and core countries. These countries usually receive a disproportionately small share of global wealth. They have weak state institutions and are dependent on—and, according to some, exploited by— more developed countries. These countries are usually behind because of obstacles such as lack of technology, unstable government, and poor education and health systems. In some instances, the exploitation of periphery countries' agriculture, cheap labor, and natural resources aid core countries in remaining dominant. This is best described by dependency theory,Thomas Shannon. An Introduction to the World-System Perspective. 1996. which is one theory on how globalization can affect the world and the countries in it. It is, however, possible for periphery countries to rise out of their status and move into semi-periphery or core status. This can be done by doing things such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongols
Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China ( Inner Mongolia and other 11 autonomous territories), as well as the republics of Buryatia and Kalmykia in Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of Mongolic peoples. The Oirats and the Buryats are classified either as distinct ethno-linguistic groups or as subgroups of Mongols. The Mongols are bound together by a common heritage and ethnic identity, descending from the Proto-Mongols. Their indigenous dialects are collectively known as the Mongolian language. The contiguous geographical area in which the Mongols primarily live is referred to as the Mongol heartland, especially in discussions of the Mongols' history under the Mongol Empire. Definition Broadly defined, the term includes the Mongols proper (also known as the Khalkha Mongols), Buryats, Oirats, the Kalmyks and the Southern Mongols. The latter comprises the Abaga Mongols, Abaganar, Aohans, Arkhorchin, Asud, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Functionalism
Structural functionalism, or simply functionalism, is "a framework for building theory that sees society as a complex system whose parts work together to promote solidarity and stability". This approach looks at society through a macro-level orientation, which is a broad focus on the social structures that shape society as a whole, and believes that society has evolved like organisms. This approach looks at both social structure and social functions. Functionalism addresses society as a whole in terms of the function of its constituent elements; namely norms, customs, traditions, and institutions. A common analogy called the organic or biological analogy, popularized by Herbert Spencer, presents these parts of society as human body "organs" that work toward the proper functioning of the "body" as a whole. In the most basic terms, it simply emphasizes "the effort to impute, as rigorously as possible, to each feature, custom, or practice, its effect on the functioning of a suppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq. The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western European nations in the early 20th century as a replacement of the term Near East (both were in contrast to the Far East). The term "Middle East" has led to some confusion over its changing definitions. Since the late 20th century, it has been criticized as being too Eurocentrism, Eurocentric. The region includes the vast majority of the territories included in the closely associated definition of West Asia, but without the South Caucasus. It also includes all of Egypt (not just the Sinai Peninsula, Sinai) and all of Turkey (including East Thrace). Most Middle Eastern countries (13 out of 18) are part of the Arab world. The list of Middle Eastern countries by population, most populous countries in the region are Egypt, Turkey, and Iran, whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
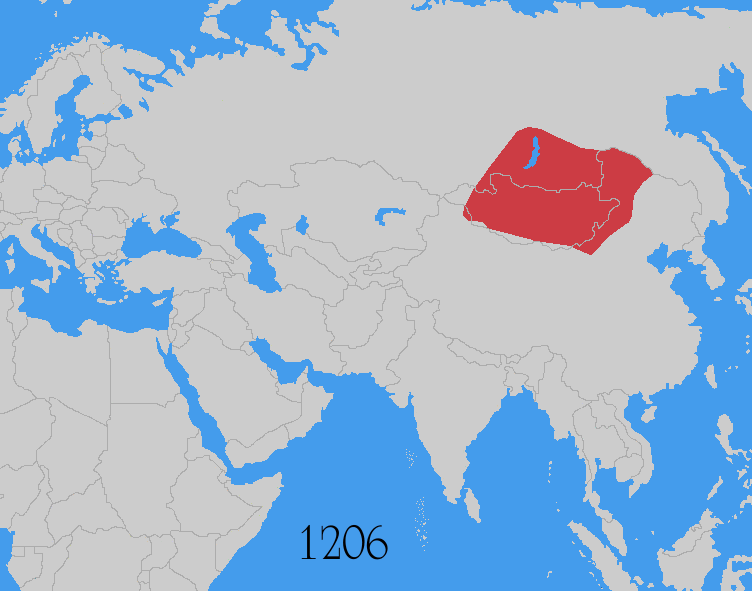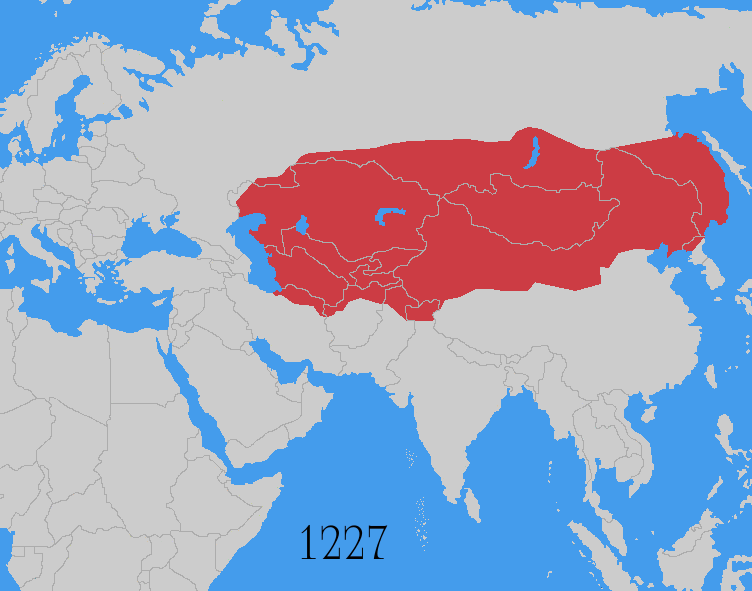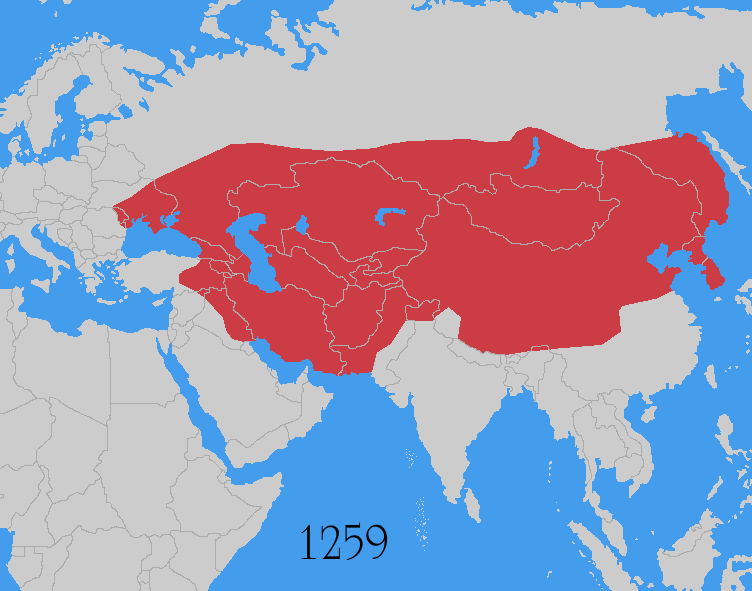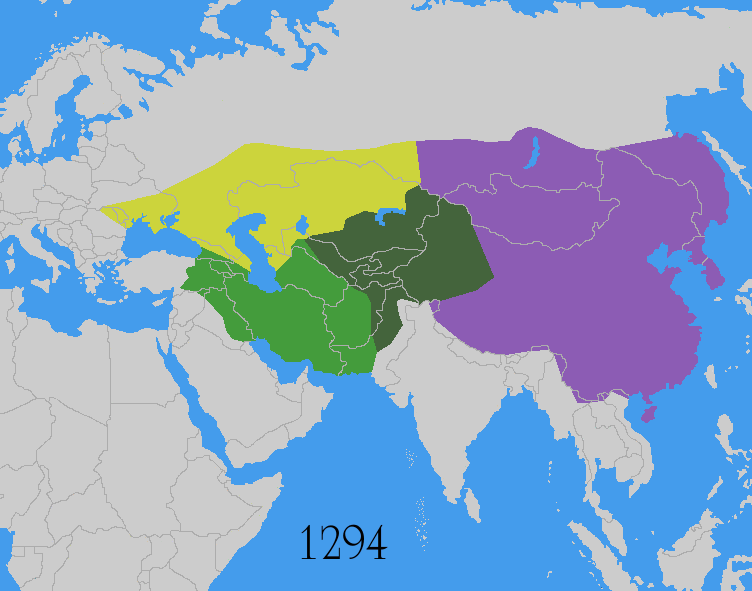
Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire was the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in human history, history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, extending northward into parts of the Arctic; eastward and southward into parts of the Indian subcontinent, mounting invasions of Southeast Asia, and conquering the Iranian plateau; and reaching westward as far as the Levant and the Carpathian Mountains. The Mongol Empire emerged from the unification of several nomad, nomadic tribes in the Mongol heartland under the leadership of Temüjin, known by the title of Genghis Khan (–1227), whom a council proclaimed as the ruler of all Mongols in 1206. The empire grew rapidly under his rule and that of his descendants, who sent out Mongol invasions, invading armies in every direction. The vast transcontinental empire connected the Eastern world, East with the Western world, West, and the Pac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Trade Map
The world is the totality of entities, the whole of reality, or everything that Existence, exists. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique, while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as #Monism and pluralism, one simple object, while others analyze the world as a complex made up of parts. In #Scientific cosmology, scientific cosmology, the world or universe is commonly defined as "the totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". #Theories of modality, Theories of modality talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. #Phenomenology, Phenomenology, starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon, or the "horizon of all horizons". In #Philosophy of mind, philosophy of mind, the world is contrasted with the mind as that which is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market. Traders generally negotiate through a medium of credit or exchange, such as money. Though some economists characterize barter (i.e. trading things without the use of money) as an early form of trade, money was invented before written history began. Consequently, any story of how money first developed is mostly based on conjecture and logical inference. Letters of credit, paper money, and non-physical money have greatly simplified and promoted trade as buying can be separated from selling, or earning. Trade between two traders is called bilateral trade, while trade involving more than two traders is called multilateral trade. In one modern view, trade exists due to specialization and the division of labor, a predominant form of economic activity in which individuals and groups ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |