|
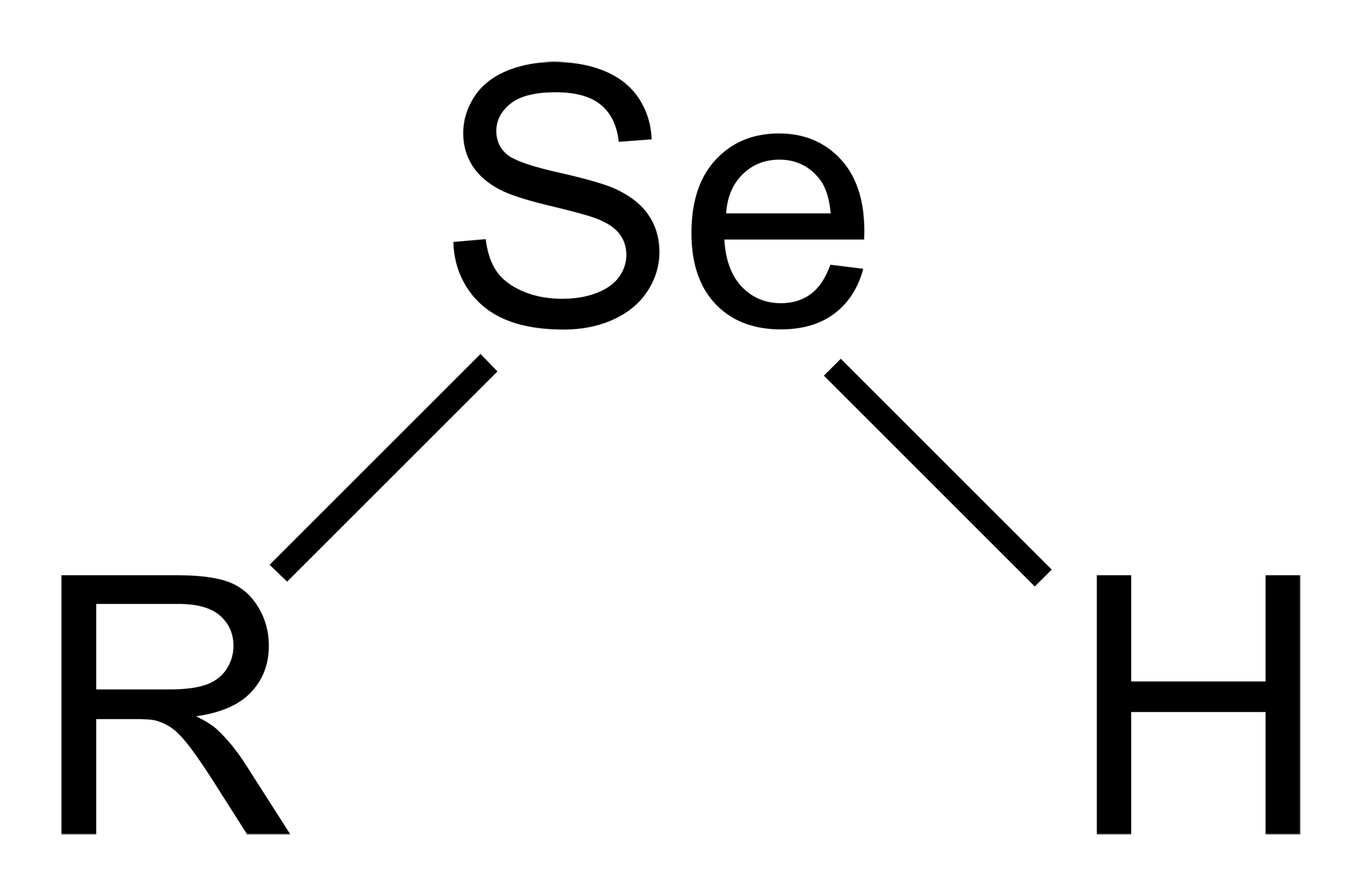
Selenol
Selenols are organic compounds that contain the functional group with the connectivity . Selenols are sometimes also called selenomercaptans and selenothiols. Selenols are one of the principal classes of organoselenium compounds. A well-known selenol is the amino acid selenocysteine. Structure and properties Selenols are structurally similar to thiols, but the bond is about 8% longer at 196 pm. The angle approaches 90°. The bonding involves almost pure p-orbitals on Se, hence the near 90 angles. The bond energy is weaker than the bond, consequently selenols are easily oxidized and serve as H-atom donors. The Se-H bond is weaker than the bond as reflected in their respective bond dissociation energy (BDE). For , the BDE is 326 kJ/mol, while for , the BDE is 368 kJ/mol. Selenols are about 1000 times stronger acids than thiols: the p''K''a of is 5.2 vs 8.3 for . Deprotonation affords the selenolate anion, , most examples of which are highly nucleophilic and rapidly o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selenocysteine
Selenocysteine (symbol Sec or U, in older publications also as Se-Cys) is the 21st proteinogenic amino acid. Selenoproteins contain selenocysteine residues. Selenocysteine is an analogue of the more common cysteine with selenium in place of the sulfur. Selenocysteine is present in several enzymes (for example glutathione peroxidases, tetraiodothyronine 5 deiodinase, tetraiodothyronine 5′ deiodinases, thioredoxin reductases, formate dehydrogenases, glycine reductases, selenophosphate synthetase 2, methionine-''R''-sulfoxide reductase B1 (SEPX1), and some hydrogenases). It occurs in all three Domain (biology), domains of life, including important enzymes (listed above) present in humans. Selenocysteine was discovered in 1974 by biochemist Thressa Stadtman at the National Institutes of Health. Chemistry Selenocysteine is the Se-analogue of cysteine. It is rarely encountered outside of living tissue (nor is it available commercially) because of its high susceptiblility to air-oxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selenenic Acid
A selenenic acid is an organoselenium compound and an oxoacid with the general formula RSeOH, where R ≠ H. It is the first member of the family of organoselenium oxoacids, which also include seleninic acids and selenonic acids, which are RSeO2H and RSeO3H, respectively. Selenenic acids derived from selenoenzymes are thought to be responsible for the antioxidant activity of these enzymes. This functional group is called ''SeO''-selenoperoxol in recent nomenclature. Properties In contrast to selenonic and seleninic acids, selenenic acids are unstable with respect to a self-condensation reaction to form the corresponding selenoseleninates or disproportionation into corresponding seleninic acids and diselenides: :4 RSeOH → 2 RSe(O)SeR + 2 H2O :4 RSeOH → 2 RSeO2H + RSeSeR Even the very bulky 2,4,6-tri-''tert''-butylbenzeneselenenic acid disproportionates readily. A stable selenenic acid was synthesized by burying the SeOH functional group within the cavity of a Calixarene, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organoselenium Compound
Organoselenium chemistry is the science exploring the properties and reactivity of organoselenium compounds, chemical compounds containing carbon-to-selenium chemical bonds. Selenium belongs with oxygen and sulfur to the group 16 elements or chalcogens, and similarities in chemistry are to be expected. Organoselenium compounds are found at trace levels in ambient waters, soils and sediments. Selenium can exist with oxidation state −2, +2, +4, +6. Se(II) is the dominant form in organoselenium chemistry. Down the group 16 column, the bond strength becomes increasingly weaker (234 kilojoule, kJ/mole (unit), mol for the bond and 272 kJ/mol for the bond) and the bond lengths longer ( 198 pm, 181 pm and 141 pm). Selenium compounds are more nucleophilic than the corresponding sulfur compounds and also more acidic. The pKa, p''K''a values of are 16 for oxygen, 7 for sulfur and 3.8 for selenium. In contrast to sulfoxides, the corresponding selenoxides are unstable in the presence of � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzeneselenol
Benzeneselenol, also known as selenophenol, is the organoselenium compound with the chemical formula , often abbreviated PhSeH. It is the selenium analog of phenol. This colourless, malodorous compound is a reagent in organic synthesis. Synthesis Benzeneselenol is prepared by the reaction of phenylmagnesium bromide and selenium: :PhMgBr + Se → PhSeMgBr :PhSeMgBr + HCl → PhSeH + MgBrCl Since benzeneselenol does not have a long shelf life, it is often generated in situ. A common method is by reduction of diphenyldiselenide. A further reason for this conversion is that often, it is the anion that is sought. Reactions More so than thiophenol, benzeneselenol is easily oxidized by air. The facility of this reaction reflects the weakness of the Se-H bond, bond dissociation energy of which is estimated to be between 67 and 74 kcal/mol. In contrast, the S-H BDE for thiophenol is near 80 kcal/mol. The product is diphenyl diselenide as shown in this idealized equation: : The presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methaneselenol
Methaneselenol is the organoselenium compound with the formula . It is the simplest selenol. A colorless, poisonous gas, it is notorious for its foul, putrid odor. It is prepared by reaction of methyl lithium or a methyl Grignard reagent with selenium followed by protonation of the product. The compound is a metabolite. According to IR spectroscopy, νSe-H = 2342 cm−1. For the other homologues, νE-H = 1995 (E = Te), 2606 (E = S), and 3710 cm−1 (E = O) for methanetellurol, methanethiol, and methanol Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical compound and the simplest aliphatic Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with the chemical formula (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often ab ....{{cite journal , doi=10.1080/00945717708069709, title=The Synthesis and the Raman and Infrared Spectra of Methanetellurol, year=1977, last1=Hamada, first1=K., last2=Morishita, first2=H., journal=Synthesis and Reactivity i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van Der Waals Bond
In molecular physics and chemistry, the van der Waals force (sometimes van der Waals' force) is a distance-dependent interaction between atoms or molecules. Unlike ionic or covalent bonds, these attractions do not result from a chemical electronic bond; they are comparatively weak and therefore more susceptible to disturbance. The van der Waals force quickly vanishes at longer distances between interacting molecules. Named after Dutch physicist Johannes Diderik van der Waals, the van der Waals force plays a fundamental role in fields as diverse as supramolecular chemistry, structural biology, polymer science, nanotechnology, surface science, and condensed matter physics. It also underlies many properties of organic compounds and molecular solids, including their solubility in polar and non-polar media. If no other force is present, the distance between atoms at which the force becomes repulsive rather than attractive as the atoms approach one another is called the van der W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deprotonation
Deprotonation (or dehydronation) is the removal (transfer) of a proton (or hydron, or hydrogen cation), (H+) from a Brønsted–Lowry acid in an acid–base reaction.Henry Jakubowski, Biochemistry Online Chapter 2A3, https://employees.csbsju.edu/hjakubowski/classes/ch331/protstructure/PS_2A3_AA_Charges.html, accessed 12/2/2020 The species formed is the conjugate base of that acid. The complementary process, when a proton is added (transferred) to a Brønsted–Lowry base, is protonation (or hydronation). The species formed is the conjugate acid of that base. A species that can either accept or donate a proton is referred to as amphiprotic. An example is the H2O (water) molecule, which can gain a proton to form the hydronium ion, H3O+, or lose a proton, leaving the hydroxide ion, OH−. The relative ability of a molecule to give up a proton is measured by its p''K''a value. A low p''K''a value indicates that the compound is acidic and will easily give up its proton to a base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons (e.g. K+ ( potassium ion)) while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons (e.g. Cl− ( chloride ion) and OH− ( hydroxide ion)). Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed ''monatomic ions'', ''atomic ions'' or ''simple ions'', while ions consisting of two or more atoms are termed polyatomic ions or ''molecular ions''. If only a + or − is present, it indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleophilic
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are Lewis bases. ''Nucleophilic'' describes the affinity of a nucleophile to bond with positively charged atomic nuclei. Nucleophilicity, sometimes referred to as nucleophile strength, refers to a substance's nucleophilic character and is often used to compare the affinity of atoms. Neutral nucleophilic reactions with solvents such as alcohols and water are named solvolysis. Nucleophiles may take part in nucleophilic substitution, whereby a nucleophile becomes attracted to a full or partial positive charge, and nucleophilic addition. Nucleophilicity is closely related to basicity. The difference between the two is, that basicity is a thermodynamic property (i.e. relates to an equilibrium state), but nucleophilicity is a kinetic property ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjugate Base
A conjugate acid, within the Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, is a chemical compound formed when an acid gives a proton () to a base—in other words, it is a base with a hydrogen ion added to it, as it loses a hydrogen ion in the reverse reaction. On the other hand, a conjugate base is what remains after an acid has donated a proton during a chemical reaction. Hence, a conjugate base is a substance formed by the removal of a proton from an acid, as it can gain a hydrogen ion in the reverse reaction. Because some acids can give multiple protons, the conjugate base of an acid may itself be acidic. In summary, this can be represented as the following chemical reaction: \text + \text \; \ce \; \text + \text Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted and Martin Lowry introduced the Brønsted–Lowry theory, which said that any compound that can give a proton to another compound is an acid, and the compound that receives the proton is a base. A proton is a subatomic particle in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Synthesis
Organic synthesis is a branch of chemical synthesis concerned with the construction of organic compounds. Organic compounds are molecules consisting of combinations of covalently-linked hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms. Within the general subject of organic synthesis, there are many different types of synthetic routes that can be completed including total synthesis, Enantioselective synthesis, stereoselective synthesis, automated synthesis, and many more. Additionally, in understanding organic synthesis it is necessary to be familiar with the methodology, techniques, and applications of the subject. Total synthesis A total synthesis refers to the complete chemical synthesis of molecules from simple, Precursor (chemistry), natural precursors. Total synthesis is accomplished either via a linear or convergent approach. In a Linear synthesis, ''linear'' synthesis—often adequate for simple structures—several steps are performed sequentially until the molecule is com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |