|
Selenocysteine ''Se''-methyltransferase
Selenocysteine (symbol Sec or U, in older publications also as Se-Cys) is the 21st proteinogenic amino acid. Selenoproteins contain selenocysteine residues. Selenocysteine is an analogue of the more common cysteine with selenium in place of the sulfur. Selenocysteine is present in several enzymes (for example glutathione peroxidases, tetraiodothyronine 5′ deiodinases, thioredoxin reductases, formate dehydrogenases, glycine reductases, selenophosphate synthetase 2, methionine-''R''-sulfoxide reductase B1 (SEPX1), and some hydrogenases). It occurs in all three domains of life, including important enzymes (listed above) present in humans. Selenocysteine was discovered in 1974 by biochemist Thressa Stadtman at the National Institutes of Health. Chemistry Selenocysteine is the Se-analogue of cysteine. It is rarely encountered outside of living tissue (nor is it available commercially) because of its high susceptiblility to air-oxidation. More common is the oxidized derivative s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merck Index
''The Merck Index'' is an encyclopedia of chemical substance, chemicals, pharmaceutical drug, drugs and biomolecule, biologicals with over 10,000 monographs on single substances or groups of related chemical compound, compounds published online by the Royal Society of Chemistry. History The first edition of the Merck's Index was published in 1889 by the German chemical company Merck Group, Emanuel Merck and was primarily used as a sales catalog for Merck's growing list of chemicals it sold. The American subsidiary was established two years later and continued to publish it. During World War I the US government seized Merck's US operations and made it a separate American "Merck" company that continued to publish the Merck Index. In 2012 the Merck Index was licensed to the Royal Society of Chemistry. An online version of The Merck Index, including historic records and new updates not in the print edition, is commonly available through research libraries. It also includes an append ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domain (biology)
In biological taxonomy, a domain ( or ) (Latin: ''regio''), also dominion, superkingdom, realm, or empire, is the highest taxonomic rank of all organisms taken together. It was introduced in the three-domain system of taxonomy devised by Carl Woese, Otto Kandler and Mark Wheelis in 1990. According to the domain system, the tree of life consists of either three domains, Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya, or two domains, Archaea and Bacteria, with Eukarya included in Archaea. In the three-domain model, the first two are prokaryotes, single-celled microorganisms without a membrane-bound nucleus. All organisms that have a cell nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles are included in Eukarya and called eukaryotes. Non-cellular life, most notably the viruses, is not included in this system. Alternatives to the three-domain system include the earlier two-empire system (with the empires Prokaryota and Eukaryota), and the eocyte hypothesis (with two domains of Bacteria and A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
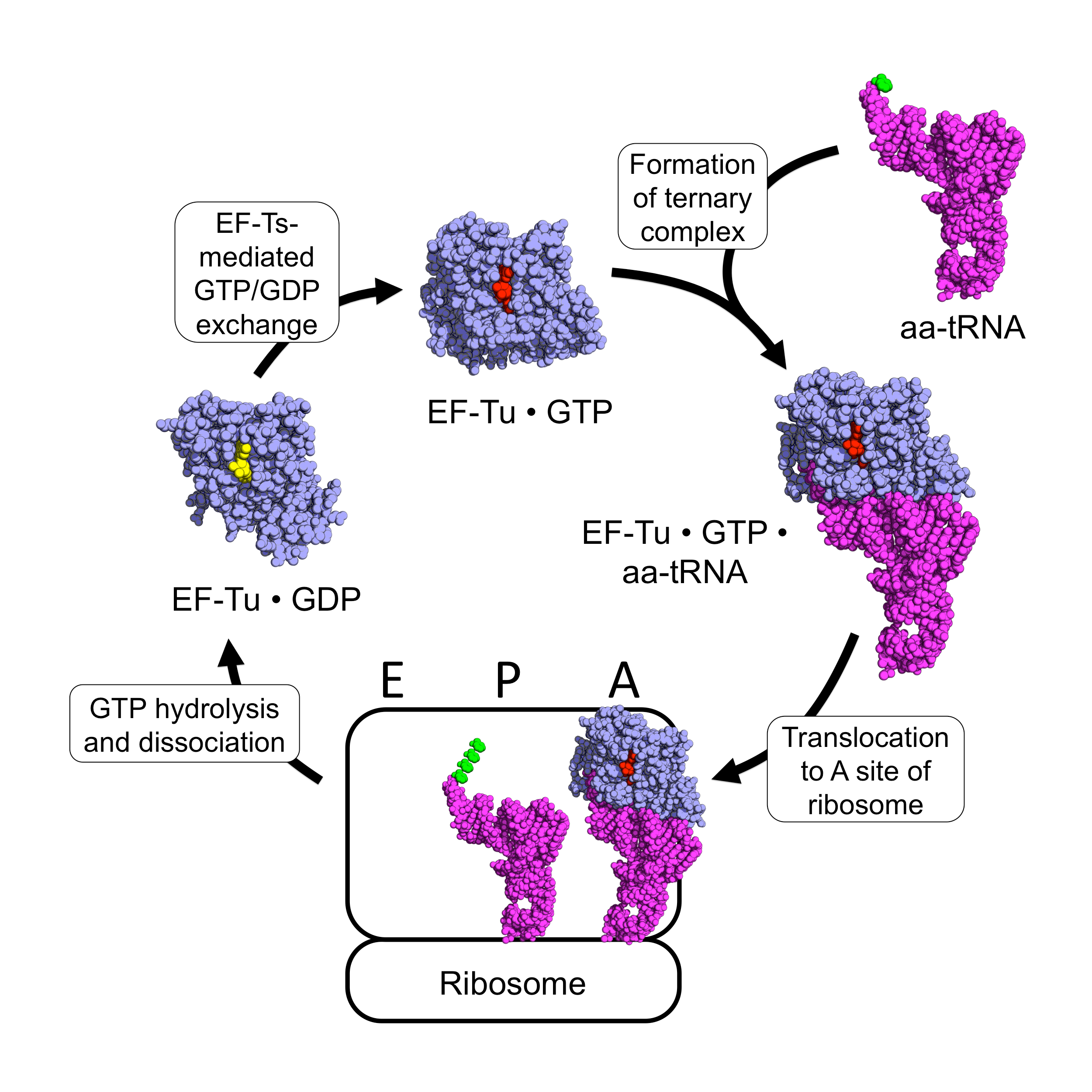
EF-Tu
EF-Tu (elongation factor thermo unstable) is a prokaryotic elongation factor responsible for catalyzing the binding of an aminoacyl-tRNA (aa-tRNA) to the ribosome. It is a G-protein, and facilitates the selection and binding of an aa-tRNA to the A-site of the ribosome. As a reflection of its crucial role in translation, EF-Tu is one of the most abundant and highly conserved proteins in prokaryotes. It is found in eukaryotic mitochondria as TUFM. As a family of elongation factors, EF-Tu also includes its eukaryotic and archaeal homolog, the alpha subunit of eEF-1 (EF-1A). Background Elongation factors are part of the mechanism that synthesizes new proteins through translation in the ribosome. Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) carry the individual amino acids that become integrated into a protein sequence, and have an anticodon for the specific amino acid that they are charged with. Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the genetic information that encodes the primary structure of a protein, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine—tRNA Ligase
In enzymology, a serine—tRNA ligase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :ATP + L-serine + tRNASer \rightleftharpoons AMP + diphosphate + L-seryl-tRNASer The 3 substrates of this enzyme are ATP, L-serine, and tRNA(Ser), whereas its 3 products are AMP, diphosphate, and L-seryl-tRNA(Ser). This enzyme belongs to the family of ligases, to be specific those forming carbon-oxygen bonds in aminoacyl-tRNA and related compounds. The systematic name of this enzyme class is L-serine:tRNASer ligase (AMP-forming). Other names in common use include seryl-tRNA synthetase, SerRS, seryl-transfer ribonucleate synthetase, seryl-transfer RNA synthetase, seryl-transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase, and serine translase. This enzyme participates in glycine, serine and threonine metabolism and aminoacyl-trna biosynthesis. Structural studies As of late 2007, 13 structures A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TRNA
Transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA), formerly referred to as soluble ribonucleic acid (sRNA), is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length (in eukaryotes). In a cell, it provides the physical link between the genetic code in messenger RNA (mRNA) and the amino acid sequence of proteins, carrying the correct sequence of amino acids to be combined by the protein-synthesizing machinery, the ribosome. Each three-nucleotide codon in mRNA is complemented by a three-nucleotide anticodon in tRNA. As such, tRNAs are a necessary component of translation, the biological synthesis of new proteins in accordance with the genetic code. Overview The process of translation starts with the information stored in the nucleotide sequence of DNA. This is first transformed into mRNA, then tRNA specifies which three-nucleotide codon from the genetic code corresponds to which amino acid. Each mRNA codon is recognized by a particular type of tRNA, which docks to it along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Chemical Sciences
The ''Journal of Chemical Sciences'' is a monthly peer-viewed scientific journal that publishes original research articles, rapid communications, reviews and perspective articles, covering many areas of Chemical Sciences. It also publishes special issues on frontier areas of the subject. It is published by the Indian Academy of Sciences and co-published by Springer. The editor-in-chief is S. Natarajan (Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru). History Originally a part of the ''Proceedings of the Indian Academy of Sciences – Section A'', started in 1934, the journal evolved into an independent journal titled ''Proceedings – Chemical Sciences'' in 1978. It was retitled ''Journal of Chemical Sciences'' in 2004. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Jou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selenoprotein
In molecular biology a selenoprotein is any protein that includes a selenocysteine (Sec, U, Se-Cys) amino acid residue. Among functionally characterized selenoproteins are five glutathione peroxidases (GPX) and three thioredoxin reductases, (TrxR/TXNRD) which both contain only one Sec. Selenoprotein P is the most common selenoprotein found in the plasma. It is unusual because in humans it contains 10 Sec residues, which are split into two domains, a longer N-terminal domain that contains 1 Sec, and a shorter C-terminal domain that contains 9 Sec. The longer N-terminal domain is likely an enzymatic domain, and the shorter C-terminal domain is likely a means of safely transporting the very reactive selenium atom throughout the body. Species distribution Selenoproteins exist in all major domains of life, eukaryotes, bacteria and archaea. Among eukaryotes, selenoproteins appear to be common in animals, but rare or absent in other phyla—one has been identified in the green alga '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glyceraldehyde
Glyceraldehyde (glyceral) is a triose monosaccharide with chemical formula C3 H6 O3. It is the simplest of all common aldoses. It is a sweet, colorless, crystalline solid that is an intermediate compound in carbohydrate metabolism. The word comes from combining glycerol and aldehyde, as glyceraldehyde is glycerol with one alcohol group oxidized to an aldehyde. Structure Glyceraldehyde has one chiral center and therefore exists as two different enantiomers with opposite optical rotation: * In the nomenclature, either from Latin ''Dexter'' meaning "right", or from Latin ''Laevo'' meaning "left" * In the R/S nomenclature, either R from Latin ''Rectus'' meaning "right", or S from Latin ''Sinister'' meaning "left" While the optical rotation of glyceraldehyde is (+) for ''R'' and (−) for ''S'', this is not true for all monosaccharides. The stereochemical configuration can only be determined from the chemical structure, whereas the optical rotation can only be determined em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chirality
Chirality () is a property of asymmetry important in several branches of science. The word ''chirality'' is derived from the Greek (''kheir''), "hand", a familiar chiral object. An object or a system is ''chiral'' if it is distinguishable from its mirror image; that is, it cannot be superposed (not to be confused with superimposed) onto it. Conversely, a mirror image of an ''achiral'' object, such as a sphere, cannot be distinguished from the object. A chiral object and its mirror image are called '' enantiomorphs'' (Greek, "opposite forms") or, when referring to molecules, ''enantiomers''. A non-chiral object is called ''achiral'' (sometimes also ''amphichiral'') and can be superposed on its mirror image. The term was first used by Lord Kelvin in 1893 in the second Robert Boyle Lecture at the Oxford University Junior Scientific Club which was published in 1894: Human hands are perhaps the most recognized example of chirality. The left hand is a non-superposable mirror ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
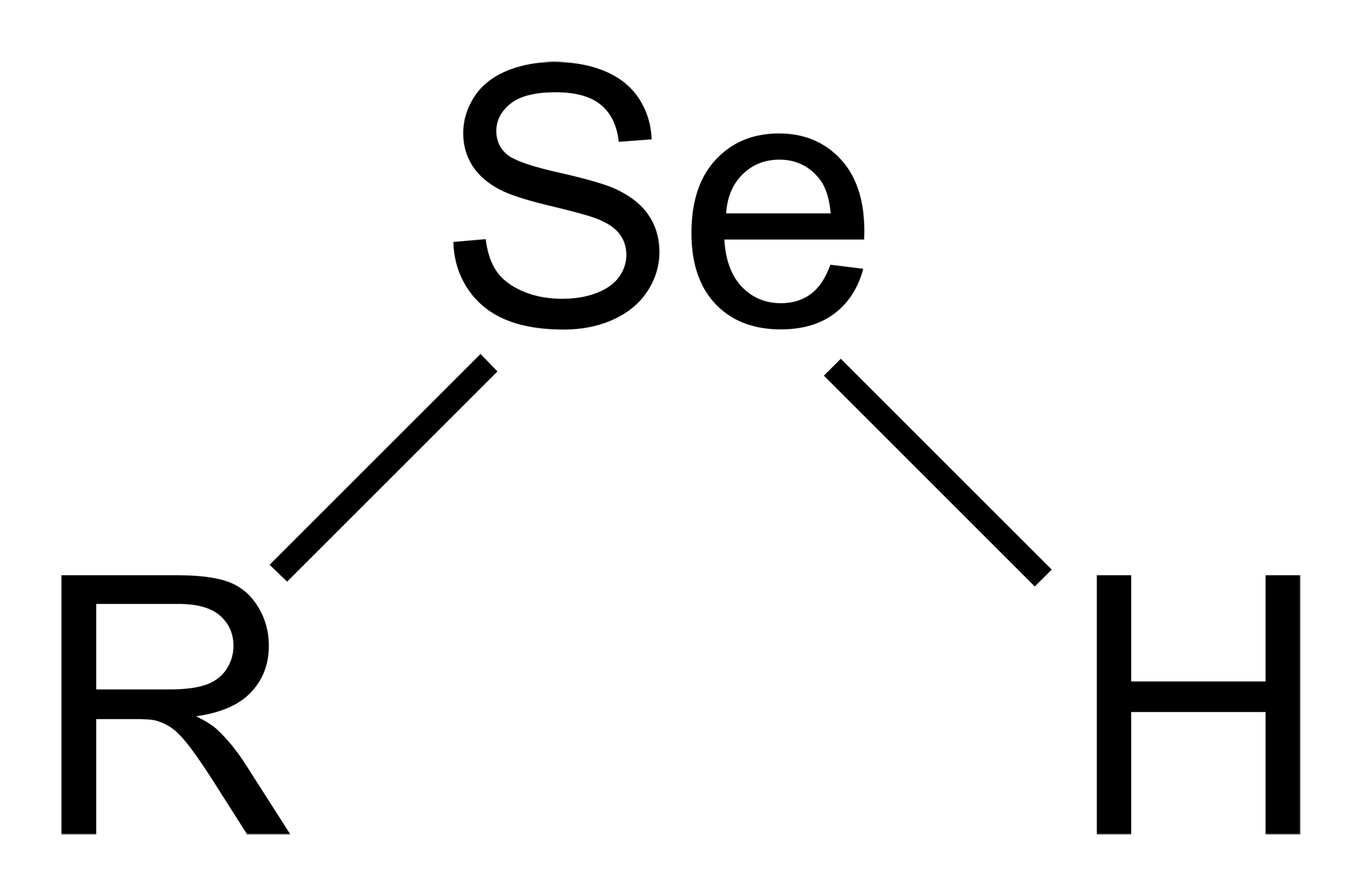
Selenol
Selenols are organic compounds that contain the functional group with the connectivity . Selenols are sometimes also called selenomercaptans and selenothiols. Selenols are one of the principal classes of organoselenium compounds. A well-known selenol is the amino acid selenocysteine. Structure and properties Selenols are structurally similar to thiols, but the bond is about 8% longer at 196 pm. The angle approaches 90°. The bonding involves almost pure p-orbitals on Se, hence the near 90 angles. The bond energy is weaker than the bond, consequently selenols are easily oxidized and serve as H-atom donors. The Se-H bond is weaker than the bond as reflected in their respective bond dissociation energy (BDE). For , the BDE is 326 kJ/mol, while for , the BDE is 368 kJ/mol. Selenols are about 1000 times stronger acids than thiols: the p''K''a of is 5.2 vs 8.3 for . Deprotonation affords the selenolate anion, , most examples of which are highly nucleophilic and rapidly o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deprotonated
Deprotonation (or dehydronation) is the removal (transfer) of a proton (or hydron, or hydrogen cation), (H+) from a Brønsted–Lowry acid in an acid–base reaction.Henry Jakubowski, Biochemistry Online Chapter 2A3, https://employees.csbsju.edu/hjakubowski/classes/ch331/protstructure/PS_2A3_AA_Charges.html, accessed 12/2/2020 The species formed is the conjugate base of that acid. The complementary process, when a proton is added (transferred) to a Brønsted–Lowry base, is protonation (or hydronation). The species formed is the conjugate acid of that base. A species that can either accept or donate a proton is referred to as amphiprotic. An example is the H2O (water) molecule, which can gain a proton to form the hydronium ion, H3O+, or lose a proton, leaving the hydroxide ion, OH−. The relative ability of a molecule to give up a proton is measured by its p''K''a value. A low p''K''a value indicates that the compound is acidic and will easily give up its proton to a base. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acta Crystallographica Section E
''Acta Crystallographica Section E: Crystallographic Communications'' is an open-access structural communications journal. It reports crystal structure determinations of inorganic, metal-organic and organic compounds. Since 2012, ''Acta Crystallogr. E'' has not been included in the Science Citation Index. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: References {{Reflist External links IUCr journals official site Chemistry journals Academic journals established in 1948 English-language journals Wiley-Blackwell academic journals Monthly journals Bimonthly journals Online-only journals Academic journals associated with learned and professional societies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |