|
Screw Sloop
A screw sloop is a propeller-driven sloop-of-war. They were popularized in the mid-19th century, during the introduction of the steam engine and the transition of fleets to this new technology. The sailing sloop The British sloop in the Age of Sail In the Age of Sail, there was a large variety of terms to describe sailing vessels. In British English, the meaning of the term 'sloop' depends on the context. The main source of confusion about the term sloop, is that for commercial vessels, 'sloop' referred and refers to a vessel with a single mast rigged fore-and-aft. If the term referred to a British warship, its meaning was heavily dependent on the number of officers and men on the vessel. Under the rating system of the Royal Navy, any vessel that did not require a post-captain as commander was a sloop. This generally referred to all vessels with fewer than 20 guns. By this system, small frigates that lost most of their guns and sailors so they could be used as transports would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Alaska
Four ships of the United States Navy have been named USS ''Alaska'' in honor of the territory acquired by the United States from Russia in 1867 which later became the state of Alaska: * , a wooden-hulled screw sloop-of-war in commission from 1869 to 1883 that saw numerous small actions * , a steam trawler chartered to serve as a minesweeper during World War I, in commission from 1918 to 1919 * , the lead ship of the of large cruisers, in commission from 1944 to 1947; she saw action in the last days of World War II * , an ''Ohio''-class ballistic missile submarine commissioned in 1986 and currently in service See also * * References * {{DEFAULTSORT:Alaska United States Navy ship names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alecto-class Sloop
The ''Alecto''-class steam vessels (SV3) later reclassed as Third Class Sloops, were designed by Sir William Symonds, the Surveyor of the Navy. The design was approved on 12 April 1839. Initially four vessels were ordered and completed. A fifth unit was ordered (Rattler), but was reordered as a screw propelled vessel. And a sixth unit had been ordered but was requested to be reordered to a different design. The screw driven ''Rattler'' participated in the first of three 'tug o- wars with the ''Alecto''. The vessels all participated during the Russian War. All had gone to the breakers by the mid-1860s. ''Alecto'' was the second named vessel since it was used for a 12-gun fireship, launched by King of Dover on 26 May 1781 and sold in 1802. ''Ardent'' was the fifth named vessel since it was used for a 64-gun third rate, launched at Blaydes of Hull on 13 August 1764, captured by the French off Plymouth on 17 August 1779, recaptured in April 1782 and renamed ''Tiger'' then sold in Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Gannet (1878)
HMS ''Gannet'' is a Royal Navy screw sloop-of-war launched on 31 August 1878. It became a training ship in the Thames in 1903, and was then loaned as a training ship for boys in the Hamble from 1913. It was restored in 1987 and is now part of the UK's National Historic Fleet. Design The ''Doterel'' class were a development of the ''Osprey''-class sloops and were of composite construction, with wooden hulls over an iron frame. The original 1874 design by the Chief Constructor, William Henry White was revised in 1877 by Sir Nathaniel Barnaby and nine were ordered. Of 1,130 tons displacement and approximately 1,100 indicated horsepower, they were armed with two 7" muzzle-loading rifled guns on pivoting mounts, and four 64-pound guns (two on pivoting mounts, and two broadside). They had a crew of around 140 men. Construction ''Gannet'' was laid down at Sheerness Royal Dockyard in 1877 and launched on 31 August 1878. She was commissioned on 17 April 1879, and was classifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
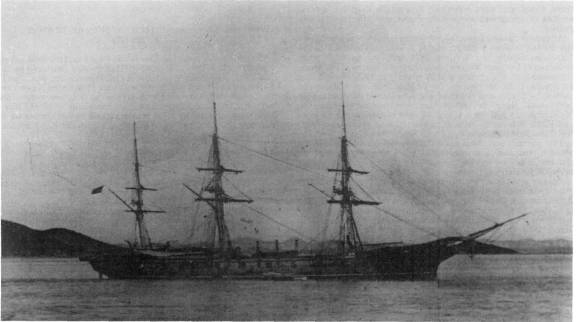
USS Contoocook (1864)
USS ''Contoocook'' was a screw sloop-of-war built for the United States Navy during the American Civil War. She is named after a river and village in New Hampshire. She was launched at Portsmouth Navy Yard and commissioned , commanded by Captain George Balch. Her first cruise, as flagship of the North Atlantic Squadron, took her to the West Indies, where she patrolled extensively for the protection of American interests during 1868 and 1869. Her name was changed to ''Albany'' on . After another cruise to the West Indies in the fall of that year, ''Albany'' was placed out of commission on . She served as a quarantine ship at New York until sold . ''Cootoocook''-class sloop * USS ''Contoocook'' (1864) * * * Cancelled ships include: * * * * The ''Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships The ''Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships'' (''DANFS'') is the official reference work for the basic facts about ships used by the United States Navy. When the writing p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Alaska (1868)
The first USS ''Alaska'' was a wooden-hulled screw sloop of war, built at the Boston Navy Yard and named for the then-newly acquired territory. The ship was launched on 31 October 1868 and sponsored by Miss Grace Hull, the daughter of Mayor Liverus Hull of Charlestown, Boston. ''Alaska'' was commissioned on 8 December 1869, with Commander Homer C. Blake in command. Service history Asiatic Squadron, 1870–1872 On 9 April 1870, ''Alaska'' got underway from New York in company with Rear Admiral John Rodger's flagship, the screw frigate ''Colorado''. However, the two warships soon parted company; and ''Alaska'' steamed independently to the Far East where she visited many of the more important ports to show the flag until May 1871. At that time, ''Alaska'' joined four other ships of the Asiatic Squadron in a visit to Korea in order to secure a treaty to open the " Hermit Kingdom" to the west. The five ships departed Nagasaki, Japan, on 16 May 1871 and arrived at Roze Roads near ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Narragansett (1859)
The first USS ''Narragansett'' was a 2nd class screw sloop in the United States Navy during the American Civil War. ''Narragansett'' was built at the Boston Navy Yard, launched on 15 February 1859, and commissioned on 6 November 1859. Service history Civil War, 1860–1865 ''Narragansett'' operated along the East Coast into the spring of 1860. On 31 March of that year she departed Norfolk, Virginia, for the Pacific, arriving at Valparaíso, Chile, 4 August. Throughout the Civil War she cruised in the Pacific with the primary mission of protecting American mail steamers from Confederate raiders. On 15 December 1864 she departed the Eastern Pacific for the East Coast, arriving at New York City on 18 March 1865. There she remained in ordinary for several years. Gulf of Mexico, 1869 Back in full service in 1869, she was ordered south, to cruise off the Cuban and Floridian coasts. With the outbreak of yellow fever in the ship in the late spring, ''Narragansett'' was ordered to Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Mohican (1859)
The first USS ''Mohican'' was a steam sloop-of-war in the United States Navy during the American Civil War. She was named for the Mohican tribe and was the first ship of her class. ''Mohican'' was laid down by Portsmouth Navy Yard, Kittery, Maine, in August 1858; launched on 15 February 1859; and commissioned on 29 November 1859, Commander Sylvanus William Godon in command. Pre-Civil War African Squadron, 1859–1861 Assigned to the African Squadron, ''Mohican'' departed Portsmouth on 19 January 1860 for the South Atlantic and for the next year and one-half cruised on patrol against pirates and slavers off the coasts of Africa and at times Brazil. On 8 August, the sloop captured the slaver ''Erie'' — commanded by Nathaniel Gordon — off the Congo and forced that ship to unload its captive cargo at Monrovia, Liberia. She remained on station until sailing for home on 13 August 1861. Civil War Battle of Port Royal, 1861 Following her arrival at Boston, Massachusetts on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Brooklyn (1858)
USS ''Brooklyn'' was a sloop-of-war authorized by the U.S. Congress and commissioned in 1859. ''Brooklyn'' was active in Caribbean operations until the start of the American Civil War at which time she became an active participant in the Union blockade of the Confederate States of America. With her one 10-inch gun and twenty 9-inch guns, ''Brooklyn '' was a formidable fighting ship that could deliver damaging broadsides, and served on the Atlantic Ocean coast as well as the Gulf Coast of the United States in intercepting blockade runners. ''Brooklyn'' also served gallantly attacking Confederate forts and other installations on the Mississippi River. Post-war, ''Brooklyn'' remained active, serving for some years in the European theatre, as well as circumnavigating the globe. She was retired in 1889 and sold in 1890 after having well served her country for over three decades. Service history Early career ''Brooklyn'' – the first ship so-named by the U.S. Navy – was th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
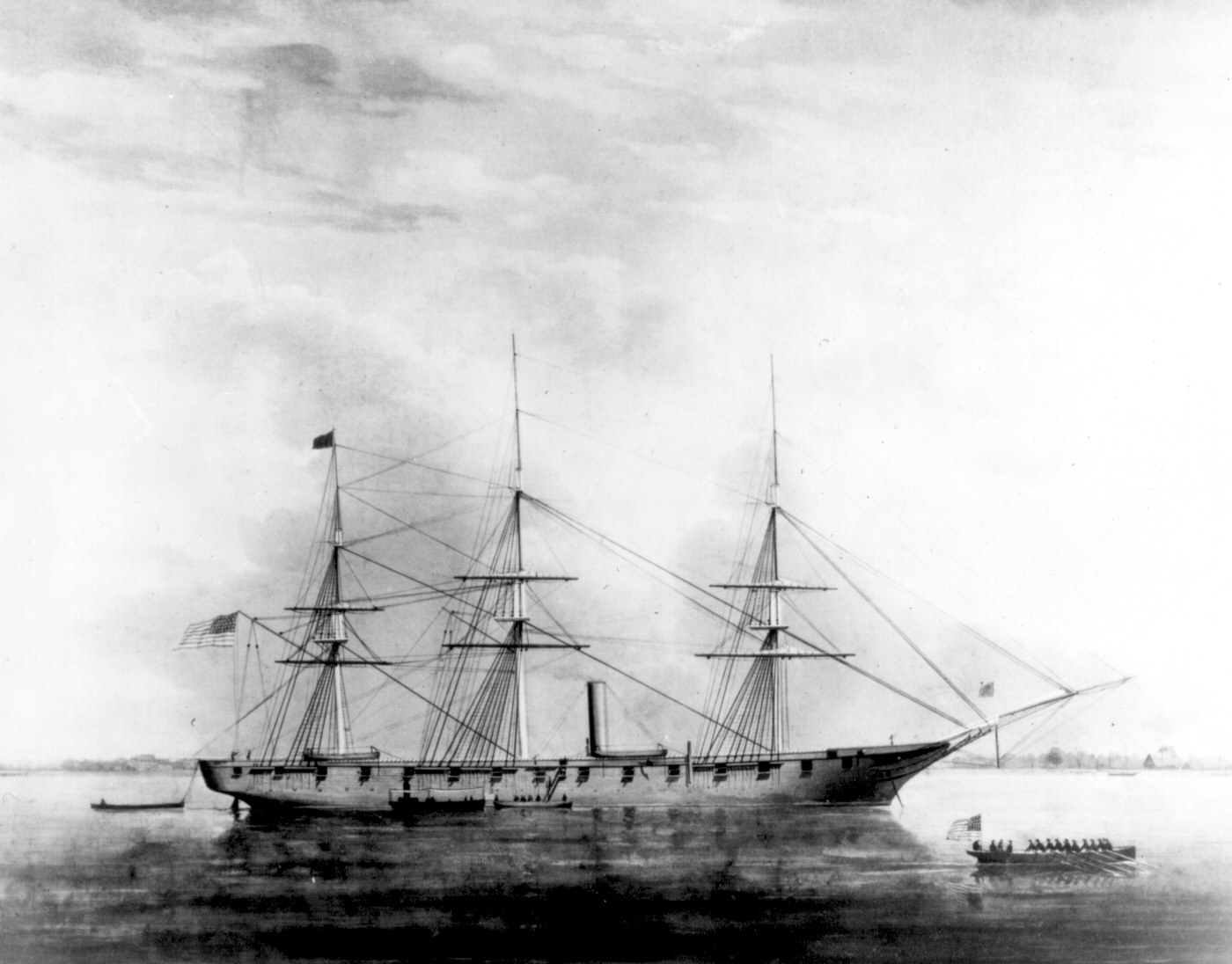
USS Hartford (1858)
USS ''Hartford'', a sloop-of-war Steamship, steamer, was the first ship of the United States Navy named for Hartford, Connecticut, Hartford, the capital of Connecticut. ''Hartford'' served in several prominent campaigns in the American Civil War as the flagship of David G. Farragut, most notably the Battle of Mobile Bay in 1864. She survived until 1956, when she sank awaiting restoration at Norfolk Navy Yard, Norfolk, Virginia. Service history East India Squadron, 1859–1861 ''Hartford'' was launched on 22 November 1858 at the Boston Navy Yard; sponsored by Miss Carrie Downes, Miss Lizzie Stringham, and Lieutenant G. J. H. Preble; and commissioned on 27 May 1859, Captain Charles Lowndes in command. After shakedown out of Boston, the new screw sloop of war, carrying Flag Officer Cornelius Stribling, Cornelius K. Stribling, the newly appointed commander of the East India Squadron, sailed for the Cape of Good Hope and the Far East. Upon reaching the Orient, ''Hartford'' relie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Ericsson
John Ericsson (born Johan Ericsson; July 31, 1803 – March 8, 1889) was a Swedish-American engineer and inventor. He was active in England and the United States. Ericsson collaborated on the design of the railroad steam locomotive Novelty (locomotive), ''Novelty'', which competed in the Rainhill Trials on the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, which were won by inventor George Stephenson's (1781–1848), Stephenson's Rocket, ''Rocket''. Later in North America, he designed the United States Navy's first screw-propelled steam-frigate , in partnership with Captain (later Commodore) Robert F. Stockton (1795–1866) of the United States Navy, U.S. Navy, who unjustly blamed him for a USS_Princeton_(1843)#1844_Peacemaker_accident, fatal accident on the new vessel in 1844. A new partnership with Cornelius H. DeLamater (1821–1889), of the DeLamater Iron Works in New York City resulted in the first armoured ironclad warship equipped with a rotating gun turret, , which dramatically saved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Princeton (1843)
USS ''Princeton'' was a screw steam warship of the United States Navy. Commanded by Captain Robert F. Stockton, ''Princeton'' was launched on September 5, 1843. On February 28, 1844, during a Potomac River pleasure cruise for dignitaries, one gun exploded, killing six people, including Secretary of State Abel P. Upshur and Secretary of the Navy Thomas Walker Gilmer, and injuring others, including a United States Senator and Captain Stockton. The disaster on board the ''Princeton'' killed more top U.S. government officials in one day than any other tragedy in American history. President John Tyler, who was aboard but below decks, was not injured. The ship's reputation in the Navy never recovered. Early history ''Princeton'' was laid down on October 20, 1842, at the Philadelphia Navy Yard as a corvette. The designer of the ship and main supervisor of construction was the Swedish inventor John Ericsson, who later designed . The construction was partly supervised by Captain S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadside (naval)
A broadside is the side of a ship, or more specifically the artillery battery, battery of cannon on one side of a warship or their coordinated fire in naval warfare, or a measurement of a warship's maximum simultaneous firepower which can be delivered upon a single target (because this concentration is usually obtained by firing a broadside). From the 16th century until the early decades of the steamship, vessels had rows of guns set in each side of the hull (watercraft), hull. Firing all guns on one side of the ship became known as a "broadside". The cannon of 18th-century man-of-war, men of war were accurate only at short range, and their penetrating power mediocre, which meant that the thick hulls of wooden ships could only be pierced at short ranges. These wooden ships sailed closer and closer towards each other until cannon fire would be effective. Each tried to be the first to fire a broadside, often giving one party a decisive headstart in the battle when it crippled the oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |