|
Scree Plot
In multivariate statistics, a scree plot is a line plot of the eigenvalues of factors or principal components in an analysis. The scree plot is used to determine the number of factors to retain in an exploratory factor analysis (FA) or principal components to keep in a principal component analysis (PCA). The procedure of finding statistically significant factors or components using a scree plot is also known as a scree test. Raymond B. Cattell introduced the scree plot in 1966. A scree plot always displays the eigenvalues in a downward curve, ordering the eigenvalues from largest to smallest. According to the scree test, the "elbow" of the graph where the eigenvalues seem to level off is found and factors or components to the left of this point should be retained as significant. Etymology The scree plot is named after the elbow's resemblance to a scree in nature. Criticism This test is sometimes criticized for its subjectivity. Scree plots can have multiple "elbows" that make ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scree
Scree is a collection of broken rock fragments at the base of a cliff or other steep rocky mass that has accumulated through periodic rockfall. Landforms associated with these materials are often called talus deposits. The term ''scree'' is applied both to an unstable steep mountain slope composed of rock fragments and other debris, and to the mixture of rock fragments and debris itself. It is loosely synonymous with talus, material that accumulates at the base of a projecting mass of rock, or talus slope, a landform composed of talus. The term ''scree'' is sometimes used more broadly for any sheet of loose rock fragments mantling a slope, while ''talus'' is used more narrowly for material that accumulates at the base of a cliff or other rocky slope from which it has obviously eroded. Scree is formed by rockfall, which distinguishes it from colluvium. Colluvium is rock fragments or soil deposited by rainwash, sheetwash, or slow downhill creep, usually at the base of gentle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
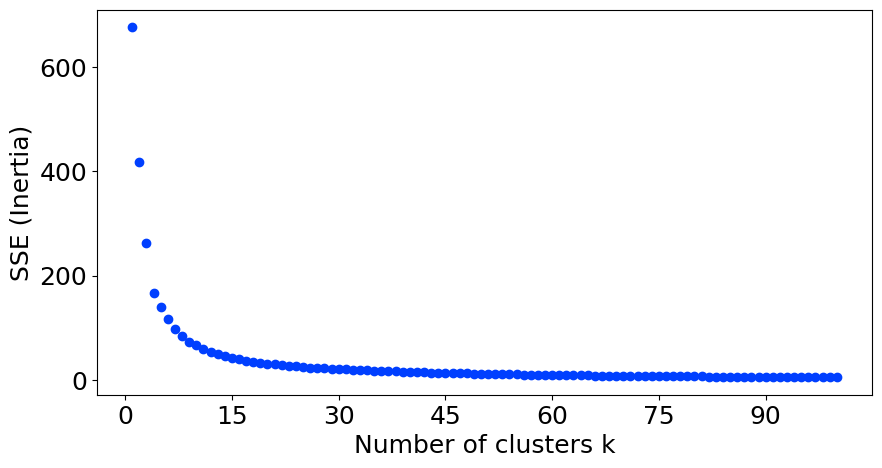
Elbow Method (clustering)
In cluster analysis, the elbow method is a heuristic used in determining the number of clusters in a data set. The method consists of plotting the explained variation as a function of the number of clusters and picking the elbow of the curve as the number of clusters to use. The same method can be used to choose the number of parameters in other data-driven models, such as the number of principal components to describe a data set. The method can be traced to speculation by Robert L. Thorndike in 1953. Intuition Using the "elbow" or "knee of a curve" as a cutoff point is a common heuristic in mathematical optimization to choose a point where diminishing returns are no longer worth the additional cost. In clustering, this means one should choose a number of clusters so that adding another cluster doesn't give much better modeling of the data. The intuition is that increasing the number of clusters will naturally improve the fit (explain more of the variation), since there are mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel Analysis
Parallel analysis, also known as Horn's parallel analysis, is a statistical method used to determine the number of components to keep in a principal component analysis or factors to keep in an exploratory factor analysis. It is named after psychologist John L. Horn, who created the method, publishing it in the journal ''Psychometrika'' in 1965. The method compares the eigenvalues generated from the data matrix to the eigenvalues generated from a Monte-Carlo simulated matrix created from random data of the same size. Evaluation and comparison with alternatives Parallel analysis is regarded as one of the more accurate methods for determining the number of factors or components to retain. In particular, unlike early approaches to dimensionality estimation (such as examining scree plots), parallel analysis has the virtue of an objective decision criterion. Since its original publication, multiple variations of parallel analysis have been proposed. Other methods of determining the num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biplot
Biplots are a type of exploratory graph used in statistics, a generalization of the simple two-variable scatterplot. A biplot overlays a ''score plot'' with a ''loading plot''. A biplot allows information on both samples and variables of a data matrix to be displayed graphically. Samples are displayed as points while variables are displayed either as vectors, linear axes or nonlinear trajectories. In the case of categorical variables, ''category level points'' may be used to represent the levels of a categorical variable. A ''generalised'' biplot displays information on both continuous and categorical variables. The biplot was introduced by K. Ruben Gabriel (1971).'Gabriel, K. R. (1971). The biplot graphic display of matrices with application to principal component analysis. ''Biometrika'', ''58''(3), 453–467. Construction A biplot is constructed by using the singular value decomposition (SVD) to obtain a low-rank approximation to a transformed version of the data matrix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Electrical And Electronics Engineers
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is an American 501(c)(3) public charity professional organization for electrical engineering, electronics engineering, and other related disciplines. The IEEE has a corporate office in New York City and an operations center in Piscataway, New Jersey. The IEEE was formed in 1963 as an amalgamation of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers and the Institute of Radio Engineers. History The IEEE traces its founding to 1884 and the American Institute of Electrical Engineers. In 1912, the rival Institute of Radio Engineers was formed. Although the AIEE was initially larger, the IRE attracted more students and was larger by the mid-1950s. The AIEE and IRE merged in 1963. The IEEE is headquartered in New York City, but most business is done at the IEEE Operations Center in Piscataway, New Jersey, opened in 1975. The Australian Section of the IEEE existed between 1972 and 1985, after which it split into state- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reliability (statistics)
In statistics and psychometrics, reliability is the overall consistency of a measure. A measure is said to have a high reliability if it produces similar results under consistent conditions:It is the characteristic of a set of test scores that relates to the amount of random error from the measurement process that might be embedded in the scores. Scores that are highly reliable are precise, reproducible, and consistent from one testing occasion to another. That is, if the testing process were repeated with a group of test takers, essentially the same results would be obtained. Various kinds of reliability coefficients, with values ranging between 0.00 (much error) and 1.00 (no error), are usually used to indicate the amount of error in the scores. For example, measurements of people's height and weight are often extremely reliable.The Marketing Accountability Standards Board (MASB) endorses this definition as part of its ongoinCommon Language: Marketing Activities and Metrics Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamnuska Bottom Cliff
Mount John Laurie is a mountain in the Canadian Rockies, in Alberta's Municipal District of Bighorn No. 8. Various names Officially named Mount John Laurie in 1961, it is also known as Mount Laurie, or by its original Stoney Nakoda name ''Îyâmnathka'', borrowed into English as Mount Yamnuska or simply Yamnuska. is a compound that includes root words meaning "mountain" and "flat", however it is usually translated more figuratively as "flat-faced mountain". John Lee Laurie, 1899–1959, was a founder of the Indian Association of Alberta. The mountain's 1961 renaming came at the request of the Stoney Nakoda First Nation. Laurie, an educator and political activist, served as secretary of the Indian Association of Alberta from 1944 to 1956, promoting the causes of First Nations in Alberta. Peak and climbing Standing at approximately above sea level, Mount John Laurie is the last mountain on the north side of the Bow River valley ( Bow Valley) as it exits the mountains fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multivariate Statistics
Multivariate statistics is a subdivision of statistics encompassing the simultaneous observation and analysis of more than one outcome variable, i.e., '' multivariate random variables''. Multivariate statistics concerns understanding the different aims and background of each of the different forms of multivariate analysis, and how they relate to each other. The practical application of multivariate statistics to a particular problem may involve several types of univariate and multivariate analyses in order to understand the relationships between variables and their relevance to the problem being studied. In addition, multivariate statistics is concerned with multivariate probability distributions, in terms of both :*how these can be used to represent the distributions of observed data; :*how they can be used as part of statistical inference, particularly where several different quantities are of interest to the same analysis. Certain types of problems involving multivariate da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raymond B
Raymond is a male given name of Germanic origin. It was borrowed into English from French (older French spellings were Reimund and Raimund, whereas the modern English and French spellings are identical). It originated as the Germanic ᚱᚨᚷᛁᚾᛗᚢᚾᛞ (''Raginmund'') or ᚱᛖᚷᛁᚾᛗᚢᚾᛞ (''Reginmund''). ''Ragin'' ( Gothic) and ''regin'' ( Old German) meant "counsel". The Old High German ''mund'' originally meant "hand", but came to mean "protection". This etymology suggests that the name originated in the Early Middle Ages, possibly from Latin. Alternatively, the name can also be derived from Germanic Hraidmund, the first element being ''Hraid'', possibly meaning "fame" (compare ''Hrod'', found in names such as Robert, Roderick, Rudolph, Roland, Rodney and Roger) and ''mund'' meaning "protector". Despite the German and French origins of the English name, some of its early uses in English documents appear in Latinized form. As a surname, its first recorded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principal Component Analysis
Principal component analysis (PCA) is a linear dimensionality reduction technique with applications in exploratory data analysis, visualization and data preprocessing. The data is linearly transformed onto a new coordinate system such that the directions (principal components) capturing the largest variation in the data can be easily identified. The principal components of a collection of points in a real coordinate space are a sequence of p unit vectors, where the i-th vector is the direction of a line that best fits the data while being orthogonal to the first i-1 vectors. Here, a best-fitting line is defined as one that minimizes the average squared perpendicular distance from the points to the line. These directions (i.e., principal components) constitute an orthonormal basis in which different individual dimensions of the data are linearly uncorrelated. Many studies use the first two principal components in order to plot the data in two dimensions and to visually identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |