|
Schizomids
Schizomida, also known as sprickets or short-tailed whip-scorpions, is an order of arachnids, generally less than in length. The order is not yet widely studied. E. O. Wilson has identified schizomids as among the "groups of organisms that desperately need experts to work on them." Taxonomy Schizomids are grouped into three families: * Calcitronidae † (fossil; dubious) * Hubbardiidae * Protoschizomidae (2 genera, 15 species) **''Agastoschizomus'' ** ''Protoschizomus'' About 300 species of schizomids have been described worldwide, most belonging to the Hubbardiidae family. A systematic review including a full catalogue may be found in Reddell & Cokendolpher (1995). The Schizomida is sister to the order Uropygi, the two clades together forming the Thelyphonida (in the broad sense of the name). Based on molecular clock dates, both orders likely originated in the late Carboniferous somewhere in the tropics of Pangea, and the Schizomida underwent substantial diversification start ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Petrunkevitch
Alexander Ivanovitch Petrunkevitch (; December 22, 1875 – March 9, 1964) was a Russian arachnologist. From 1910 to 1939, he described over 130 spider species. One of his most famous essays was "The Spider and the Wasp." In it he uses effective word choices and some comic touch. Biography His aristocratic father, Ivan Illitch Petrunkevitch, was a liberal member of the First Duma and founded the Constitutional Democratic Party. After finishing his studies in Moscow and in Freiburg under August Weismann, Alexander settled in Yale in 1910, becoming a full professor in 1917. Apart from describing present-day species, he was a major figure in the study of fossil arachnids, including those in amber and from the Coal Measures. He also experimented with live specimens and worked on insects. Petrunkevitch's formulation of the principle of plural effects (every cause is potentially capable of producing several effects) and the principle of the limits of possible oscillations (th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
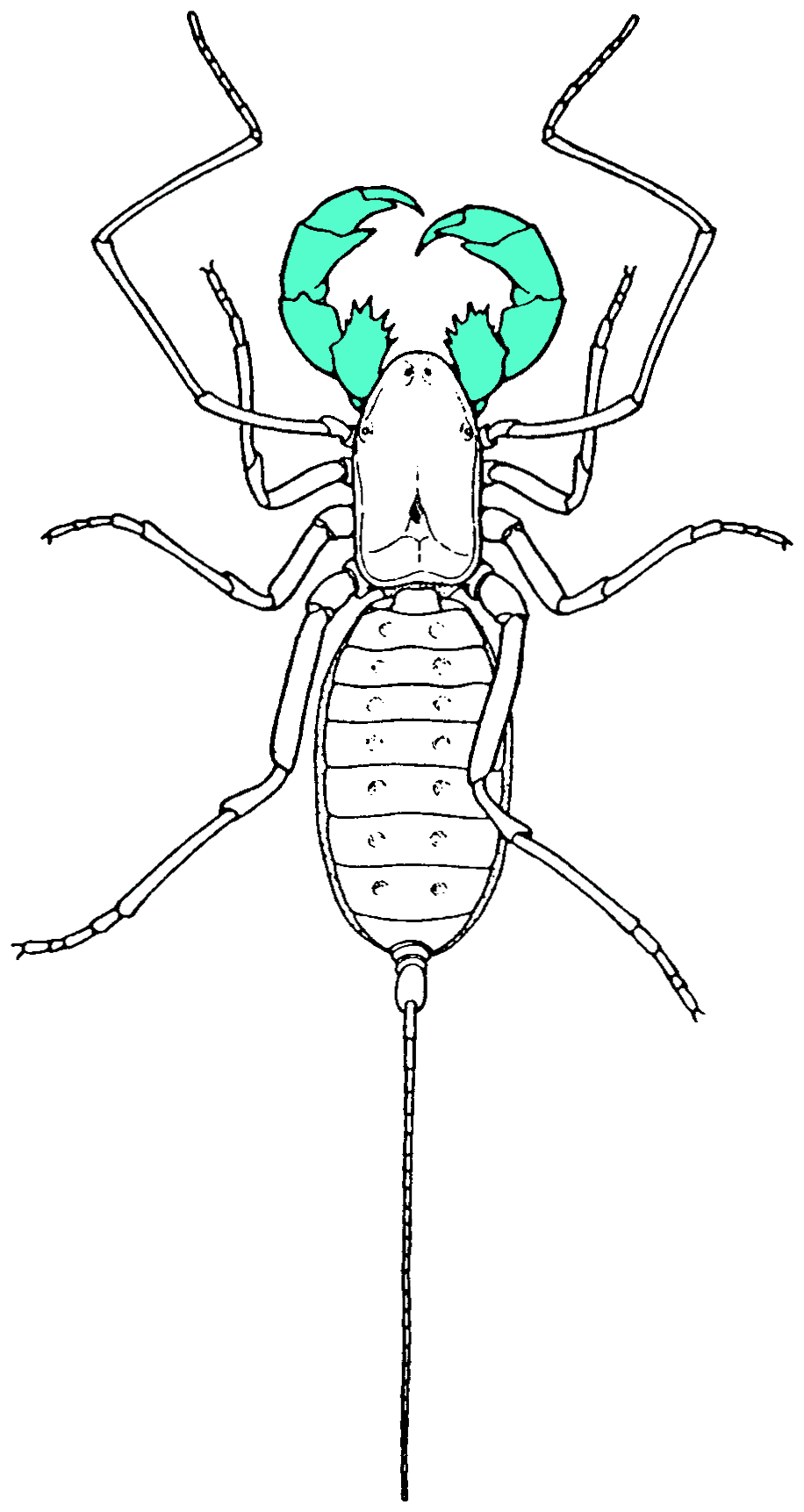
Uropygi
Uropygi is an arachnid order comprising invertebrates commonly known as whip scorpions or vinegaroons (also spelled vinegarroons and vinegarones). They are often called uropygids. The name "whip scorpion" refers to their resemblance to scorpion, true scorpions and possession of a whiplike tail, and "vinegaroon" refers to their ability when attacked to discharge an offensive, vinegar-smelling liquid, which contains acetic acid. The order may also be called Thelyphonida. Both names, Uropygi and Thelyphonida, may be used either in a narrow sense for the order of whip scorpions, or in a broad sense which includes the order Schizomida. Taxonomy Carl Linnaeus first described a whip scorpion in 1758, although he did not distinguish it from what are now regarded as different kinds of arachnid, calling it ''Phalangium caudatum''. ''Phalangium'' is now used as a name for a genus of harvestmen (Opiliones). In 1802, Pierre André Latreille was the first to use a genus name solely for whip s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Lungs
A book lung is a type of respiration organ used for atmospheric gas-exchange that is present in many arachnids, such as scorpions and spiders. Each of these organs is located inside an open, ventral-abdominal, air-filled cavity (atrium) and connects with its surroundings through a small opening for the purpose of respiration. Structure and function Book lungs are not related to the lungs of modern land-dwelling vertebrates. Their name instead describes their structure and purpose as a case of convergent evolution. Stacks of alternating air pockets and tissue filled with hemolymph give them an appearance similar to a "folded" book. Their number varies from just one pair in most spiders to four pairs in scorpions. The unfolded "pages" (plates) of the book lung are filled with hemolymph. The folds maximize the surface exposed to air, and thereby maximize the amount of gas exchanged with the environment. In most species, no motion of the plates is needed to facilitate this kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedipalp
Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi) are the secondary pair of forward appendages among Chelicerata, chelicerates – a group of arthropods including spiders, scorpions, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. The pedipalps are lateral to the chelicerae ("jaws") and anterior to the first pair of walking legs. Overview Pedipalps are composed of six segments or articles. From the proximal end (where they are attached to the body) to the distal, they are: the coxa, the Arthropod leg#Trochanter, trochanter, the Arthropod leg#Femur, femur, the short Glossary_of_spider_terms#patella, patella, the Glossary_of_spider_terms#tibia, tibia, and the Arthropod_leg#Tarsus, tarsus. In spiders, the coxae frequently have extensions called Glossary_of_spider_terms#maxilla , maxillae or gnathobases, which function as mouth parts with or without some contribution from the coxae of the anterior arthropod leg, legs. The limbs themselves may be simple tactile organs outwardly resembling the legs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solifugae
Solifugae is an Order (biology), order of Arachnid, arachnids known variously as solifuges, sun spiders, camel spiders, and wind scorpions. The order includes more than 1,000 described species in about 147 genus, genera. Despite the common names, they are neither true spiders (order Araneae), nor true scorpions (order Scorpiones). Most species of solifuges live in dry climates and feed opportunistically on ground-dwelling arthropods and other small animals. The largest species grow to a length of , including legs. A number of urban legends exaggerate the size and speed of solifuges, and their potential danger to humans, which is negligible. Etymology The order's name is derived from the Latin ''sol'' meaning "sun" and ''fugere'' meaning "to flee". Put together, it means "those that flee from the sun". These animals have a number of common names, including sun spiders, wind scorpions, wind spiders, red romans, and camel spiders. In Afrikaans, they are known as ''haarskeerders'' ("h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amblypygi
Amblypygi is an order of arachnids also known as whip-spiders or tailless whip-scorpions, not to be confused with whip-scorpions or vinegaroons that belong to the related order Thelyphonida. The name "amblypygid" means "blunt tail", a reference to a lack of the flagellum that is otherwise seen in whip-scorpions. Amblypygids possess no silk glands or venom. They rarely bite if threatened but can grab fingers with their pedipalps, resulting in thorn-like puncture-injuries. As of 2023, five families, 17 genera, and around 260 species had been discovered and described. They are found in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide, mainly in warm and humid environments. They like to stay protected and hidden within leaf litter, caves, or underneath bark. Some species are subterranean; all are nocturnal. Fossilized amblypygids have been found dating back to the Carboniferous period, such as '' Weygoldtina''. Description Body-plan Being arachnids, Amblypygi possess two body-segm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagellum
A flagellum (; : flagella) (Latin for 'whip' or 'scourge') is a hair-like appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, from fungal spores ( zoospores), and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are known as flagellates. A microorganism may have from one to many flagella. A gram-negative bacterium '' Helicobacter pylori'', for example, uses its flagella to propel itself through the stomach to reach the mucous lining where it may colonise the epithelium and potentially cause gastritis, and ulcers – a risk factor for stomach cancer. In some swarming bacteria, the flagellum can also function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to wetness outside the cell. Across the three domains of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryota, the flagellum has a different structure, protein composition, and mechanism of propulsion but shares the same function of providing motility. The Latin word means " whip" to describe its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pygidium
The pygidium (: pygidia) is the posterior body part or shield of crustaceans and some other arthropods, such as insects and the extinct trilobites. In groups other than insects, it contains the anus and, in females, the ovipositor. It is composed of fused body segments, sometimes with a tail, and separated from thoracic segments by an articulation.Shultz, J.W. (1990). Evolutionary Morphology And Phylogeny of Arachnida. Cladistics 6: 1–38. Chelicerates In arachnids, the pygidium is formed by reduction of the last three opisthosomal segments to rings where there is no distinction between tergites and sternites. A pygidium is present in Palpigradi, Amblypygi, Uropygi, Schizomida, Ricinulei and in the extinct order Trigonotarbida. It is also present in early fossil representatives of horseshoe crabs. Trilobites In trilobites, the pygidium can range from extremely small (much smaller than the head, or cephalon) to larger than the cephalon. They can be smooth, as in order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedicel (spider)
The anatomy of spiders includes many characteristics shared with other arachnids. These characteristics include bodies divided into two tagmata (sections or segments), eight jointed legs, no wings or antennae, the presence of chelicerae and pedipalps, simple eyes, and an exoskeleton, which is periodically shed. Spiders also have several adaptations that distinguish them from other arachnids. All spiders are capable of producing silk of various types, which many species use to build webs to ensnare prey. Most spiders possess venom, which is injected into prey (or defensively, when the spider feels threatened) through the fangs of the chelicerae. Male spiders have specialized pedipalps that are used to transfer sperm to the female during mating. Many species of spiders exhibit a great deal of sexual dimorphism. External anatomy Spiders, unlike insects, have only two main body parts ( tagmata) instead of three: a fused head and thorax (called a cephalothorax or prosoma) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opisthosoma
The opisthosoma is the posterior part of the body in some arthropods, behind the prosoma ( cephalothorax). It is a distinctive feature of the subphylum Chelicerata (arachnids, horseshoe crabs and others). Although it is similar in most respects to an abdomen (and is often referred to as such), the opisthosoma is differentiated by its inclusion of the respiratory organs ( book lungs or book gills) and the heart. Segments The number of segments and appendages on the opisthosoma vary. Scorpions have 13, but the first is only seen during its embryological development. Other arachnids have fewer; harvestmen, for instance, have only ten. In general, appendages are absent or reduced, although in horseshoe crabs they persist as large plate-like limbs, called opercula or branchiophores, bearing the book gills, and that function in locomotion and gas exchange. In most chelicerates the opisthosomal limbs are greatly reduced and persist only as specialized structures, such as the silk- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubbardia Pentapeltis Male Flagellum
''Hubbardia'' is a genus in the grass family that is endemic to India. It is the only genus in the tribe Hubbardieae of the subfamily Micrairoideae. Species Species include: * '' Hubbardia diandra'' Chandore, Gosavi & S.R.Yadav — native to the Western Ghats, in Maharashtra and Karnataka states. * '' Hubbardia heptaneuron'' Bor — native to Karnataka Karnataka ( ) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed as Mysore State on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, States Re ... state. References Micrairoideae Endemic flora of India (region) Grasses of India Flora of Karnataka Flora of Maharashtra Flora of the Western Ghats Poaceae genera Taxa named by Norman Bor {{Poaceae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metapeltidium
Peltidium is a prodorsal shield found in animals of the subphylum Chelicerata, in the phylum Arthropoda. In some groups (Schizomida, Palpigradi, Solpugida and Opiliones The Opiliones (formerly Phalangida) are an Order (biology), order of arachnids, Common name, colloquially known as harvestmen, harvesters, harvest spiders, or daddy longlegs (see below). , over 6,650 species of harvestmen have been discovered w ...), the peltidium, also known as the schizopeltid, can be subdivided into the propeltidium, a carapace-like shield that covers the proterosoma, which comprises the fused acron (protocerebral region) and first four segments, and two free segments, the mesopeltidium and metapeltidium (Online Dictionary of Invertebrate Zoology). External links Online Dictionary of Invertebrate Zoology References {{reflist Chelicerate anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |