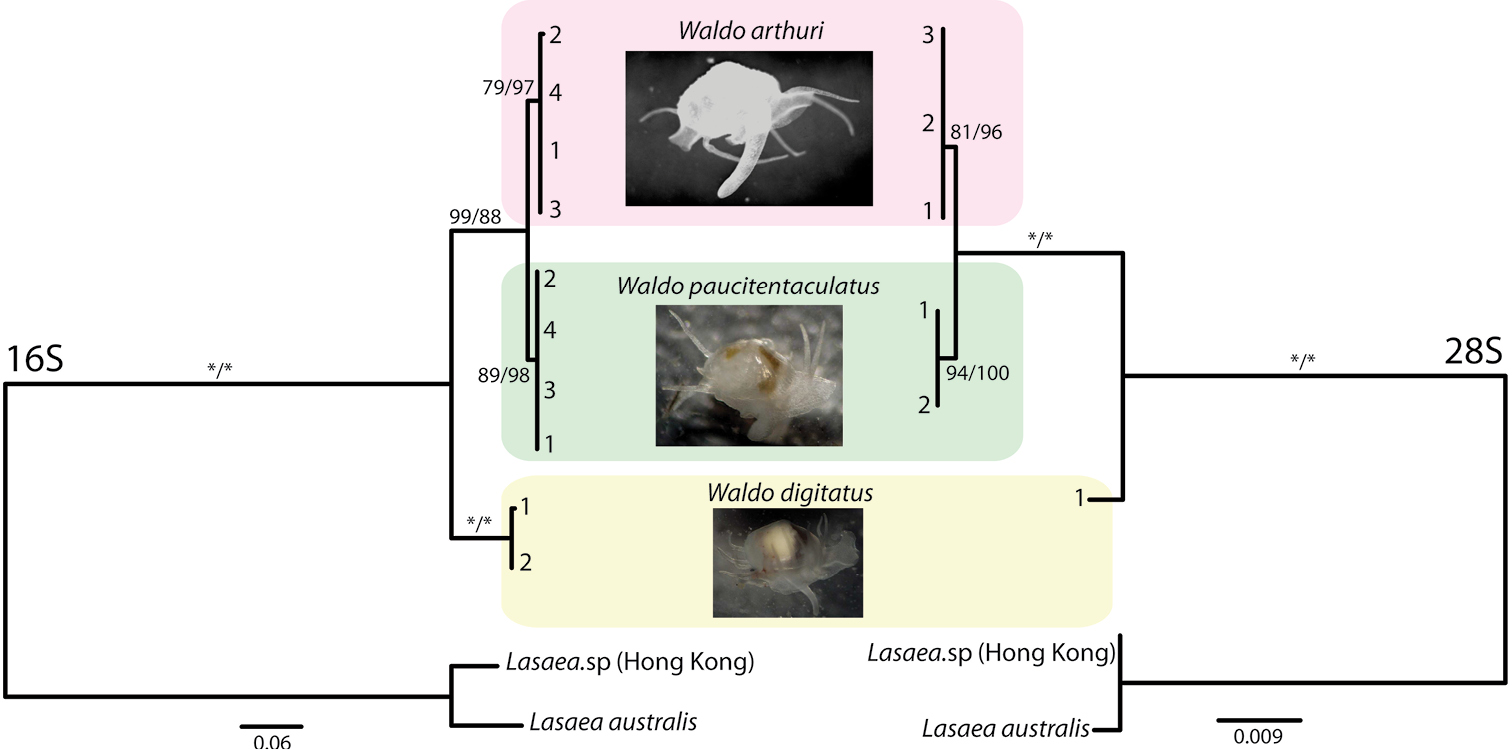
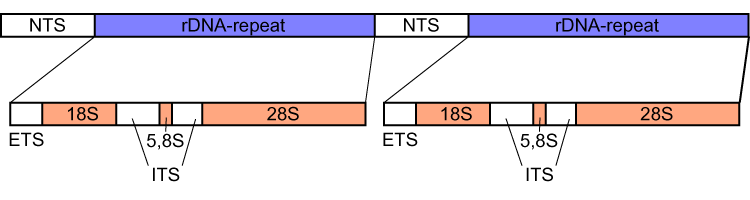
|
Schistosoma Spindale
''Schistosoma spindale'' is a species of digenetic trematode in the family Schistosomatidae. It causes intestinal schistosomiasis in the ruminants. The distribution of ''Schistosoma spindale'' includes Sri Lanka, India, Bangladesh, Thailand, Malaysia, and Laos. The tegument of ''Schistosoma spindale'' under scanning electron microscope was studied in 1983. It is non-tuberculated. The first intermediate host is a freshwater snail '' Indoplanorbis exustus'' that may be the sole natural intermediate host for ''Schistosoma spindale'' (and other two ''Schistosoma'' species) on the Indian sub-continent. One snail can produce up to 7,000 cercariae in one day. The cercariae usually infect some hairy host (low host specificity) in shallow and muddy waters. The definitive hosts of ''Schistosoma spindale'' are (mainly) ruminants and ''Schistosoma spindale'' cause intestinal schistosomiasis of ruminants (Artiodactyla, Ruminantia). Surveillance for cattle schistosomiasis is generally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digenea
Digenea (Gr. ''Dis'' – double, ''Genos'' – race) is a class of trematodes in the Platyhelminthes phylum, consisting of parasitic flatworms (known as ''flukes'') with a syncytial tegument and, usually, two suckers, one ventral and one oral. Adults commonly live within the digestive tract, but occur throughout the organ systems of all classes of vertebrates. Once thought to be related to the Monogenea, it is now recognised that they are closest to the Aspidogastrea and that the Monogenea are more closely allied with the Cestoda. Around 6,000 species have been described to date. Morphology Key features Characteristic features of the Digenea include a syncytial tegument; that is, a tegument where the junctions between cells are broken down and a single continuous cytoplasm surrounds the entire animal. A similar tegument is found in other members of the Neodermata; a group of platyhelminths comprising the Digenea, Aspidogastrea, Monogenea and Cestoda. Digeneans possess a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandicota Indica
The greater bandicoot rat or Indian bandicoot rat (''Bandicota indica'') is a species of rodent in the family Muridae found in Bangladesh, China, India, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Taiwan, Thailand, and Vietnam. It can grow to about 30–45 cm without including the tail which can grow to 28 cm. These should not be confused with marsupial bandicoots which inhabit Australia and neighbouring New Guinea, which were named after the bandicota rats. Description The greater bandicoot rat has a dark gray-brown upper parts with a profusion of long, black hairs. Sides are gray with a few long, black hairs. Short, light gray fur occurs on the ventral surfaces. It has a dark and naked, scaly tail, and dark feet with light-colored claws. The young are much lighter in colour. In Sinhala, the bandicoot rat is known as - , and in Malayalam, it is known as - . Both names directly translate to "pig-rat". These are one of several animals called in the Nepali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schistosoma Mattheei
''Schistosoma'' is a genus of trematodes, commonly known as blood flukes. They are parasitic flatworms responsible for a highly significant group of infections in humans termed ''schistosomiasis'', which is considered by the World Health Organization to be the second-most socioeconomically devastating parasitic disease (after malaria), infecting millions worldwide. Adult flatworms parasitize blood capillaries of either the mesenteries or plexus of the bladder, depending on the infecting species. They are unique among trematodes and any other flatworms in that they are dioecious with distinct sexual dimorphism between male and female. Thousands of eggs are released and reach either the bladder or the intestine (according to the infecting species), and these are then excreted in urine or feces to fresh water. Larvae must then pass through an intermediate snail host before the next larval stage of the parasite emerges that can infect a new mammalian host by directly penetrating t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schistosoma Bovis
''Schistosoma bovis'' is a two-host blood fluke, that causes intestinal schistosomiasis in ruminants in North Africa, Mediterranean Europe and the Middle East. ''S. bovis'' is mostly transmitted by ''Bulinus'' freshwater snail species. It is one of nine haematobium group species and exists in the same geographical areas as ''Schistosoma haematobium'', with which it can hybridise. ''S. bovis-haematobium'' hybrids can infect humans, and have been reported in Senegal since 2009, and a 2013 outbreak in Corsica. Taxonomy and identification ''Schistosoma bovis'' is a digenetic, two-host blood fluke. It was discovered by Italian parasitologist Prospero Sonsino at Zagazig meat market in Egypt in 1876 from a bull. It is generally similar to other schistosomes, but Sonsino knew that it was larger and its eggs were different from those of the human species (first and only known schistosome at the time), ''Schistosoma haematobium'', discovered by a German physician Theodor Bilharz in 1852, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schistosoma Intercalatum
''Schistosoma intercalatum'' is a parasitic worm found in parts of western and central Africa. There are two strains: the Lower Guinea strain and the Zaire strain. ''S. intercalatum'' is one of the major agents of the rectal form of schistosomiasis, also called bilharzia. It is a trematode, and being part of the genus ''Schistosoma'', it is commonly referred to as a blood-fluke since the adult resides in blood vessels. Humans are the definitive host and two species of freshwater snail make up the intermediate host, '' Bulinus forskalii'' for the Lower Guinea strain and '' Bulinus africanus'' for the Zaire strain.Tchuem Tchuenté LA, Southgate, VR, Jourdane J, Webster BL, Vercruysse J (2003) ''Schistosoma intercalatum'': an endangered species in Cameroon? ''Trends Parasitol'' 19: 141-153. Morphology The clinically defining characteristic of most schistosome species are their eggs' size and shape. The eggs of ''Schistosoma intercalatum'' have a terminal spine and tend to be moder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schistosoma Curassoni
''Schistosoma'' is a genus of trematodes, commonly known as blood flukes. They are parasitic flatworms responsible for a highly significant group of infections in humans termed ''schistosomiasis'', which is considered by the World Health Organization to be the second-most socioeconomically devastating parasitic disease (after malaria), infecting millions worldwide. Adult flatworms parasitize blood capillaries of either the mesenteries or plexus of the bladder, depending on the infecting species. They are unique among trematodes and any other flatworms in that they are dioecious with distinct sexual dimorphism between male and female. Thousands of eggs are released and reach either the bladder or the intestine (according to the infecting species), and these are then excreted in urine or feces to fresh water. Larvae must then pass through an intermediate snail host before the next larval stage of the parasite emerges that can infect a new mammalian host by directly penetrating the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Subunit Of Cytochrome C Oxidase
Cytochrome c oxidase I (COX1) also known as mitochondrially encoded cytochrome c oxidase I (MT-CO1) is a protein that is encoded by the ''MT-CO1'' gene in eukaryotes. The gene is also called ''COX1'', ''CO1'', or ''COI''. Cytochrome c oxidase I is the main subunit of the cytochrome c oxidase complex. In humans, mutations in MT-CO1 have been associated with Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON), acquired idiopathic sideroblastic anemia, Complex IV deficiency, colorectal cancer, sensorineural deafness, and recurrent myoglobinuria. Structure In humans, the MT-CO1 gene is located from nucleotide pairs 5904 to 7444 on the guanine-rich heavy (H) section of mtDNA. The gene product is a 57 kDa protein composed of 513 amino acids. Function Cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (CO1 or MT-CO1) is one of three mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) encoded subunits (MT-CO1, MT-CO2, MT-CO3) of cytochrome c oxidase, also known as complex IV. Cytochrome c oxidase () is a key enzyme in aerobic metaboli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
28S Ribosomal RNA
28S ribosomal RNA is the structural ribosomal RNA (rRNA) for the large subunit (LSU) of eukaryotic cytoplasmic ribosomes, and thus one of the basic components of all eukaryotic cells. It has a size of 25S in plants and 28S in mammals, hence the alias of 25S–28S rRNA. Combined with 5.8S rRNA to the 5' side, it is the eukaryotic nuclear homologue of the prokaryotic 23S and mitochondrial 16S ribosomal RNAs. Use in phylogeny The genes coding for 28S rRNA are referred to as 28S rDNA. The comparison of the sequences from these genes are sometimes used in molecular analysis to construct phylogenetic trees, for example in protists, fungi, insects, arachnids, tardigrades, and vertebrates. Structure The 28S rRNA is typically 4000–5000 nt long. Some eukaryotes cleave 28S rRNA into two parts before assembling both into the ribosome, a phenomenon termed the "hidden break". Databases Several databases provide alignments and annotations of LSU rRNA sequences for compar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18S Ribosomal RNA
18S ribosomal RNA (abbreviated 18S rRNA) is a part of the ribosomal RNA in eukaryotes. It is a component of the Eukaryotic small ribosomal subunit (40S) and the cytosolic homologue of both the 12S ribosomal RNA, 12S rRNA in mitochondria and the 16S ribosomal RNA, 16S rRNA in plastids and prokaryotes. Similar to the prokaryotic 16S rRNA, the genes of the 18S ribosomal RNA have been widely used for Phylogenetics, phylogenetic studies and biodiversity screening of eukaryotes. Research history Along with the 28S ribosomal RNA, 28S and 5.8S ribosomal RNA, 5.8S rRNA in eukaryotes, the 18S rRNA was early identified as integral structural element of ribosomes which were first characterized by their sedimentation properties and named according to measured Svedberg, Svedberg units. Given its ubiquitous presence in eukaryotic life, the evolution of the 18S rRNA was soon proposed as marker for phylogenetics, phylogenetic studies to resolve the evolution of eukaryotes. Structure and function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to descendants, nor does it show how much they have changed, so many differing evolutionary trees can be consistent with the same cladogram. A cladogram uses lines that branch off in different directions ending at a clade, a group of organisms with a last common ancestor. There are many shapes of cladograms but they all have lines that branch off from other lines. The lines can be traced back to where they branch off. These branching off points represent a hypothetical ancestor (not an actual entity) which can be inferred to exhibit the traits shared among the terminal taxa above it. This hypothetical ancestor might then provide clues about the order of evolution of various features, adaptation, and other e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cercarial Dermatitis
Swimmer's itch, cercarial dermatitis or schistosome dermatitis is a short-term allergic contact dermatitis occurring in the skin of humans that have been infected by water-borne schistosomes, a type of flatworm. It is common in freshwater, brackish and marine habitats worldwide. The incidence of this condition may be increasing, although this may be attributed to better monitoring and reporting. Nevertheless, the condition is considered to be an emerging infectious disease. The main symptom is itchy papules (raised skin) that commonly occur within 2 days of infection. Initially, wheals develop quickly, then turn into maculae in about half an hour. Within 10–12 hours these turn into very itchy papules that reach their worst by the second or third day. The papules disappear in 1–2 weeks but secondary effects from scratching can continue longer. The intense itching, which peaks after 48–72 hours, is associated with pain and swelling of the affected areas. People repeatedly e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |