|
Scatterplots
A scatter plot, also called a scatterplot, scatter graph, scatter chart, scattergram, or scatter diagram, is a type of plot or mathematical diagram using Cartesian coordinates to display values for typically two variables for a set of data. If the points are coded (color/shape/size), one additional variable can be displayed. The data are displayed as a collection of points, each having the value of one variable determining the position on the horizontal axis and the value of the other variable determining the position on the vertical axis. History According to Michael Friendly and Daniel Denis, the defining characteristic distinguishing scatter plots from line charts is the representation of specific observations of bivariate data where one variable is plotted on the horizontal axis and the other on the vertical axis. The two variables are often abstracted from a physical representation like the spread of bullets on a target or a geographic or celestial projection. While ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Correlation
In statistics, correlation or dependence is any statistical relationship, whether causal or not, between two random variables or bivariate data. Although in the broadest sense, "correlation" may indicate any type of association, in statistics it usually refers to the degree to which a pair of variables are '' linearly'' related. Familiar examples of dependent phenomena include the correlation between the height of parents and their offspring, and the correlation between the price of a good and the quantity the consumers are willing to purchase, as it is depicted in the demand curve. Correlations are useful because they can indicate a predictive relationship that can be exploited in practice. For example, an electrical utility may produce less power on a mild day based on the correlation between electricity demand and weather. In this example, there is a causal relationship, because extreme weather causes people to use more electricity for heating or cooling. However, in g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scatter Plot
A scatter plot, also called a scatterplot, scatter graph, scatter chart, scattergram, or scatter diagram, is a type of plot or mathematical diagram using Cartesian coordinates to display values for typically two variables for a set of data. If the points are coded (color/shape/size), one additional variable can be displayed. The data are displayed as a collection of points, each having the value of one variable determining the position on the horizontal axis and the value of the other variable determining the position on the vertical axis. History According to Michael Friendly and Daniel Denis, the defining characteristic distinguishing scatter plots from line charts is the representation of specific observations of bivariate data where one variable is plotted on the horizontal axis and the other on the vertical axis. The two variables are often abstracted from a physical representation like the spread of bullets on a target or a geographic or celestial projection. Wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data And Information Visualization
Data and information visualization (data viz/vis or info viz/vis) is the practice of designing and creating graphic or visual representations of a large amount of complex quantitative and qualitative data and information with the help of static, dynamic or interactive visual items. Typically based on data and information collected from a certain domain of expertise, these visualizations are intended for a broader audience to help them visually explore and discover, quickly understand, interpret and gain important insights into otherwise difficult-to-identify structures, relationships, correlations, local and global patterns, trends, variations, constancy, clusters, outliers and unusual groupings within data (''exploratory visualization''). When intended for the general public (mass communication) to convey a concise version of known, specific information in a clear and engaging manner (''presentational'' or ''explanatory visualization''), it is typically called information gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Regression
Local regression or local polynomial regression, also known as moving regression, is a generalization of the moving average and polynomial regression. Its most common methods, initially developed for scatterplot smoothing, are LOESS (locally estimated scatterplot smoothing) and LOWESS (locally weighted scatterplot smoothing), both pronounced . They are two strongly related non-parametric regression methods that combine multiple regression models in a ''k''-nearest-neighbor-based meta-model. In some fields, LOESS is known and commonly referred to as Savitzky–Golay filter (proposed 15 years before LOESS). LOESS and LOWESS thus build on "classical" methods, such as linear and nonlinear least squares regression. They address situations in which the classical procedures do not perform well or cannot be effectively applied without undue labor. LOESS combines much of the simplicity of linear least squares regression with the flexibility of nonlinear regression. It does this b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Regression
In statistics, linear regression is a statistical model, model that estimates the relationship between a Scalar (mathematics), scalar response (dependent variable) and one or more explanatory variables (regressor or independent variable). A model with exactly one explanatory variable is a ''simple linear regression''; a model with two or more explanatory variables is a multiple linear regression. This term is distinct from multivariate linear regression, which predicts multiple correlated dependent variables rather than a single dependent variable. In linear regression, the relationships are modeled using linear predictor functions whose unknown model parameters are estimation theory, estimated from the data. Most commonly, the conditional mean of the response given the values of the explanatory variables (or predictors) is assumed to be an affine function of those values; less commonly, the conditional median or some other quantile is used. Like all forms of regression analysis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rug Plot
A carpet is a textile floor covering typically consisting of an upper layer of Pile (textile), pile attached to a backing. The pile was traditionally made from wool, but since the 20th century synthetic fiber, synthetic fibres such as polypropylene, nylon, and polyester have often been used, as these fibres are less expensive than wool. The pile usually consists of twisted Tufting, tufts that are typically heat-treated to maintain their structure. The term ''carpet'' is often used in a similar context to the term rug, but rugs are mostly considered to be smaller than a room and not attached to the floor. Carpets are used for a variety of purposes. These include insulating a person's feet from a cold tile or concrete floor, making a room more comfortable as a place to sit on the floor (e.g., when playing with children or as a prayer rug), reducing sound from walking (particularly in apartment buildings), and adding decoration or colour to a room. Carpets can be made in any colo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matriz De Gráficos De Dispersão
Matriz may refer to the following subjects: Places in Portugal * Matriz (Borba), a civil parish in the municipality of Borba * Matriz (Horta), a civil parish in the municipality of Horta, island of Faial (Azores) * Matriz (Ribeira Grande), a civil parish in the municipality of Ribeira Grande, island of São Miguel (Azores) *Matriz, the former name of São Sebastião (Ponta Delgada), a civil parish in the municipality of Ponta Delgada, island of São Miguel (Azores) Other uses * ''Matriz'' (album), by Brazilian singer-songwriter Pitty {{geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
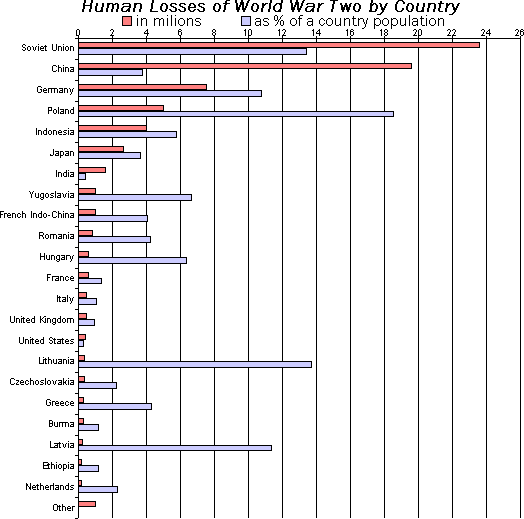
Bar Chart
A bar chart or bar graph is a chart or graph that presents categorical variable, categorical data with rectangular bars with heights or lengths proportional to the values that they represent. The bars can be plotted vertically or horizontally. A vertical bar chart is sometimes called a column chart and has been identified as the prototype of charts. A bar graph shows comparisons among discrete variable, discrete categorical variable, categories. One axis of the chart shows the specific categories being compared, and the other axis represents a measured value. Some bar graphs present bars clustered or stacked in groups of more than one, showing the values of more than one measured variable. History Many sources consider William Playfair (1759-1824) to have invented the bar chart and the ''Exports and Imports of Scotland to and from different parts for one Year from Christmas 1780 to Christmas 1781'' graph from his ''The Commercial and Political Atlas'' to be the first bar chart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluctuation Diagram , price fluctuation
{{disambiguation ...
Fluctuation may refer to: Physics and mathematics * Statistical fluctuations, in statistics, statistical mechanics, and thermodynamics ** Thermal fluctuations, statistical fluctuations in a thermodynamic variable * Quantum fluctuation, arising from the uncertainty principle ** Primordial fluctuations, density variations in the early universe ** Universal conductance fluctuations, a quantum physics phenomenon encountered in electrical transport experiments in mesoscopic species Finance and economics * Economic conjuncture, a critical combination of events in economics * Volatility (finance) In finance, volatility (usually denoted by "sigma, σ") is the Variability (statistics), degree of variation of a trading price series over time, usually measured by the standard deviation of logarithmic returns. Historic volatility measures a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
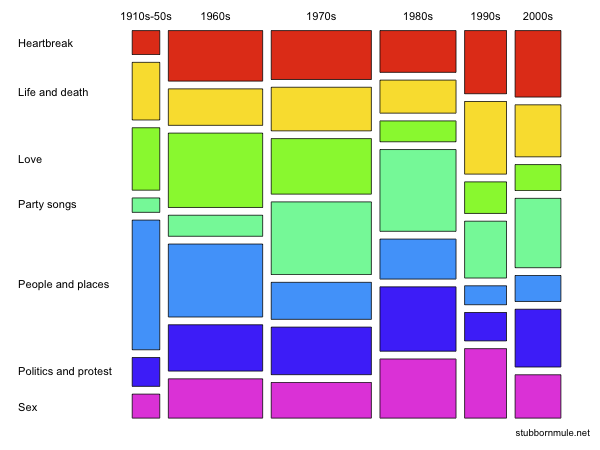
Mosaic Plot
A mosaic plot, Marimekko chart, Mekko chart, or sometimes percent stacked bar plot, is a graphical visualization of data from two or more qualitative variables. It is the multidimensional extension of spineplots, which graphically display the same information for only one variable. It gives an overview of the data and makes it possible to recognize relationships between different variables. For example, independence is shown when the boxes across categories all have the same areas. Mosaic plots were introduced by Hartigan and Kleiner in 1981 and expanded on by Friendly in 1994. Mosaic plots are also called Marimekko or Mekko charts because they resemble some Marimekko prints. However, in statistical applications, mosaic plots can be colored and shaded according to deviations from independence, whereas Marimekko charts are colored according to the category levels, as in the image. As with bar charts and spineplots, the area of the tiles, also known as the bin size, is proportional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Chart
A line chart or line graph, also known as curve chart, is a type of chart that displays information as a series of data points called 'markers' connected by straight wikt:line, line segments. It is a basic type of chart common in many fields. It is similar to a scatter plot except that the measurement points are ordered (typically by their x-axis value) and joined with straight line segments. A line chart is often used to visualize a trend in data over intervals of time – a time series – thus the line is often drawn chronologically. In these cases they are known as run charts. History Some of the earliest known line charts are generally credited to Francis Hauksbee, Nicolaus Samuel Cruquius, Johann Heinrich Lambert and the Scottish engineer William Playfair. Line charts often display time as a variable on the x-axis. Playfair was one of the first to visualize data this way. In 1786, he plotted ten years of money spent by the Royal Navy. He supplemented the chart with a det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |