|
Scale (geography)
In geography, scale is the level at which a geographical phenomenon occurs or is described. This concept is derived from the map scale in cartography. Geographers describe geographical phenomena and differences using different scales. From an epistemological perspective, scale is used to describe how detailed an observation is, while ontologically, scale is inherent in the complex interaction between society and nature. Scale effect The concept of scale is central to geography. To study any geographical phenomenon, one must first determine the scale or resolution, because different scales or resolutions may result in different observations and hence different conclusions. This problem is called scale effect or scale dependency. For example, the answer to the famous question "''How Long Is the Coast of Britain''" is highly dependent on the choice of cartographic scales. In cartography and spatial analysis, scale effect and zoning effect (different ways of zoning lead to differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography
Geography (from Ancient Greek ; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and world, its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other Astronomical object, celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. Geography has been called "a bridge between natural science and social science disciplines." Origins of many of the concepts in geography can be traced to Greek Eratosthenes of Cyrene, who may have coined the term "geographia" (). The first recorded use of the word Geography (Ptolemy), γεωγραφία was as the title of a book by Greek scholar Claudius Ptolemy (100 – 170 AD). This work created the so-called "Ptolemaic tradition" of geography, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scale (map)
The scale of a map is the ratio of a distance on the map to the corresponding distance on the ground. This simple concept is complicated by the curvature of the Earth's surface, which forces scale to vary across a map. Because of this variation, the concept of scale becomes meaningful in two distinct ways. The first way is the ratio of the size of the generating globe to the size of the Earth. The generating globe is a conceptual model to which the Earth is shrunk and from which the map is Map projection, projected. The ratio of the Earth's size to the generating globe's size is called the nominal scale (also called principal scale or representative fraction). Many maps state the nominal scale and may even display a bar scale (sometimes merely called a "scale") to represent it. The second distinct concept of scale applies to the variation in scale across a map. It is the ratio of the mapped point's scale to the nominal scale. In this case 'scale' means the scale factor (also ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartography
Cartography (; from , 'papyrus, sheet of paper, map'; and , 'write') is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an imagined reality) can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively. The fundamental objectives of traditional cartography are to: * Set the map's agenda and select traits of the object to be mapped. This is the concern of map editing. Traits may be physical, such as roads or land masses, or may be abstract, such as toponyms or political boundaries. * Represent the terrain of the mapped object on flat media. This is the concern of map projections. * Eliminate the mapped object's characteristics that are irrelevant to the map's purpose. This is the concern of Cartographic generalization, generalization. * Reduce the complexity of the characteristics that will be mapped. This is also the concern of generalization. * Orchestrate the elements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epistemology
Epistemology is the branch of philosophy that examines the nature, origin, and limits of knowledge. Also called "the theory of knowledge", it explores different types of knowledge, such as propositional knowledge about facts, practical knowledge in the form of skills, and knowledge by acquaintance as a familiarity through experience. Epistemologists study the concepts of belief, truth, and justification to understand the nature of knowledge. To discover how knowledge arises, they investigate sources of justification, such as perception, introspection, memory, reason, and testimony. The school of skepticism questions the human ability to attain knowledge while fallibilism says that knowledge is never certain. Empiricists hold that all knowledge comes from sense experience, whereas rationalists believe that some knowledge does not depend on it. Coherentists argue that a belief is justified if it coheres with other beliefs. Foundationalists, by contrast, maintain th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontology
Ontology is the philosophical study of existence, being. It is traditionally understood as the subdiscipline of metaphysics focused on the most general features of reality. As one of the most fundamental concepts, being encompasses all of reality and every entity within it. To articulate the basic structure of being, ontology examines the commonalities among all things and investigates their classification into basic types, such as the Theory of categories, categories of particulars and Universal (metaphysics), universals. Particulars are unique, non-repeatable entities, such as the person Socrates, whereas universals are general, repeatable entities, like the color ''green''. Another distinction exists between Abstract and concrete, concrete objects existing in space and time, such as a tree, and abstract objects existing outside space and time, like the number 7. Systems of categories aim to provide a comprehensive inventory of reality by employing categories such as Substance t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Resolution
In physics and geosciences, the term spatial resolution refers to distance between independent measurements, or the physical dimension that represents a pixel of the image. While in some instruments, like cameras and telescopes, spatial resolution is directly connected to angular resolution, other instruments, like synthetic aperture radar or a network of weather stations, produce data whose spatial sampling layout is more related to the Earth's surface, such as in remote sensing and satellite imagery. See also * Image resolution Image resolution is the level of detail of an image. The term applies to digital images, film images, and other types of images. "Higher resolution" means more image detail. Image resolution can be measured in various ways. Resolution quantifies ... * Ground sample distance * Level of detail * Resel References Accuracy and precision {{physics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
How Long Is The Coast Of Britain? Statistical Self-Similarity And Fractional Dimension
The coastline paradox is the counterintuitive observation that the coastline of a landmass does not have a well-defined length. This results from the fractal curve-like properties of coastlines; i.e., the fact that a coastline typically has a fractal dimension. Although the "paradox of length" was previously noted by Hugo Steinhaus, the first systematic study of this phenomenon was by Lewis Fry Richardson, and it was expanded upon by Benoit Mandelbrot. The measured length of the coastline depends on the method used to measure it and the degree of cartographic generalization. Since a landmass has features at all scales, from hundreds of kilometers in size to tiny fractions of a millimeter and below, there is no obvious size of the smallest feature that should be taken into consideration when measuring, and hence no single well-defined perimeter to the landmass. Various approximations exist when specific assumptions are made about minimum feature size. The problem is fundamen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Analysis
Spatial analysis is any of the formal Scientific technique, techniques which study entities using their topological, geometric, or geographic properties, primarily used in Urban design, Urban Design. Spatial analysis includes a variety of techniques using different analytic approaches, especially ''spatial statistics''. It may be applied in fields as diverse as astronomy, with its studies of the placement of galaxies in the cosmos, or to chip fabrication engineering, with its use of "place and route" algorithms to build complex wiring structures. In a more restricted sense, spatial analysis is geospatial analysis, the technique applied to structures at the human scale, most notably in the analysis of geographic data. It may also applied to genomics, as in Spatial transcriptomics, transcriptomics data, but is primarily for spatial data. Complex issues arise in spatial analysis, many of which are neither clearly defined nor completely resolved, but form the basis for current resear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
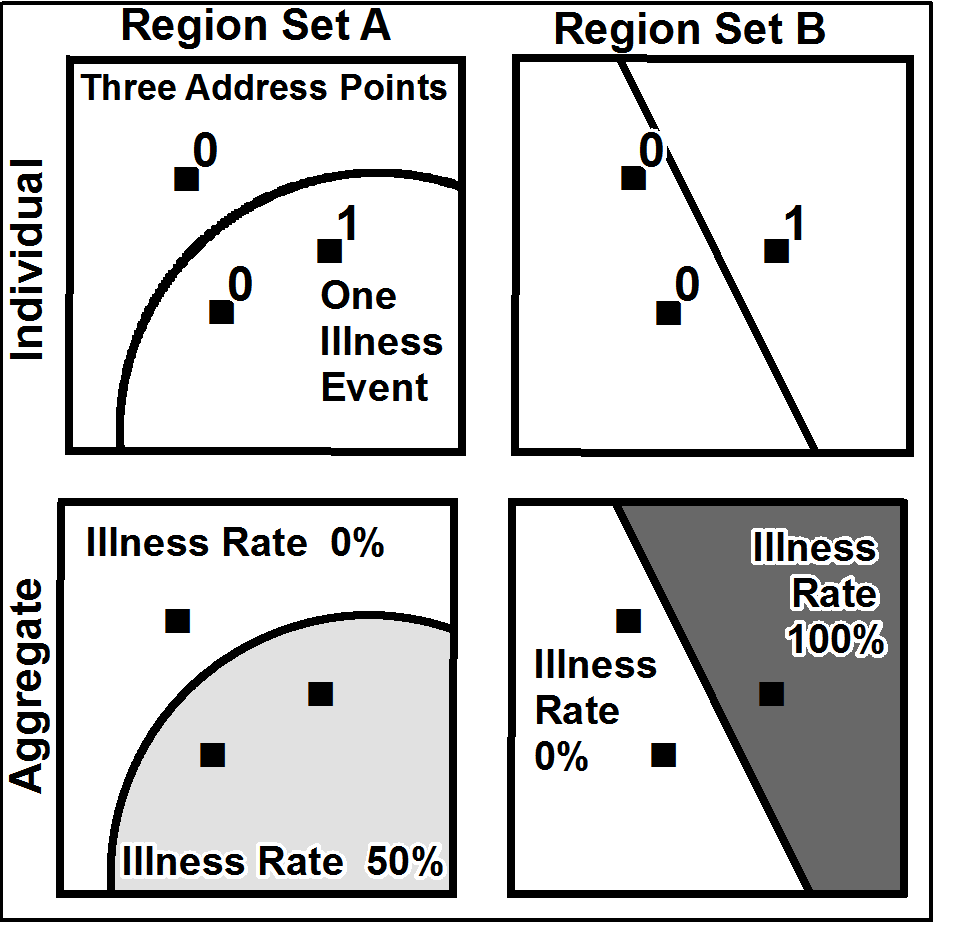
Modifiable Areal Unit Problem
__NOTOC__ The modifiable areal unit problem (MAUP) is a source of statistical bias that can significantly impact the results of statistical hypothesis tests. MAUP affects results when point-based measures of spatial phenomena are Aggregate data, aggregated into spatial partitions or ''areal units'' (such as regions or districts) as in, for example, population density or illness rates. The resulting summary values (e.g., totals, rates, proportions, densities) are influenced by both the shape and Scale (geography), scale of the aggregation unit. For example, census data may be aggregated into county districts, census tracts, postcode areas, police precincts, or any other arbitrary spatial partition. Thus the results of data aggregation are dependent on the mapmaker's choice of which "modifiable areal unit" to use in their analysis. A census choropleth map calculating population density using state boundaries will yield radically different results from a map that calculates density ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landscape Ecology
Landscape ecology is the science of studying and improving relationships between ecological processes in the environment and particular ecosystems. This is done within a variety of landscape scales, development spatial patterns, and organizational levels of research and policy. Landscape ecology can be described as the science of "landscape diversity" as the synergetic result of biodiversity and geodiversity. As a highly interdisciplinary field in systems science, landscape ecology integrates biophysical and Analytic induction, analytical approaches with humanistic and holistic perspectives across the natural sciences and social sciences. Landscapes are spatially heterogeneous geographic areas characterized by diverse interacting patches or ecosystems, ranging from relatively natural terrestrial and aquatic systems such as forests, grasslands, and lakes to human-dominated environments including agricultural and urban settings. The most salient characteristics of landscape ecol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous states border Canada to the north and Mexico to the south, with the semi-exclave of Alaska in the northwest and the archipelago of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The United States asserts sovereignty over five Territories of the United States, major island territories and United States Minor Outlying Islands, various uninhabited islands in Oceania and the Caribbean. It is a megadiverse country, with the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest land area and List of countries and dependencies by population, third-largest population, exceeding 340 million. Its three Metropolitan statistical areas by population, largest metropolitan areas are New York metropolitan area, New York, Greater Los Angeles, Los Angel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orogeny
Orogeny () is a mountain-mountain formation, building process that takes place at a convergent boundary, convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An or develops as the compressed plate crumples and is tectonic uplift, uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges. This involves a series of geological processes collectively called orogenesis. These include both structural deformation (physics), deformation of existing continental crust and the creation of new continental crust through volcanism. Magma rising in the orogen carries less dense material upwards while leaving more dense material behind, resulting in compositional differentiation of Earth's lithosphere (crust (geology), crust and uppermost mantle (geology), mantle). A synorogenic (or synkinematic) process or event is one that occurs during an orogeny. The word ''orogeny'' comes . Although it was used before him, the American geologist Grove Karl Gilbert, G. K. Gilbert used the term in 1890 to me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |