|
Scaenae Frons
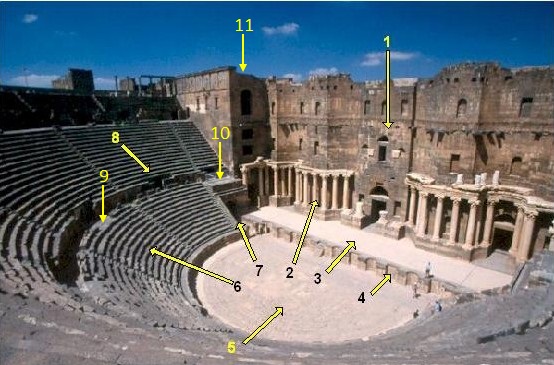
The scaenae frons () is the elaborately decorated permanent architectural background of a Roman theatre (structure), Roman theatre stage. The form may have been intended to resemble the facades of imperial palaces. It could support a permanent roof or awnings. The Roman scaenae frons was also used both as the backdrop to the stage and behind as the actors' dressing room. Largely through reconstruction or restoration, there are a number of well-preserved examples. This form was influenced by Greek theatre#Architecture, Greek theatre, which had an equivalent but simpler ''Skene (theatre), skene'' building (meaning "tent", showing the original nature of it). This led to the stage or space before the ''skene'' being called the proscenium. In the Hellenistic period the ''skene'' became more elaborate, perhaps with columns, but also used to support painted scenery. The Roman scaenae frons was also used both as the backdrop to the stage and behind as the actors' dressing room. It no l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palmyra Theater02(js)
Palmyra ( ; Palmyrene dialect, Palmyrene: (), romanized: ''Tadmor''; ) is an ancient city in central Syria. It is located in the eastern part of the Levant, and archaeological finds date back to the Neolithic period, and documents first mention the city in the early second millennium BCE. Palmyra changed hands on a number of occasions between different empires before becoming a subject of the Roman Empire in the first century CE. The city grew wealthy from caravan (travellers), trade caravans; the Palmyrenes became renowned as merchants who established colonies along the Silk Road and operated throughout the Roman Empire. Palmyra's wealth enabled the construction of monumental projects, such as the Great Colonnade at Palmyra, Great Colonnade, the Temple of Bel, and the distinctive tower tombs. Ethnically, the Palmyrenes combined elements of Amorites, Arameans, and Arabs. Socially structured around kinship and clans, Palmyra's inhabitants spoke Palmyrene Aramaic, a variety of A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrea Palladio
Andrea Palladio ( , ; ; 30 November 1508 – 19 August 1580) was an Italian Renaissance architect active in the Venetian Republic. Palladio, influenced by Roman and Greek architecture, primarily Vitruvius, is widely considered to be one of the most influential individuals in the history of architecture. While he designed churches and palaces, he was best known for country houses and villas. His teachings, summarized in the architectural treatise, '' The Four Books of Architecture'', gained him wide recognition. The city of Vicenza, with its 23 buildings designed by Palladio, and his 24 villas in the Veneto are listed by UNESCO as part of a World Heritage Site named City of Vicenza and the Palladian Villas of the Veneto. The churches of Palladio are to be found within the "Venice and its Lagoon" UNESCO World Heritage Site. Biography and major works Palladio was born on 30 November 1508 in Padua and was given the name Andrea di Pietro della Gondola (). His father, Pie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Theatre At Palmyra
The Roman Theatre at Palmyra () is a Roman theatre (structure), Roman theatre in ancient Palmyra in the Syrian Desert. The unfinished theatre dates back to the second-century CE Severan dynasty, Severan period. The theatre's remains have since been restored. It was occupied by the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) in Palmyra offensive (May 2015), May 2015 and recaptured by the government forces in Palmyra offensive (March 2016), March 2016 with the support of Russian airstrikes. Overview The second-century CE theatre was built in the centre of a semicircular colonnaded piazza which opens up to the South Gate of Palmyra. The piazza was located to the south-west of the main Great Colonnade at Palmyra, colonnaded street. The unfinished ''cavea'' is in diameter and consists of only an ''ima cavea'', the lowest section of the ''cavea'', immediately surrounding the ''orchestra''. The ''ima cavea'' is organized into eleven ''cunei'' of twelve rows each and faces north-northea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, the east and southeast, Jordan to Jordan–Syria border, the south, and Israel and Lebanon to Lebanon–Syria border, the southwest. It is a republic under Syrian transitional government, a transitional government and comprises Governorates of Syria, 14 governorates. Damascus is the capital and largest city. With a population of 25 million across an area of , it is the List of countries and dependencies by population, 57th-most populous and List of countries and dependencies by area, 87th-largest country. The name "Syria" historically referred to a Syria (region), wider region. The modern state encompasses the sites of several ancient kingdoms and empires, including the Eblan civilization. Damascus was the seat of the Umayyad Caliphate and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palmyra
Palmyra ( ; Palmyrene dialect, Palmyrene: (), romanized: ''Tadmor''; ) is an ancient city in central Syria. It is located in the eastern part of the Levant, and archaeological finds date back to the Neolithic period, and documents first mention the city in the early second millennium BCE. Palmyra changed hands on a number of occasions between different empires before becoming a subject of the Roman Empire in the first century CE. The city grew wealthy from caravan (travellers), trade caravans; the Palmyrenes became renowned as merchants who established colonies along the Silk Road and operated throughout the Roman Empire. Palmyra's wealth enabled the construction of monumental projects, such as the Great Colonnade at Palmyra, Great Colonnade, the Temple of Bel, and the distinctive tower tombs. Ethnically, the Palmyrenes combined elements of Amorites, Arameans, and Arabs. Socially structured around kinship and clans, Palmyra's inhabitants spoke Palmyrene Aramaic, a variety of A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
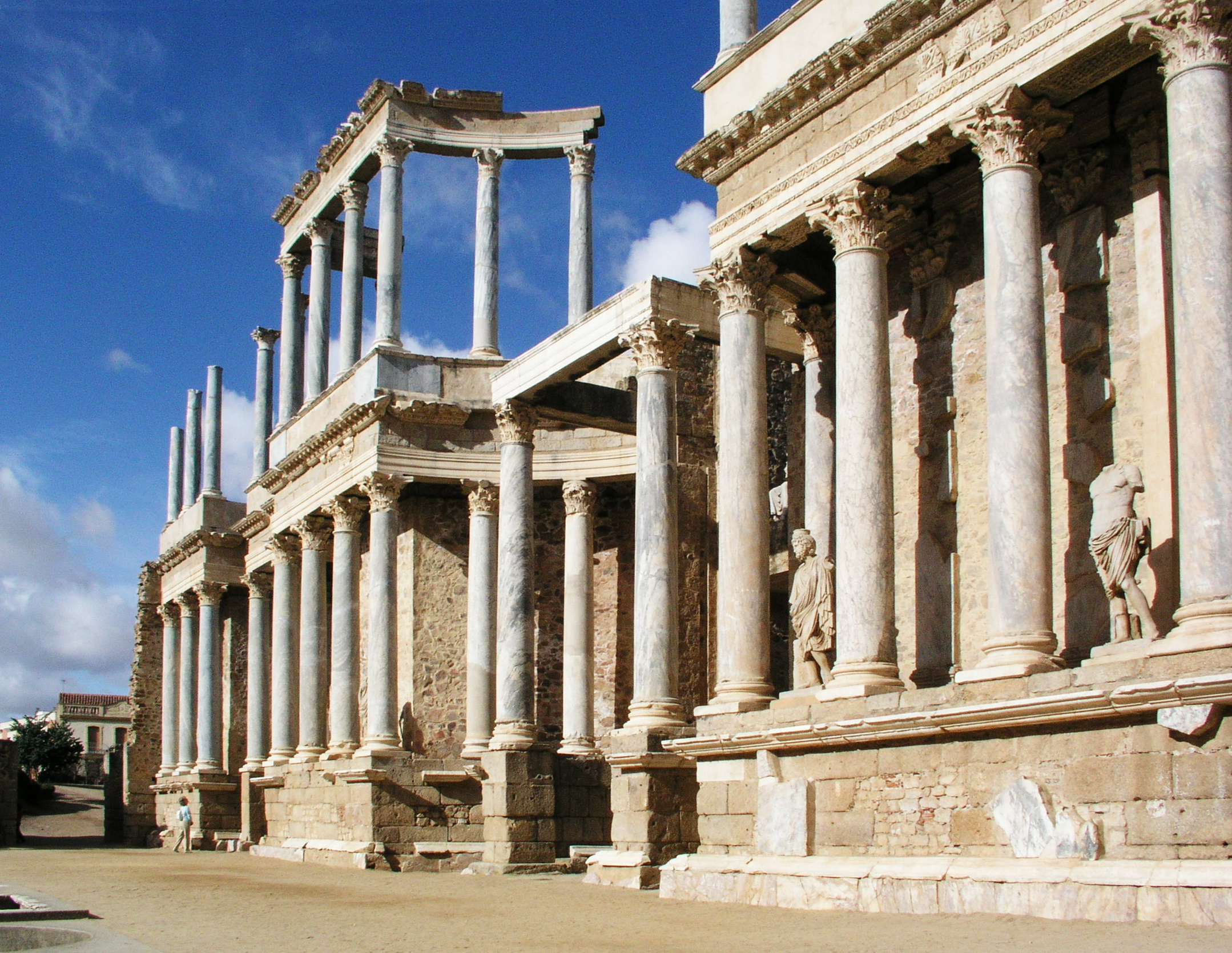
Merida Roman Theatre1
Mérida or Merida may refer to: Places *Mérida (state), one of the 23 states which make up Venezuela *Mérida, Mérida, the capital city of the state of Mérida, Venezuela *Merida, Leyte, Philippines, a municipality in the province of Leyte *Mérida, Spain, the capital city of the autonomous community of Extremadura *Mérida, Yucatán, Mexico, the capital city of the state of Yucatán * or , an ancient name for Mardin, Turkey Football clubs *CP Mérida, a defunct club in Mérida, Spain *Mérida UD, a defunct club in Mérida, Spain *Mérida AD, a club in Mérida, Spain *Imperio de Mérida CP, Mérida, Spain *Estudiantes de Mérida, Venezuela * Mérida F.C., Mexico Other uses *Merida (Brave), the main character of the 2012 animated film ''Brave'' *Merida (Dragon Prince), a fictional people created by fantasy author Melanie Rawn for her ''Dragon Prince'' series * ''Merida'' (moth), a genus of moth in the family Geometridae *Merida Bikes, one of the world's largest bicycle make ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Theatre (Mérida)
The Roman Theatre of Mérida is a Roman theatre in the Roman '' colonia'' of Emerita Augusta –present-day Mérida, Spain–, capital of the Roman province of Lusitania. Its construction was promoted by the consul Vipsanius Agrippa and was built in 16–15 BCE. It was used for Roman theatrical performances during ancient Rome. Since 1933, it houses the . The theatre has undergone several renovations, notably at the end of the 1st century or early 2nd century CE (possibly during the reign of Emperor Trajan), when the current facade of the ''scaenae frons'' was erected, and another in the time of Constantine I (between 330 and 340 CE), which introduced new decorative-architectural elements and a walkway around the monument. Following the theatre's abandonment in Late Antiquity, it was slowly covered with earth, with only the upper tiers of seats (''summa cavea'') remaining visible. In local folklore the site was referred to as "The Seven Chairs", where, according to tradition, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Europe and the fourth-most populous European Union member state. Spanning across the majority of the Iberian Peninsula, its territory also includes the Canary Islands, in the Eastern Atlantic Ocean, the Balearic Islands, in the Western Mediterranean Sea, and the Autonomous communities of Spain#Autonomous cities, autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla, in mainland Africa. Peninsular Spain is bordered to the north by France, Andorra, and the Bay of Biscay; to the east and south by the Mediterranean Sea and Gibraltar; and to the west by Portugal and the Atlantic Ocean. Spain's capital and List of largest cities in Spain, largest city is Madrid, and other major List of metropolitan areas in Spain, urban areas include Barcelona, Valencia, Seville, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mérida, Spain
Mérida () is a city and Municipalities of Spain, municipality of Spain, part of the Province of Badajoz, and capital of the autonomous community of Extremadura. Located in the western-central part of the Iberian Peninsula at 217 metres above sea level, the city is crossed by the Guadiana and Albarregas rivers. The population was 60,119 in 2017. Etymology The place name of ''Mérida'' derives from the Latin ''Emerita'', with a meaning of ''retired'' or ''veteran''. It is part of the name that the city received after its foundation by the emperor Augustus in 25 BC, ''Augusta Emerita'', colony in which veteran soldiers or emeritus settled. History Prehistory Mérida has been populated since prehistoric times, as demonstrated by a prestigious hoard of gold jewellery excavated from a girl's grave in 1870. Consisting of two penannular bracelets, an armlet, and a chain of six spiral wire rings, the hoard is now preserved at the British Museum. Antiquity The town was founded in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emerita Augusta
Augusta Emerita, also called Emerita Augusta, was a Roman '' colonia'' founded in 25 BC in present day Mérida, Spain. The city was founded by Roman Emperor Augustus to resettle Emeriti soldiers from the veteran legions of the Cantabrian Wars, these being Legio V Alaudae, Legio X Gemina, and possibly Legio XX Valeria Victrix. The city, one of the largest in Hispania, was the capital of the Roman province of Lusitania, controlling an area of over . It had three aqueducts and two '' fora''. The city was situated at the junction of several important routes. It sat near a crossing of the Guadiana river. Roman roads connected the city west to Felicitas Julia Olisippo (Lisbon), south to Hispalis (Seville), northwest to the gold mining area, and to Corduba (Córdoba) and Toletum (Toledo). Today the Archaeological Ensemble of Mérida is one of the largest and most extensive archaeological sites in Spain and a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1993. Roman theatre The theatre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabratha - Bühnenhaus Des Theaters 2
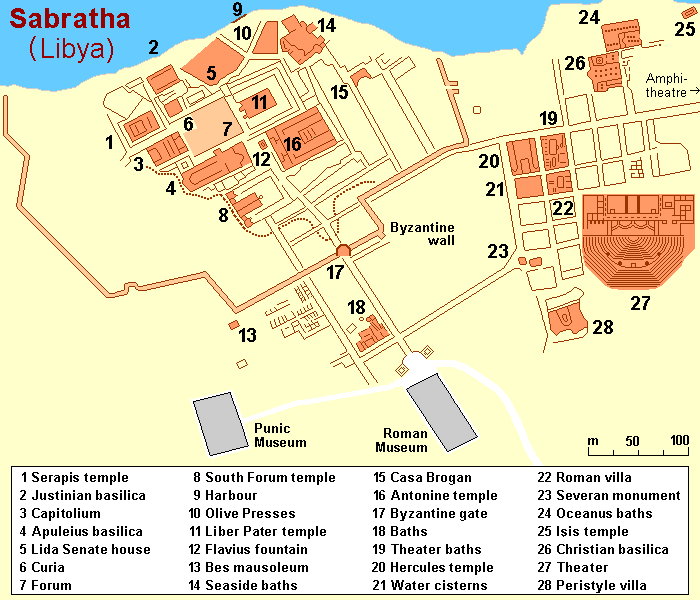
Sabratha (; also ''Sabratah'', ''Siburata''), in the Zawiya District''شعبيات الجماهيرية العظمى''Sha'biyat of Great Jamahiriya accessed 20 July 2009, in Arabic of , was the westernmost of the ancient "three cities" of Roman Tripolis, alongside and . From 2001 to 2007 it was the capit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libya
Libya, officially the State of Libya, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya border, the east, Sudan to Libya–Sudan border, the southeast, Chad to Chad–Libya border, the south, Niger to Libya–Niger border, the southwest, Algeria to Algeria–Libya border, the west, and Tunisia to Libya–Tunisia border, the northwest. With an area of almost , it is the 4th-largest country in Africa and the Arab world, and the List of countries and outlying territories by total area, 16th-largest in the world. Libya claims 32,000 square kilometres of southeastern Algeria, south of the Libyan town of Ghat, Libya, Ghat. The largest city and capital is Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli, which is located in northwestern Libya and contains over a million of Libya's seven million people. Libya has been inhabited by Berber people, Berbers since the late Bronze Age as descendants from Iberomaurusian and Capsian cultures. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |