|
Sauropod Hiatus
The sauropod hiatus is a geological period in the North American dinosaur fossil record for most of the Late Cretaceous noted for its lack of remains of sauropod dinosaurs. It may represent an extinction event, possibly caused by competition with ornithischian herbivores, habitat loss from the expansion of the Western Interior Seaway, or both. Alternatively, it has been argued that the hiatus represents a decrease in inland deposits that would have effectively preserved the animals, creating the illusion of an extinction. The sauropod hiatus ended shortly before the end of the Cretaceous, with the appearance of ''Alamosaurus'', most likely an immigrant from South America, in the southwestern parts of North America. History of the concept Definite evidence of Late Cretaceous sauropods in North America was first discovered in 1922, when Charles Whitney Gilmore described ''Alamosaurus sanjuanensis''. The term "sauropod hiatus" was coined by researchers Spencer G. Lucas and Adrian P. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Period
The geologic time scale or geological time scale (GTS) is a representation of time based on the geologic record, rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating stratum, strata to time) and geochronology (a scientific branch of geology that aims to determine the age of rocks). It is used primarily by Earth science, Earth scientists (including geologists, paleontology, paleontologists, geophysics, geophysicists, geochemistry, geochemists, and paleoclimatology, paleoclimatologists) to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history. The time scale has been developed through the study of rock layers and the observation of their relationships and identifying features such as lithology, lithologies, paleomagnetism, paleomagnetic properties, and fossils. The definition of standardised international units of geological time is the responsibility of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camarasaurus
''Camarasaurus'' ( ) is a genus of sauropod dinosaur that lived in North America during the Late Jurassic period. Its fossil remains have been found in the Morrison Formation, dating to the Kimmeridgian and Tithonian ages of the Jurassic, between 155 and 145 million years ago (mya). ''Camarasaurus'' presented a distinctive cranial profile of a blunt snout and an arched skull that was remarkably square, typical of basal macronarians. The generic name means "chambered lizard", referring to the hollow chambers, known as pleurocoels, in its cervical vertebrae (Greek (') meaning "vaulted chamber", or anything with an arched cover, and (') meaning "lizard"). ''Camarasaurus'' contains four species that are commonly recognized as valid: '' Camarasaurus grandis'', '' Camarasaurus lentus'', '' Camarasaurus lewisi'', and '' Camarasaurus supremus''. ''C. supremus'', the type species, is the largest and geologically youngest of the four. ''Camarasaurus'' is the type genus of Camaras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cedarosaurus
''Cedarosaurus'' (meaning "Cedar lizard" - named after the Cedar Mountain Formation, in which it was discovered) is a genus of nasal-crested macronarian dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous Period (Valanginian). It was a sauropod which lived in what is now Utah. The fossils were discovered in 1996 in eastern Utah within the rocks of the Yellow Cat Member of the Cedar Mountain Formation. It was officially named and described by Tidwell, Carpenter and Brooks in 1999. It shows similarities to the brachiosaurid ''Eucamerotus'' from the Wessex Formation of southern England, as well as to ''Brachiosaurus'' from the Morrison Formation. Description ''Cedarosaurus'' was identified as a brachiosaurid sauropod. Prior to its classification as a new genus, brachiosaurid fossil material from the early and middle Cretaceous Period which had been found in North America was ascribed to the genus ''Pleurocoelus'', which is now regarded as a junior synonym of ''Astrodon''. However, the shape of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
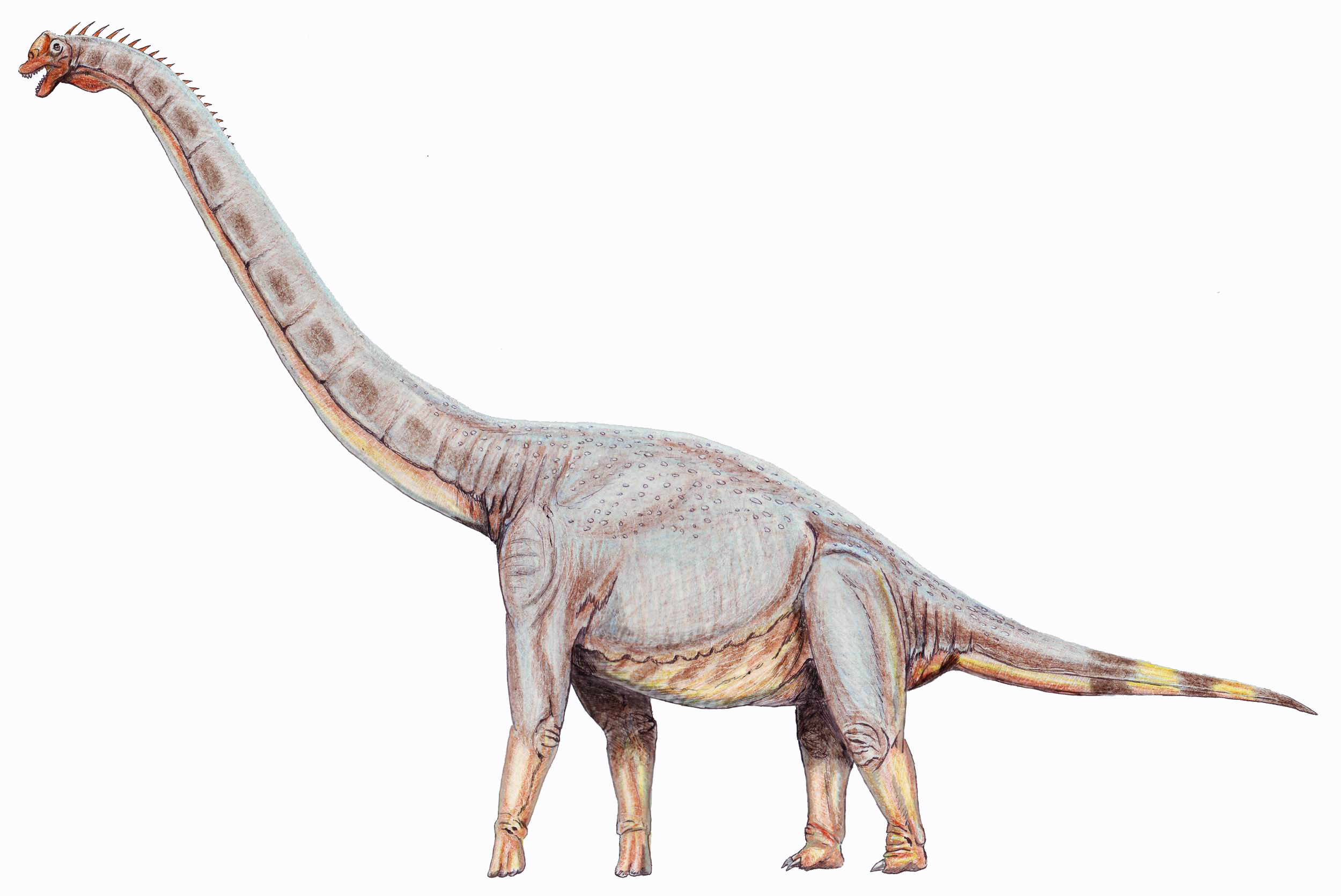
Brachiosaurids
The Brachiosauridae ("arm lizards", from Greek ''brachion'' (βραχίων) = "arm" and ''sauros'' = "lizard") are a family or clade of herbivorous, quadrupedal sauropod dinosaurs. Brachiosaurids had long necks that enabled them to access the leaves of tall trees that other sauropods would have been unable to reach. In addition, they possessed thick spoon-shaped teeth which helped them to consume tough plants more efficiently than other sauropods. They have also been characterized by a few unique traits or synapomorphies; dorsal vertebrae with 'rod-like' transverse processes and an ischium with an abbreviated pubic peduncle. ''Brachiosaurus'' is one of the best-known members of the Brachiosauridae, and was once thought to be the largest land animal to ever live. Brachiosaurids thrived in the regions which are now North and South America, Africa, Europe, and Asia. They first appear in the fossil record in the Late Jurassic Period (possibly even earlier in the Middle Jurassic) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moabosaurus
''Moabosaurus'' (meaning "Moab reptile") is a genus of turiasaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous Cedar Mountain Formation of Utah, United States. Description ''Moabosaurus'' is characterized by a suite of features including: extremely low neural spines that are thin, transverse ridges in the posterior cervical vertebrae and anterior dorsal vertebrae; strongly procoelous proximal and distal caudal vertebrae; and an ulna with well-developed lateral and medial anteroproximal ridges combined with a large olecranon process. According to the 2017 article which officially named and described ''Moabosaurus'', the animal was said to reach 10 meters (32.8 feet) long. However, the specimens which were examined belonged to juveniles and sub-adults, so it's possible that the creature measured longer when fully-grown. Discovery and naming ''Moabosaurus'' was collected from the Dalton Wells Quarry, which is about 20 km northwest of Moab, Utah. Between 1975 and 2005, the q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turiasaurs
Turiasauria is an unranked clade of eusauropod dinosaurs known from Middle Jurassic to Early Cretaceous deposits in Europe, North America, and Africa. Description Turiasauria was originally erected by Royo-Torres et al. (2006) to include '' Turiasaurus'', ''Galvesaurus'' and ''Losillasaurus'', all of which hail from the Villar del Arzobispo Formation (Tithonian-Berriasian) of Spain. Turiasuria was defined by the authors as "all Eusauropoda closer to ''Turiasaurus riodevensis'' than to ''Saltasaurus loricatus''". Cladistic analysis (Royo-Torres ''et al.'', 2006; 1927) of 309 characters and 33 taxa suggests that the turiasaurians lie outside the Neosauropoda and form a monophyletic group. The clade is diagnosed by the presence of vertical neural spines, posterior centroparapohyseal laminae on the dorsal vertebrae, the absence of pre- and postspinal laminae on the dorsal vertebrae, the absence of a scapular acromial crest, the presence of a prominent humeral deltopectoral crest, med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morrison Formation
The Morrison Formation is a distinctive sequence of Upper Jurassic sedimentary rock found in the western United States which has been the most fertile source of dinosaur fossils in North America. It is composed of mudstone, sandstone, siltstone, and limestone and is light gray, greenish gray, or red. Most of the fossils occur in the green siltstone beds and lower sandstones, relics of the rivers and floodplains of the Jurassic period. It is centered in Wyoming and Colorado, with outcrops in Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, Nebraska, Kansas, the panhandles of Oklahoma and Texas, New Mexico, Arizona, Utah, and Idaho. Equivalent rocks under different names are found in Canada. It covers an area of 1.5 million square kilometers (600,000 square miles), although only a tiny fraction is exposed and accessible to geologists and paleontologists. Over 75% is still buried under the prairie to the east, and much of its western paleogeographic extent was eroded during exhuma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era is the Era (geology), era of Earth's Geologic time scale, geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Period (geology), Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian reptiles such as the dinosaurs, and of Gymnosperm, gymnosperms such as cycads, ginkgoaceae and Araucariaceae, araucarian conifers; a hot Greenhouse and icehouse earth, greenhouse climate; and the tectonic break-up of Pangaea. The Mesozoic is the middle of the three eras since Cambrian explosion, complex life evolved: the Paleozoic, the Mesozoic, and the Cenozoic. The era began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, the largest mass extinction in Earth's history, and ended with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, another mass extinction whose victims included the non-avian dinosaurs, Pterosaur, pterosaurs, Mosasaur, mosasaurs, and Plesiosaur, plesiosaurs. The Mesozoic was a time of significant tectonic, climatic, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmopolitan Distribution
In biogeography, a cosmopolitan distribution is the range of a taxon that extends across most or all of the surface of the Earth, in appropriate habitats; most cosmopolitan species are known to be highly adaptable to a range of climatic and environmental conditions, though this is not always so. Killer whales ( orcas) are among the most well-known cosmopolitan species on the planet, as they maintain several different resident and transient (migratory) populations in every major oceanic body on Earth, from the Arctic Circle to Antarctica and every coastal and open-water region in-between. Such a taxon (usually a species) is said to have a ''cosmopolitan'' distribution, or exhibit cosmopolitanism, as a species; another example, the rock dove (commonly referred to as a ' pigeon'), in addition to having been bred domestically for centuries, now occurs in most urban areas around the world. The extreme opposite of a cosmopolitan species is an endemic (native) species, or one foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Variability And Change
Climate variability includes all the variations in the climate that last longer than individual weather events, whereas the term climate change only refers to those variations that persist for a longer period of time, typically decades or more. ''Climate change'' may refer to any time in Earth's history, but the term is now commonly used to describe contemporary climate change, often popularly referred to as global warming. Since the Industrial Revolution, the climate has increasingly been affected by human activities. The climate system receives nearly all of its energy from the sun and radiates energy to outer space. The balance of incoming and outgoing energy and the passage of the energy through the climate system is Earth's energy budget. When the incoming energy is greater than the outgoing energy, Earth's energy budget is positive and the climate system is warming. If more energy goes out, the energy budget is negative and Earth experiences cooling. The energy moving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaurs
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutionary history, evolution of dinosaurs is a subject of active research. They became the dominant terrestrial vertebrates after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event 201.3 mya and their dominance continued throughout the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The fossil record shows that birds are feathered dinosaurs, Evolution of birds, having evolved from earlier Theropoda, theropods during the Late Jurassic epoch, and are the only dinosaur lineage known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event approximately 66 mya. Dinosaurs can therefore be divided into avian dinosaurs—birds—and the extinct non-avian dinosaurs, which are all dinosaurs other than birds. Dinosaurs are varied from taxonomy (biology), taxonomic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach to taxonomy adopted by most biological fields. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or Extant taxon, extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed ''monophyletic'' (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming Taxon, taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not Monophyly, monophyletic. Some of the relationships between organisms that the molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |