|
Saccadic
In vision science, a saccade ( ; ; ) is a quick, simultaneous movement of both eyes between two or more phases of focal points in the same direction. In contrast, in smooth-pursuit movements, the eyes move smoothly instead of in jumps. Controlled cortically by the frontal eye fields (FEF), or subcortically by the superior colliculus, saccades serve as a mechanism for focal points, rapid eye movement, and the fast phase of optokinetic nystagmus. The word appears to have been coined in the 1880s by French ophthalmologist Émile Javal, who used a mirror on one side of a page to observe eye movement in silent reading, and found that it involves a succession of discontinuous individual movements. Function Humans and many organisms do not look at a scene in steadiness; instead, the eyes move around, locating interesting parts of the scene and building up a three-dimensional 'map' corresponding to the scene (as opposed to the graphical map of avians, which often relies upon detect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccadic Main Sequence
In vision science, a saccade ( ; ; ) is a quick, simultaneous movement of both Eye movement (sensory), eyes between two or more phases of focal points in the same direction. In contrast, in Smooth pursuit, smooth-pursuit movements, the eyes move smoothly instead of in jumps. Controlled cortically by the frontal eye fields (FEF), or subcortically by the superior colliculus, saccades serve as a mechanism for focal points, rapid eye movement, and the fast phase of optokinetic reflex, optokinetic nystagmus. The word appears to have been coined in the 1880s by French ophthalmologist Louis Émile Javal, Émile Javal, who used a mirror on one side of a page to observe eye movement in silent reading, and found that it involves a succession of discontinuous individual movements. Function Humans and many organisms do not look at a scene in steadiness; instead, the eyes move around, locating interesting parts of the scene and building up a three-dimensional 'map' corresponding to the scen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsaccade
Microsaccades are a kind of fixational eye movement. They are small, jerk-like, involuntary eye movements, similar to miniature versions of voluntary saccades. They typically occur during prolonged visual fixation (of at least several seconds), not only in humans, but also in animals with foveal vision (primates, cats, dogs etc.). Microsaccade amplitudes vary from 2 to 120 arcminutes. The first empirical evidence for their existence was provided by Robert Darwin, the father of Charles Darwin. Function The role of microsaccades in visual perception has been a highly debated topic that is still largely unresolved. It has been proposed that microsaccades correct displacements in eye position produced by drifts, although non-corrective microsaccades also occur. Some work has suggested that microsaccades are directly correlated with the perception of illusory motion. Although microsaccades can enhance vision of fine spatial detail, they can also impair visual perception in that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smooth Pursuit
In the scientific study of vision, smooth pursuit describes a type of eye movement in which the eyes remain fixated on a moving object. It is one of two ways that visual animals can voluntarily shift gaze, the other being saccadic eye movements. Pursuit differs from the vestibulo-ocular reflex, which only occurs during movements of the head and serves to stabilize gaze on a stationary object. Most people are unable to initiate pursuit without a moving visual signal. The pursuit of targets moving with velocities of greater than 30°/s tends to require catch-up saccades. Smooth pursuit is asymmetric: most humans and primates tend to be better at horizontal than vertical smooth pursuit, as defined by their ability to pursue smoothly without making ''catch-up saccades''. Most humans are also better at downward than upward pursuit. Pursuit is modified by ongoing visual feedback. Measurement There are two basic methods for recording smooth pursuit eye movements, and eye movement in g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
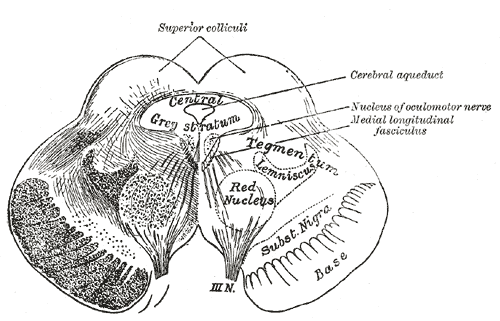
Superior Colliculus
In neuroanatomy, the superior colliculus () is a structure lying on the tectum, roof of the mammalian midbrain. In non-mammalian vertebrates, the Homology (biology), homologous structure is known as the optic tectum or optic lobe. The adjective form ''tectum, tectal'' is commonly used for both structures. In mammals, the superior colliculus forms a major component of the midbrain. It is a paired structure and together with the paired inferior colliculi forms the corpora quadrigemina. The superior colliculus is a layered structure, with a pattern that is similar in all mammals. The layers can be grouped into the superficial layers (retinal nerve fiber layer, stratum opticum and above) and the deeper remaining layers. Neurons in the superficial layers receive direct input from the retina and respond almost exclusively to visual stimuli. Many neurons in the deeper layers also respond to other modalities, and some respond to stimuli in multiple modalities. The deeper layers also conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Tracking
Eye tracking is the process of measuring either the point of gaze (where one is looking) or the motion of an eye relative to the head. An eye tracker is a device for measuring eye positions and eye movement. Eye trackers are used in research on the visual system, in psychology, in psycholinguistics, marketing, as an input device for human-computer interaction, and in product design. In addition, eye trackers are increasingly being used for assistive and rehabilitative applications such as controlling wheelchairs, robotic arms, and prostheses. Recently, eye tracking has been examined as a tool for the early detection of autism spectrum disorder. There are several methods for measuring eye movement, with the most popular variant using video images to extract eye position. Other methods use search coils or are based on the electrooculogram. History In the 1800s, studies of eye movement were made using direct observations. For example, Louis Émile Javal observed in 187 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
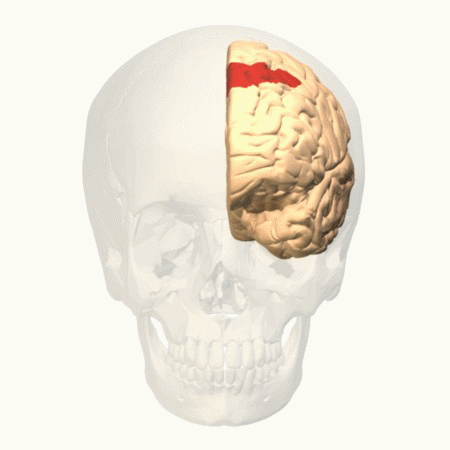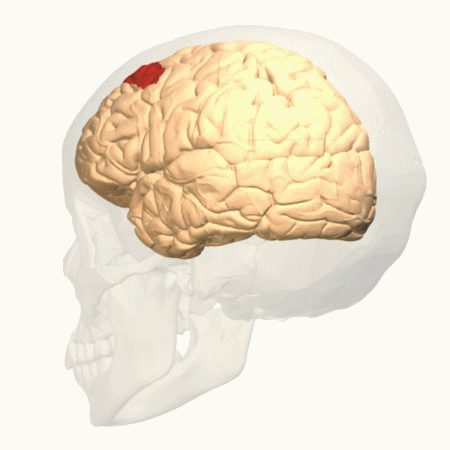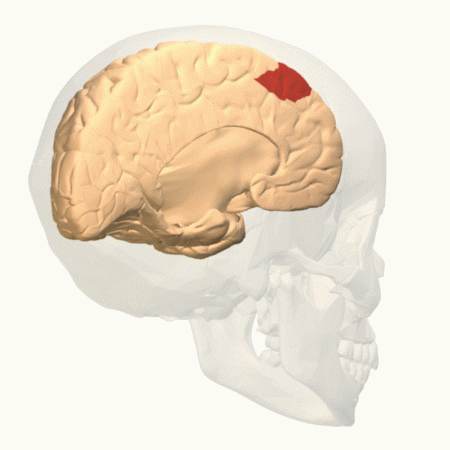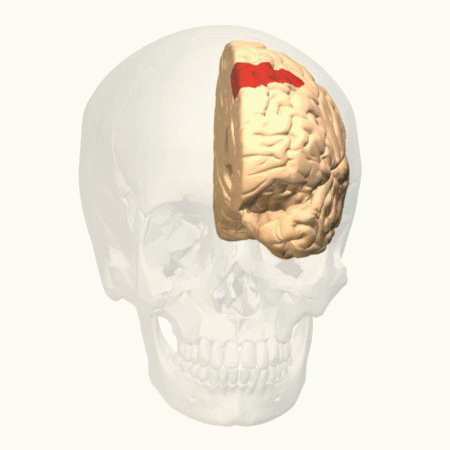
Frontal Eye Fields
The frontal eye fields (FEF) are a region located in the frontal cortex, more specifically in Brodmann area 8 or BA8, of the primate brain. In humans, it can be more accurately said to lie in a region around the intersection of the middle frontal gyrus with the precentral gyrus, consisting of a frontal and parietal portion. The FEF is responsible for Saccade, saccadic eye movements for the purpose of visual field perception and awareness, as well as for voluntary eye movement. The FEF communicates with extraocular muscles indirectly via the paramedian pontine reticular formation. Destruction of the FEF causes deviation of the eyes to the ipsilateral side. Function The cortical area called the frontal eye field (FEF) plays an important role in the control of visual attention and eye movements. Electrical stimulation in the FEF elicits saccadic eye movements. The FEF have a topographic structure and represents saccade targets in retinotopic coordinates. The frontal eye field is rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parietal Cortex
The parietal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The parietal lobe is positioned above the temporal lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus. The parietal lobe integrates sensory information among various modalities, including spatial sense and navigation (proprioception), the main sensory receptive area for the sense of touch in the somatosensory cortex which is just posterior to the central sulcus in the postcentral gyrus, and the dorsal stream of the visual system. The major sensory inputs from the skin (touch, temperature, and pain receptors), relay through the thalamus to the parietal lobe. Several areas of the parietal lobe are important in language processing. The somatosensory cortex can be illustrated as a distorted figure – the cortical homunculus (Latin: "little man") in which the body parts are rendered according to how much of the somatosensory cortex is devoted to them. The superior parietal lobule an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bang–bang Control
In control theory, a bang–bang controller (hysteresis, 2 step or on–off controller), is a feedback controller that switches abruptly between two states. These controllers may be realized in terms of any element that provides hysteresis. They are often used to control a plant that accepts a binary input, for example a furnace that is either completely on or completely off. Most common residential thermostats are bang–bang controllers. The Heaviside step function in its discrete form is an example of a bang–bang control signal. Due to the discontinuous control signal, systems that include bang–bang controllers are variable structure systems, and bang–bang controllers are thus variable structure controllers. Bang–bang solutions in optimal control In optimal control problems, it is sometimes the case that a control is restricted to be between a lower and an upper bound. If the optimal control switches from one extreme to the other (i.e., is strictly never in between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a classification of stars which appear on plots of stellar color index, color versus absolute magnitude, brightness as a continuous and distinctive band. Stars on this band are known as main-sequence stars or dwarf stars, and positions of stars on and off the band are believed to indicate their physical properties, as well as their progress through several types of star life-cycles. These are the most numerous true stars in the universe and include the Sun. Color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell. After condensation and ignition of a star, it generates thermal energy in its dense stellar core, core region through nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium. During this stage of the star's lifetime, it is located on the main sequence at a position determined primarily by its mass but also based on its chemical composition and age. The cores of main-sequence stars are in hydros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocular Drift
An eye is a sensory organ that allows an organism to perceive visual information. It detects light and converts it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons (neurones). It is part of an organism's visual system. In higher organisms, the eye is a complex optical system that collects light from the surrounding environment, regulates its intensity through a diaphragm, focuses it through an adjustable assembly of lenses to form an image, converts this image into a set of electrical signals, and transmits these signals to the brain through neural pathways that connect the eye via the optic nerve to the visual cortex and other areas of the brain. Eyes with resolving power have come in ten fundamentally different forms, classified into compound eyes and non-compound eyes. Compound eyes are made up of multiple small visual units, and are common on insects and crustaceans. Non-compound eyes have a single lens and focus light onto the retina to form a single image. This type of eye i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |