|
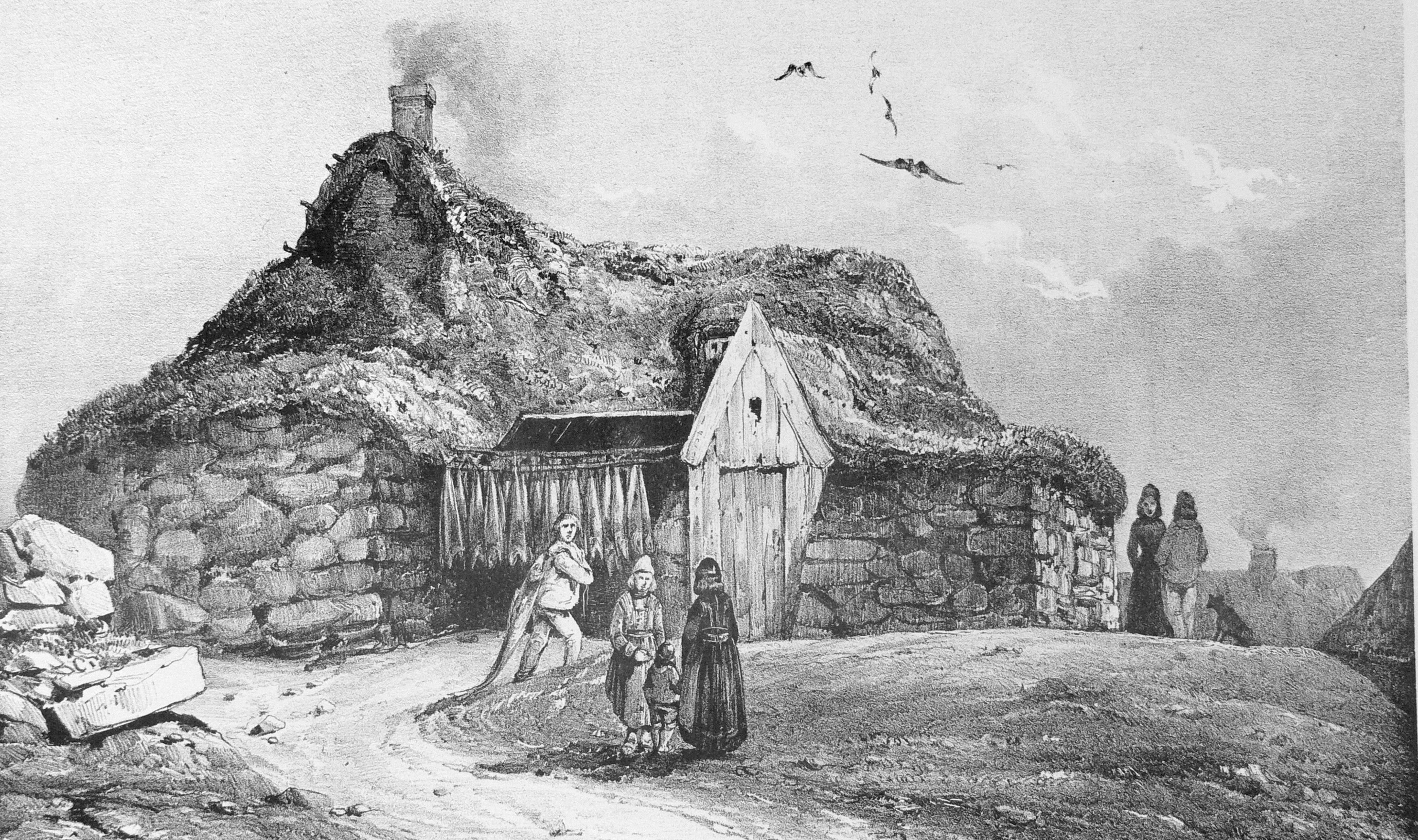
Rúgbrauð
(, ) is an Icelandic straight rye bread. It is traditionally baked in a Pottery, pot or steamed in special wooden casks by burying it in the ground near a geyser, in which case it is known as or "hot-spring-bread". Modern is usually made in a square baking pan. The bread is crustless, dark and very dense, usually rather sweet, and keeps for a long time. It is often served with butter, mutton pâté, hangikjöt (smoked lamb), or pickled herring. Dry would be ground and mixed with buttermilk to form a kind of porridge. Stale is often soaked, then made into (, "bread soup") – that is, simmered with raisins and flavorings (usually lemon) and served hot with whipped cream as a dessert. Excessive consumption of this bread is said to cause flatulence, earning it its nickname , which roughly translates as "thunderbread" or "thunderer". There are, however, varieties of the traditional rye bread with wheat and whole grain added to make it less dense, but also called . These varie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icelandic Cuisine
The cuisine of Iceland has a long history. Important parts of Iceland, Icelandic cuisine are lamb, dairy, and Fish as food, fish, the latter because Iceland has traditionally been inhabited only near its coastline. Popular foods in Iceland include skyr, hangikjöt (smoked lamb), kleina, kleinur, laufabrauð, and bolla (food), bollur. Þorramatur is a traditional buffet served at midwinter festivals called Þorrablót; it includes a selection of traditionally cured meat and fish products served with ''rúgbrauð'' (dense dark and sweet rye bread) and brennivín (an Icelandic akvavit). The flavors of this traditional country food originate in its food preservation, preservation methods: pickling in fermented whey or brine, drying, and smoking. Modern Icelandic chefs usually emphasise the quality of available ingredients rather than age-old cooking traditions and methods. Numerous restaurants in Iceland specialise in seafood. At the annual Food and Fun chef's competition (held sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iceland
Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the region's westernmost and most list of countries and dependencies by population density, sparsely populated country. Its Capital city, capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which is home to about 36% of the country's roughly 380,000 residents (excluding nearby towns/suburbs, which are separate municipalities). The official language of the country is Icelandic language, Icelandic. Iceland is on a rift between Plate tectonics, tectonic plates, and its geologic activity includes geysers and frequent Types of volcanic eruptions, volcanic eruptions. The interior consists of a volcanic plateau with sand and lava fields, mountains and glaciers, and many Glacial stream, glacial rivers flow to the sea through the Upland and lowland, lowlands. Iceland i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hangikjöt
Hangikjöt (; lit. "hung meat") is a traditional festive food in Iceland, served at Christmas. Etymology and history This Icelandic smoked lamb, mutton, or horse meat is usually boiled and served either hot or cold in slices, traditionally with potatoes in béchamel sauce and green peas, or in thin slices on bread Bread is a baked food product made from water, flour, and often yeast. It is a staple food across the world, particularly in Europe and the Middle East. Throughout recorded history and around the world, it has been an important part of many cu ... such as '' flatkaka'' or '' rúgbrauð'' or '' laufabrauð''. It takes its name from the old tradition of smoking food in order to preserve it by hanging it from the rafters of a smoking shed. Sometimes, bits of string are present in the meat, having been tied around the meat to compress it and hold it together as it is being smoked; the strings are not eaten. There are several types of hangikjöt. The meat can co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flatbrauð
Flatkaka (, lit. "flat cake") or flatbrauð (, lit. "flat bread") is an Icelandic unleavened rye flatbread. ''Flatkaka'' is soft, round, thin and dark with a characteristic pattern from the pan. Traditionally, ''flatkaka'' was baked on hot stones or straight on the embers of the fire, later on small but heavy cast iron frying pans, and today, when making ''flatkaka'' at home, people sometimes bake them directly on an electric hot plate to get the desired result. There usually is a difference between home-made ''flatkaka'' and the varieties sold in stores, the latter being somewhat thicker and dryer because of added wheat flour. It is assumed that the Icelandic tradition of baking flatbread goes back to the settlement of Iceland in the 9th century. Historically, Iceland moss (''Cetraria islandica'') was sometimes used as a supplement because of a lack of grain on the island. ''Flatkaka'' is usually served cut into halves or quarters, with a topping of butter or mutton pâté, wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vísir
''Vísir'' was an Icelandic newspaper founded in December 1910 by Einar Gunnarsson, originally only distributed in and around Reykjavík. In 1967, Jónas Kristjánsson (newspaper editor), Jónas Kristjánsson became its editor. In 1975, he left the paper after a conflict with the ownership group of on his editorial policy and founded Dagblaðið. On 26 November 1981, Vísir and Dagblaðið merged to form Dagblaðið Vísir. References 1910 establishments in Iceland Newspapers established in 1910 Daily newspapers published in Iceland Defunct newspapers published in Iceland Mass media in Reykjavík Publications disestablished in 1981 {{Iceland-newspaper-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
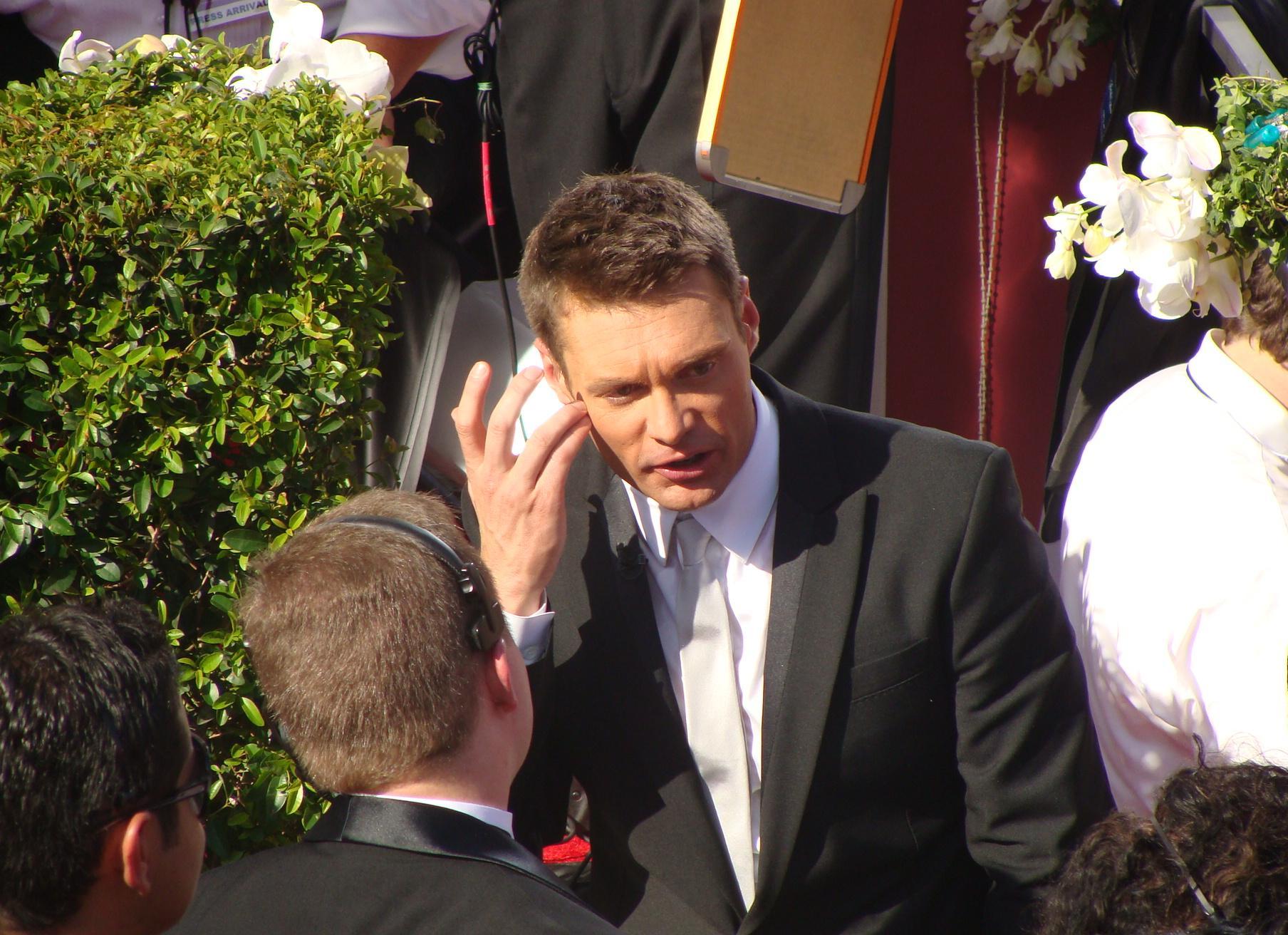
Ryan Seacrest
Ryan John Seacrest (born December 24, 1974) is an American television presenter and producer. Seacrest is the host of '' Wheel of Fortune'', having hosted since replacing long-time host Pat Sajak in September 2024. Seacrest co-hosted and served as executive producer of '' Live with Kelly and Ryan'', and has hosted other media including ''American Idol'', ''American Top 40'', and ''On Air with Ryan Seacrest''. He became co-host of '' Dick Clark's New Year's Rockin' Eve'' in 2005, and became the sole host following Clark's death in 2012. Seacrest received Emmy Award nominations for ''American Idol'' each year from 2004 to 2013, and once more in 2016. He won an Emmy for '' Jamie Oliver's Food Revolution'' in 2010, and was nominated once more in 2012. In 2018, he received nominations for ''Live with Kelly and Ryan'' for Outstanding Talk Show Entertainment and Outstanding Entertainment Talk Show Host. Early life Ryan John Seacrest was born in Atlanta on December 24, 1974, the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Fernando Valley
The San Fernando Valley, known locally as the Valley, is an urbanized valley in Los Angeles County, Los Angeles County, California. Situated to the north of the Los Angeles Basin, it comprises a large portion of Los Angeles, the Municipal corporation, incorporated cities of Burbank, California, Burbank, Calabasas, California, Calabasas, Glendale, California, Glendale, Hidden Hills, California, Hidden Hills and San Fernando, California, San Fernando, plus several unincorporated areas. The valley is the home of Warner Bros. Studios Burbank, Warner Bros. Studios, Walt Disney Studios (Burbank), Walt Disney Studios, and the Universal Studios Hollywood theme park. Geography The valley of San Fernando is an area of , bounded by the San Gabriel Mountains in the northeast, the Verdugo Mountains in the east, the Santa Monica Mountains and Chalk Hills in the south, the Simi Hills in the west, and the Santa Susana Mountains in the northwest. The northern Sierra Pelona Mountains, northweste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julian Lozos
Julian may refer to: People * Julian (emperor) (331–363), Roman emperor from 361 to 363 * Julian, of the Roman gens Julia, with imperial dynasty offshoots * Saint Julian (other), several Christian saints * Julian (given name), people with the given name Julian * Julian (surname), people with the surname Julian * Julian (singer), Russian pop singer Places * Julian, California, a census-designated place in San Diego County * Julian, Kansas, an unincorporated community in Stanton County * Julian, Nebraska, a village in Nemaha County * Julian, North Carolina, a census-designated place in Guilford County * Julian, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community and census-designated place in Centre County * Julian, West Virginia, an unincorporated community in Boone County Other uses * ''Julian'' (album), a 1976 album by Pepper Adams * ''Julian'' (novel), a 1964 novel by Gore Vidal about the emperor * ''Julian'' (play), an 1823 play by Mary Russell Mitford * Julian (geolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismologist
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes (or generally, quakes) and the generation and propagation of elastic waves through planetary bodies. It also includes studies of the environmental effects of earthquakes such as tsunamis; other seismic sources such as volcanoes, plate tectonics, glaciers, rivers, oceanic microseisms, and the atmosphere; and artificial processes such as explosions. Paleoseismology is a related field that uses geology to infer information regarding past earthquakes. A recording of Earth's motion as a function of time, created by a seismograph is called a seismogram. A seismologist is a scientist who works in basic or applied seismology. History Scholarly interest in earthquakes can be traced back to antiquity. Early speculations on the natural causes of earthquakes were included in the writings of Thales of Miletus () ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of Denmark
The monarchy of Denmark is a constitutional political system, institution and a historic office of the Kingdom of Denmark. The Kingdom includes Denmark proper and the autonomous administrative division, autonomous territories of the Faroe Islands and Greenland. The Kingdom of Denmark was already consolidated in the 8th century, whose rulers are consistently referred to in Franks, Frankish sources (and in some late Frisians, Frisian sources) as "kings" (). Under the rule of King Gudfred in 804 the Kingdom may have included all the major Lands of Denmark, provinces of medieval Denmark. The current unified Kingdom of Denmark was founded or re-united by the Vikings, Viking kings Gorm the Old and Harald Bluetooth in the 10th century. Originally an elective monarchy, it became hereditary monarchy, hereditary only in the 17th century during the reign of Frederick III of Denmark, Frederick III. A decisive transition to a constitutional monarchy occurred in 1849 with the writing of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monopoly
A monopoly (from Greek language, Greek and ) is a market in which one person or company is the only supplier of a particular good or service. A monopoly is characterized by a lack of economic Competition (economics), competition to produce a particular thing, a lack of viable substitute goods, and the possibility of a high monopoly price well above the seller's marginal cost that leads to a high monopoly profit. The verb ''monopolise'' or ''monopolize'' refers to the ''process'' by which a company gains the ability to raise prices or exclude competitors. In economics, a monopoly is a single seller. In law, a monopoly is a business entity that has significant market power, that is, the power to charge Monopoly price, overly high prices, which is associated with unfair price raises. Although monopolies may be big businesses, size is not a characteristic of a monopoly. A small business may still have the power to raise prices in a small industry (or market). A monopoly may als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Modern Period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There is no exact date that marks the beginning or end of the period and its extent may vary depending on the area of history being studied. In general, the early modern period is considered to have lasted from around the start of the 16th century to the start of the 19th century (about 1500–1800). In a European context, it is defined as the period following the Middle Ages and preceding the advent of modernity; but the dates of these boundaries are far from universally agreed. In the context of World history (field), global history, the early modern period is often used even in contexts where there is no equivalent "medieval" period. Various events and historical transitions have been proposed as the start of the early modern period, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |