|
Régiment De Penthièvre
''For the 8th Dragoons in the British Army, see 8th King's Royal Irish Hussars.'' The 8th Dragoon Regiment (''8e régiment de dragons'' or ''8e RD'') was a cavalry regiment in the French Army created under the ''Ancien Régime'' in 1674 by the Marquis of Heudicourt. History Under the ''Ancien Régime'' In 1674, a new regiment was created by the Marquis of Heudicourt, named the Heudicourt Regiment. It was renamed multiple times under the command of the Ancien Régime:{{Citation needed, date=September 2024 • Choiseul-Praslin Regiment (1688) • Toulouse Regiment (1693) • Penthièvre Regiment (1737), later also "Penthièvre Regiment Dragoons"(1776) This regiment would initially first serve in the Dutch Wars, and the Siege of Luxembourg, playing minor roles. They would enter combat at numerous points in the War of the League of Augsburg, the Battle of Neerwinden, the early bombardment of Brussels, and the War of the Spanish Succession, proving effective in most of these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragoon
Dragoons were originally a class of mounted infantry, who used horses for mobility, but dismounted to fight on foot. From the early 17th century onward, dragoons were increasingly also employed as conventional cavalry and trained for combat with swords and firearms from horseback. While their use goes back to the late 16th century, dragoon regiments were established in most European armies during the 17th and early 18th centuries; they provided greater mobility than regular infantry but were far less expensive than cavalry. The name reputedly derives from a type of firearm, called a ''Dragon (firearm), dragon'', which was a handgun version of a blunderbuss, carried by dragoons of the French Army. The title has been retained in modern times by a number of armoured warfare, armoured or ceremonial mounted regiments. Origins and name The establishment of dragoons evolved from the practice of sometimes transporting infantry by horse when speed of movement was needed. During th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict fought between 1701 and 1714. The immediate cause was the death of the childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700, which led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between supporters of the French House of Bourbon, Bourbons and the Austrian House of Habsburg, Habsburgs. Charles had named as his heir Philip V of Spain, Philip of Anjou, a grandson of Louis XIV of France, whose claim was backed by Kingdom of France, France and most of Habsburg Spain, Spain. His Habsburg rival, Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor, Archduke Charles, was supported by the Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), Grand Alliance, whose primary members included Habsburg monarchy, Austria, the Dutch Republic, and Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain. Significant related conflicts include the Great Northern War (1700–1721) and Queen Anne's War (1702–1713). Although by 1701 Spain was no longer the predominant European power, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Marengo
The Battle of Marengo was fought on 14 June 1800 between French forces under the First Consul Napoleon Bonaparte and Austrian forces near the city of Alessandria, in Piedmont, Italy. Near the end of the day, the French overcame General Michael von Melas's surprise attack, drove the Austrians out of Italy and consolidated Bonaparte's political position in Paris as First Consul of France in the wake of his coup d'état the previous November. Surprised by the Austrian advance toward Genoa in mid-April 1800, Bonaparte hastily led his army over the Alps in mid-May and reached Milan on 2 June. After cutting Melas's line of communications by crossing the river Po and defeating '' Feldmarschallleutnant'' (FML) Peter Karl Ott von Bátorkéz at Montebello on 9 June, the French closed in on the Austrian Army, which had massed in Alessandria. Deceived by a local double agent, Bonaparte dispatched large forces to the north and the south, but the Austrians launched a surprise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coup Of 18 Brumaire
The Coup of 18 Brumaire () brought Napoleon Bonaparte to power as First Consul of the French First Republic. In the view of most historians, it ended the French Revolution and would soon lead to the coronation of Napoleon as Emperor of the French. This bloodless coup d'état overthrew the Directory, replacing it with the French Consulate. This occurred on 9 November 1799, which was 18 Brumaire, Year VIII, under the short-lived French Republican calendar system. Context After Habsburg-controlled Austria declared war on France on 12 March 1799, emergency measures were adopted and the pro-war Jacobin faction, the Montagnards, triumphed in the 1799 French legislative election held in April. With Napoleon and the republic's best army engaged in the French invasion of Egypt and Syria, France suffered a series of reverses on the battlefield in the spring and summer of 1799. The Coup of 30 Prairial VII (18 June) ousted the Jacobins and left Emmanuel Joseph Sieyès, a member o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Rivoli
The Battle of Rivoli (14 January 1797) was a key military engagement during the War of the First Coalition near the village of Rivoli Veronese, Rivoli, then part of the Republic of Venice. In the climax of the Italian Campaign of 1796-1797, Italian campaign of 1796-1797, the outnumbered French Army of Italy (France), Army of Italy commanded by General Napoleon, Napoleon Bonaparte decisively defeated the attacking Austrian army commanded by Feldzeugmeister, General of the Artillery Jozsef Alvinczi, who was attempting to march south in a fourth and final attempt to relieve the Siege of Mantua (1796-1797), siege of Mantua. The French victory at Rivoli further demonstrated Bonaparte's capability and deftness as a military commander, and led to the Austrian surrender of Mantua in February, French consolidation of northern Italy, and ultimately France's victory over Austria in the war later that year. Forces See order of battle at the Battle of Rivoli. Prelude Alvinczi's plan was to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Mantua (1796–97)
Siege of Mantua can refer to: * Siege of Mantua (1630) (War of the Mantuan Succession, French defending) * Siege of Mantua (1702) (War of the Spanish Succession, French defending) * Siege of Mantua (1796–97) (First Coalition, French besieging) * Siege of Mantua (1799) (Second Coalition, French defending) {{Disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
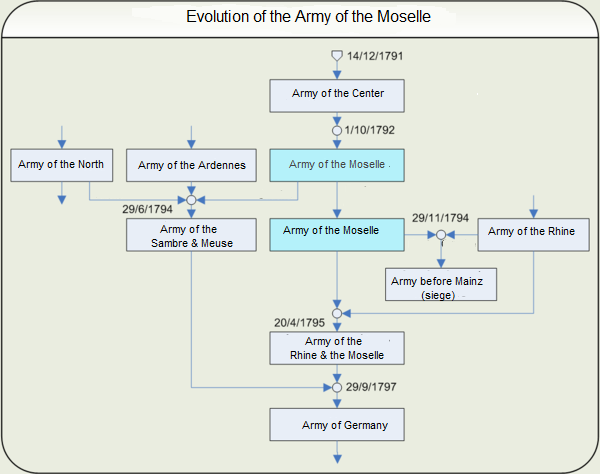
Army Of The Moselle
The Army of the Moselle (''Armée de la Moselle'') was a French Revolutionary Army from 1791 through 1795. It was first known as the '' Army of the Centre'' and it fought at Valmy. In October 1792 it was renamed and subsequently fought at Trier, First Arlon, Biesingen, Kaiserslautern, Froeschwiller and Second Wissembourg. In the spring of 1794 the left wing was detached and fought at Second Arlon, Lambusart and Fleurus before being absorbed by the '' Army of Sambre-et-Meuse''. In late 1794, the army captured Trier and initiated the Siege of Luxembourg. During the siege, the army was discontinued and its divisions were assigned to other armies. History Originally known as the '' Army of the Centre'', it was renamed by decree of the National Convention on 1 October 1792 and kept under that name in the decrees of 1 March and 30 April 1793. By the decree of 29 June 1794 its left wing joined with the '' Army of the Ardennes'' and the right wing of the ''Army of the North'' to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of Wissembourg (1793)
The Second Battle of Wissembourg from 26 December 1793 to 29 December 1793 saw an army of the First French Republic under General Lazare Hoche fight a series of clashes against an army of Austrians, Prussians, Bavarians, and Hessians led by General Dagobert Sigmund von Wurmser. There were significant actions at Wœrth on 22 December and Geisberg on 26 and 27 December. In the end, the French forced their opponents to withdraw to the east bank of the Rhine River. The action occurred during the War of the First Coalition phase of the French Revolutionary Wars. Background During the First Battle of Wissembourg on 13 October 1793, the Lines of Weissenburg, defended by the French Army of the Rhine, were stormed by an Austrian-Allied army under Wurmser. A month later, Austrian engineer Franz von Lauer compelled Fort-Louis on the Rhine to surrender to the Allies. The French government responded to the crisis by sending reinforcements from the Army of the Moselle. On 17 November, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Mainz (1793)
In the siege of Mainz (), from 14 April to 23 July 1793, a coalition of Prussia, Austria, and other German states led by the Holy Roman Empire besieged and captured Mainz from revolutionary French forces. The allies, especially the Prussians, first tried negotiations, but this failed, and the bombardment of the city began on the night of 17 June. Siege Within the town the siege and bombardment led to stress between citizens, municipality and the French war council, governing since 2 April. The city administration was displaced on 13 July; this increased the stubbornness of the remaining population. Since a relief army was missing, the war council was forced to take up negotiations with the allied forces on 17 July; the remaining soldiers capitulated on 23 July. Nearly 19,000 French troops surrendered at the end of the siege, but were allowed to return to France if they promised not to fight against the allies for one year. Consequently, they were used to fight French royalist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Of The Rhine (1791–1795)
The Army of the Rhine (; ) was formed in December 1791, for the purpose of bringing the French Revolution to the German states along the Rhine River. During its first year in action (1792), under command of Adam Philippe, Comte de Custine, Adam Philippe Custine, the Army of the Rhine participated in several victories, including Siege of Mainz (1792), Mainz, Frankfurt and Speyer. Subsequently, the army underwent several reorganizations and merged with the Army of the Moselle to form the Army of the Rhine and Moselle on 20 April 1795. Revolutionary Wars The Army of the Rhine (''Armée du Rhin'') was one of the main French Revolutionary Army, French Revolutionary armies operated in the Rhineland theater, principally in the Rhine River valley, from 1791 to 1795. At its creation, the Army of the Rhine had 88,390 men. It was formed on 14 December 1791, to defend France's eastern frontier in conjunction with two other armies, the Army of the North (France), Army of the North and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Of The Alps
The Army of the Alps (''Armée des Alpes'') was one of the French Revolutionary armies. It existed from 1792–1797 and from July to August 1799, and the name was also used on and off until 1939 for France's army on its border with Italy. 1792–1797 The Army of the Alps was created by a decree of the French Convention on 1 October 1792 which divided the Army of the Midi into the Army of the Alps and the Army of the Pyrenees. On 1 November 1793 it was itself divided into the Army of Savoy and the Army of Italy by a ''conseil exécutif'' decree. Following the decrees of 27–29 November 1792 which brought Savoy into the First French Republic under the name of Mont-Blanc department the Army of Savoy was renamed the Army of the Alps, before having the Army before Lyon split off from it between 8 August and 29 October 1793. The Army of the Alps was suppressed by a decree of 21 August 1797 (21 Fructidor year V), put into effect on 13 September, with its men and theatre transferr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1772 - Louis XV - Cavalerie - Rég
Year 177 ( CLXXVII) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar The Julian calendar is a solar calendar of 365 days in every year with an additional leap day every fourth year (without exception). The Julian calendar is still used as a religious calendar in parts of the Eastern Orthodox Church and in parts .... At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Commodus and Plautius (or, less frequently, year 930 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 177 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Commodus, Lucius Aurelius Commodus Caesar (age 15) and Marcus Peducaeus Plautius Quintillus become Roman Consuls. * Commodus is given the title ''Augustus (honorific), Augustus'', and is made co-emperor, with the same status as his father, Marcus Aurelius. * A systematic persecution of Christianity, Christians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |