|
Rose Fish
''Sebastes norvegicus'', the rose fish, rock fish, ocean perch, Atlantic redfish, Norway haddock, golden redfish, pinkbelly rosefish, Norway seaperch, Scottish seaperch or bergylt, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae, the rockfishes, part of the Family (biology), family Scorpaenidae. It is found in the North Atlantic Ocean. It is a large, slow-growing, late-maturing fish and the subject of a fishery. Taxonomy ''Sebastes norvegicus'' was first formally Species description, described as ''Perca norvegicus'' in 1772 by the Norwegian biologist Peter Ascanius with the Type locality (biology), type locality given as Norway. The specific name refers to the type locality. In the past, the scientific name ''Sebastes marinus'' was frequently used, but this is actually a Synonym (taxonomy), synonym of ''Painted comber, Serranus scriba''. ''S. norvegicus'' was designated as the type species of the genus ''Sebastes'' by Pieter Bleeker in 1876. This ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Ascanius
Peter Ascanius (24 May 1723 – 4 June 1803) was a Norway, Norwegian-Denmark, Danish biologist and geologist. He was a professor of zoology and mineralogy. Early life and education He was born at Aure (village), Aure in Møre og Romsdal, Romsdalen county, Norway. In 1742 he graduated from Trondheim Cathedral School and attended the University of Copenhagen where he studied medicine and took a Bachelor's degree in 1747. From 1752 he stayed a couple of years at Uppsala University where he was a student of Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778). He studied natural history with Linnaeus and chemistry and metallurgy with Johan Gottschalk Wallerius (1709–1785). Ascanius undertook a Grand Tour, study trip in the years 1753 to 1758, visiting the Netherlands, England, France, Italy and Austria. Career After returning from his European study trip, in 1759, Ascanius was appointed professor of natural history at the Royal Danish Academy of Fine Arts which was established at Charlottenborg at Copenha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sebastes
''Sebastes'' is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae part of the family Scorpaenidae, most of which have the common name of rockfish. A few are called ocean perch, sea perch or redfish instead. They are found in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Taxonomy ''Sebastes'' was first described as a genus in 1829 by the French zoologist Georges Cuvier, the Dutch ichthyologist Pieter Bleeker designated ''Perca norvegica'', which may have been originally described by the Norwegian zoologist Peter Ascanius in 1772, as the type species in 1876. The genus is the type genus of both the tribe Sebastini and the subfamily Sebastinae, although some authorities treat these as the subfamily Sebastinae and the family Sebastidae, separating the Sebastidae as a distinct family from the Scorpaenidae. but other authorities place it in the Perciformes in the suborder Scorpaenoidei. Some authorities subdivide this large genus into subgenera as follows: * ''Sebastes'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barents Sea
The Barents Sea ( , also ; , ; ) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located off the northern coasts of Norway and Russia and divided between Norwegian and Russian territorial waters.World Wildlife Fund, 2008. It was known earlier among Russians as the Northern Sea, Pomorsky Sea or Murman Sea ("Norse Sea"); the current name of the sea is after the historical Netherlands, Dutch navigator Willem Barentsz. The Barents Sea is a rather shallow Continental shelf, shelf sea with an average depth of , and it is an important site for both fishing and hydrocarbon exploration.O. G. Austvik, 2006. It is bordered by the Kola Peninsula to the south, the shelf edge towards the Norwegian Sea to the west, the archipelagos of Svalbard to the northwest, Franz Josef Land to the northeast and Novaya Zemlya to the east. The islands of Novaya Zemlya, an extension of the northern end of the Ural Mountains, separate the Barents Sea from the Kara Sea. Although part of the Arctic Ocean, the Barents Sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Sea in the north. It is more than long and wide, covering . It hosts key north European shipping lanes and is a major fishery. The coast is a popular destination for recreation and tourism in bordering countries, and a rich source of energy resources, including wind energy, wind and wave power. The North Sea has featured prominently in geopolitical and military affairs, particularly in Northern Europe, from the Middle Ages to the modern era. It was also important globally through the power northern Europeans projected worldwide during much of the Middle Ages and into the modern era. The North Sea was the centre of the Viking Age, Vikings' rise. The Hanseatic League, the Dutch Golden Age, Dutch Republic, and Kingdom of Great Britain, Brita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kattegat
The Kattegat (; ; ) is a sea area bounded by the peninsula of Jutland in the west, the Danish straits islands of Denmark and the Baltic Sea to the south and the Swedish provinces of Bohuslän, Västergötland, Halland and Scania in Sweden in the east. The Baltic Sea drains into the Kattegat through the Danish straits. The sea area is a continuation of the Skagerrak and may be seen as a bay of the North Sea and North Atlantic Ocean, though this is not the case in traditional Scandinavian usage. The Kattegat is a rather shallow sea and can be dangerous to navigate due to many sandy, stony reefs and the tricky shifting currents. In modern times, artificial seabed channels have been dug, many reefs have been dredged either by sand pumping or boulder clearance, and a well-developed light signaling network has been installed to protect the heavy international traffic on this small sea. There are several large cities and major ports on the Kattegat, including, in descendin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
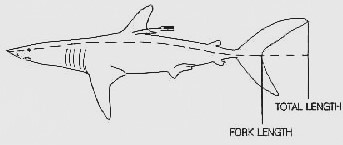
Total Length
Fish measurement is the measuring of individual fish and various parts of their anatomies, for data used in many areas of ichthyology, including taxonomy and fishery biology. Overall length Standard length (SL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the posterior end of the last vertebra or to the posterior end of the midlateral portion of the hypural plate. This measurement excludes the length of the caudal (tail) fin. Total length (TL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the tip of the longer lobe of the caudal fin, usually measured with the lobes compressed along the midline. It is a straight-line measure, not measured over the curve of the body. Standard length measurements are used with Teleostei (most bony fish), while total length measurements are used with Myxini (hagfish), Petromyzontiformes ( lampreys) and usually Elasmobranchii (shark Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operculum (fish)
The operculum is a series of bones found in bony fish and chimaeras that serves as a facial support structure and a protective covering for the gills; it is also used for respiration and feeding. Anatomy The opercular series contains four bone segments known as the preoperculum, suboperculum, interoperculum and operculum. The preoperculum is a crescent-shaped structure that has a series of ridges directed posterodorsally to the organism’s canal pores. The preoperculum can be located through an exposed condyle that is present immediately under its ventral margin; it also borders the operculum, suboperculum, and interoperculum posteriorly. The suboperculum is rectangular in shape in most bony fish and is located ventral to the preoperculum and operculum components. It is the thinnest bone segment out of the opercular series and is located directly above the gills. The interoperculum is triangular shaped and borders the suboperculum posterodorsally and the preoperculum anterodo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleithrum
The cleithrum (: cleithra) is a membrane bone which first appears as part of the skeleton in primitive Osteichthyes, bony fish, where it runs vertically along the scapula. Its name is derived from Greek κλειθρον = "key (lock)", by analogy with "clavicle" from Latin ''clavicula'' = "little key". In modern fishes, the cleithrum is a large bone that extends upwards from the base of the pectoral fin and anchors to the cranium above the gills, forming the posterior edge of the gill chamber. The bone has scientific use as a means to determine the age of fishes. The lobe-finned fishes share this arrangement. In the labyrinthodontia, earliest amphibians however, the cleithrum/clavicle complex came free of the skull roof, allowing for a movable neck. The cleithrum disappeared early in the evolution of reptiles, and in amniotes is very small or absent. It has been argued based on position, muscle connectivity, and developmental origin that the nuchal element of the turtle Turtle sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsal Fin
A dorsal fin is a fin on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates. Dorsal fins have evolved independently several times through convergent evolution adapting to marine environments, so the fins are not all homologous. They are found in most fish, in mammals such as whales, and in extinct ancient marine reptiles such as ichthyosaurs. Most have only one dorsal fin, but some have two or three. Wildlife biologists often use the distinctive nicks and wear patterns which develop on the dorsal fins of whales to identify individuals in the field. The bones or cartilages that support the dorsal fin in fish are called pterygiophores. Functions The main purpose of the dorsal fin is usually to stabilize the animal against rolling and to assist in sudden turns. Some species have further adapted their dorsal fins to other uses. The sunfish uses the dorsal fin (and the anal fin Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvic Fin
Pelvic fins or ventral fins are paired fins located on the ventral (belly) surface of fish, and are the lower of the only two sets of paired fins (the other being the laterally positioned pectoral fins). The pelvic fins are homologous to the hindlimbs of tetrapods, which evolved from lobe-finned fish during the Middle Devonian. Structure and function Structure In actinopterygians, the pelvic fin consists of two endochondrally-derived bony girdles attached to bony radials. Dermal fin rays ( lepidotrichia) are positioned distally from the radials. There are three pairs of muscles each on the dorsal and ventral side of the pelvic fin girdle that abduct and adduct the fin from the body. Pelvic fin structures can be extremely specialized in actinopterygians. Gobiids and lumpsuckers modify their pelvic fins into a sucker disk that allow them to adhere to the substrate or climb structures, such as waterfalls. In priapiumfish, males have modified their pelvic structures into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pectoral Fin
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish aquatic locomotion, swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the vertebral column, back bone and are supported only by muscles. Fish fins are distinctive anatomical features with varying structures among different clades: in ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii), fins are mainly composed of bone, bony spine (zoology), spines or ray (fish fin anatomy), rays covered by a thin stretch of fish scale, scaleless skin; in lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygii) such as coelacanths and lungfish, fins are short rays based around a muscular central limb bud, bud supported by appendicular skeleton, jointed bones; in cartilaginous fish (Chondrichthyes) and jawless fish (Agnatha), fins are fleshy "flipper (anatomy), flippers" supported by a cartilaginous skeleton. Fins at different locations of the fish body serve different purposes, and are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anal Fin
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the back bone and are supported only by muscles. Fish fins are distinctive anatomical features with varying structures among different clades: in ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii), fins are mainly composed of bony spines or rays covered by a thin stretch of scaleless skin; in lobe-finned fish ( Sarcopterygii) such as coelacanths and lungfish, fins are short rays based around a muscular central bud supported by jointed bones; in cartilaginous fish ( Chondrichthyes) and jawless fish ( Agnatha), fins are fleshy " flippers" supported by a cartilaginous skeleton. Fins at different locations of the fish body serve different purposes, and are divided into two groups: the midsagittal ''unpaired fins'' and the more laterally located ''paired fins''. Unpaired fins are pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |