|
Rolling Resistance
Rolling resistance, sometimes called rolling friction or rolling drag, is the force resisting the Motion (physics), motion when a body (such as a ball, tire, or wheel) Rolling, rolls on a surface. It is mainly caused by Plasticity (physics), non-elastic effects; that is, not all the energy needed for deformation (or movement) of the wheel, roadbed, etc., is recovered when the pressure is removed. Two forms of this are hysteresis losses (see rolling resistance#Primary cause, below), and permanent plastic deformation, (plastic) deformation of the object or the surface (e.g. soil). Note that the frictional contact mechanics, slippage between the wheel and the surface also results in energy dissipation. Although some researchers have included this term in rolling resistance, some suggest that this dissipation term should be treated separately from rolling resistance because it is due to the applied torque to the wheel and the resultant slip between the wheel and ground, which is called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolling Resistance 2
Rolling is a type of motion that combines rotation (commonly, of an axially symmetric object) and translation of that object with respect to a surface (either one or the other moves), such that, if ideal conditions exist, the two are in contact with each other without sliding. Rolling where there is no sliding is referred to as ''pure rolling''. By definition, there is no sliding when there is a frame of reference in which all points of contact on the rolling object have the same velocity as their counterparts on the surface on which the object rolls; in particular, for a frame of reference in which the rolling plane is at rest (see animation), the instantaneous velocity of all the points of contact (for instance, a generating line segment of a cylinder) of the rolling object is zero. In practice, due to small deformations near the contact area, some sliding and energy dissipation occurs. Nevertheless, the resulting rolling resistance is much lower than sliding friction, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dependence On Diameter
Dependency, dependence, dependent or depend may refer to: Computer science * Dependency (computer science) or coupling, a state in which one object uses a function of another object * Data dependency, which describes a dependence relation between statements in a program * Dependence analysis, in compiler theory * Dependency (UML), a relationship between one element in the Unified Modeling Language * Dependency relation, a type of binary relation in mathematics and computer science. * Functional dependency, a relationship between database attributes allowing normalization. * Dependent type, in computer science and logic, a type that depends on a value * Hidden dependency, a relation in which a change in many areas of a program produces unexpected side-effects * Library dependency, a relationship described in and managed by a software dependency manager tool to mitigate dependency hell Economics * Dependant (British English) (Dependent - American English), a person who depend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depends On Applied Torque
Depend is a Kimberly-Clark brand of absorbent, disposable undergarments for people with urinary or fecal incontinence. It positions its products as an alternative to typical adult diapers. Depend is the dominant brand of disposable incontinence garments in the United States with a 49.4 share of the market. History Kimberly-Clark has been making Huggies disposable diapers for infants since 1978. In 1984, the Depend products for adults were introduced. Depend was originally test marketed as the Conform brand in Green Bay, WI. The original products begun being made in 1983 and were liners, available in regular and extra absorbencies. They could be worn inside underwear or alone, and were held on by small elastic belts. In 1984, Depend Shields were added for slight incontinence in regular and extra absorbencies. These were intended for moderate to heavy bladder incontinence. Beginning in 1985, fitted briefs for heavy to complete bladder incontinence as well as bowel incontinence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Rolling Resistance Tires
Low rolling resistance tires are designed to reduce the energy loss as a tire rolls, decreasing the required rolling effort — and in the case of automotive applications, improving vehicle fuel efficiency as approximately 5–15% of the fuel consumed by a typical gas car may be used to overcome rolling resistance. Such tires are now commonly installed as standard, either mandated by law or to meet eco labelling standards. Measuring rolling resistance in tires Rolling resistance can be expressed by the rolling resistance coefficient (RRC or Crr), which is the value of the rolling resistance force divided by the wheel load. A lower coefficient means the tires will use less energy to travel a certain distance. The coefficient is mostly considered as independent of speed, but for precise calculations it is tabled at several speeds or an additional speed-dependent part is used. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) has developed test practices to measure the RRC of tires. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundant families of materials, existing as a compound of several minerals and as a synthetic product. Examples include fused quartz, fumed silica, opal, and aerogels. It is used in structural materials, microelectronics, and as components in the food and pharmaceutical industries. All forms are white or colorless, although impure samples can be colored. Silicon dioxide is a common fundamental constituent of glass. Structure In the majority of silicon dioxides, the silicon atom shows Tetrahedral molecular geometry, tetrahedral coordination, with four oxygen atoms surrounding a central Si atomsee 3-D Unit Cell. Thus, SiO2 forms 3-dimensional network solids in which each silicon atom is covalently bonded in a tetrahedral manner to 4 oxygen atoms. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
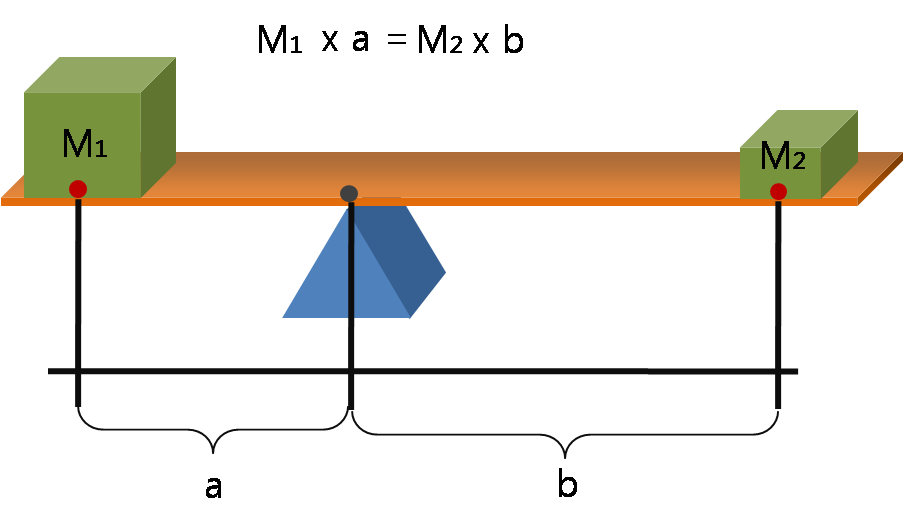
Moment (physics)
A moment is a mathematical expression involving the product of a distance and a physical quantity such as a force or electric charge. Moments are usually defined with respect to a fixed reference point and refer to physical quantities located some distance from the reference point. For example, the moment of force, often called torque, is the product of a force on an object and the distance from the reference point to the object. In principle, any physical quantity can be multiplied by a distance to produce a moment. Commonly used quantities include forces, masses, and electric charge distributions; a list of examples is provided later. Elaboration In its most basic form, a moment is the product of the distance to a point, raised to a power, and a physical quantity (such as force or electrical charge) at that point: : \mu_n = r^n\,Q, where Q is the physical quantity such as a force applied at a point, or a point charge, or a point mass, etc. If the quantity is not concen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Force
In physics, a force is an influence that can cause an Physical object, object to change its velocity unless counterbalanced by other forces. In mechanics, force makes ideas like 'pushing' or 'pulling' mathematically precise. Because the Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude and Direction (geometry, geography), direction of a force are both important, force is a Euclidean vector, vector quantity. The SI unit of force is the newton (unit), newton (N), and force is often represented by the symbol . Force plays an important role in classical mechanics. The concept of force is central to all three of Newton's laws of motion. Types of forces often encountered in classical mechanics include Elasticity (physics), elastic, frictional, Normal force, contact or "normal" forces, and gravity, gravitational. The rotational version of force is torque, which produces angular acceleration, changes in the rotational speed of an object. In an extended body, each part applies forces on the adjacent pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Of Action
In physics, the line of action (also called line of application) of a force () is a geometric representation of how the force is applied. It is the straight line through the point at which the force is applied, and is in the same direction as the vector . The lever arm is the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation to the line of action. The concept is essential, for instance, for understanding the net effect of multiple forces applied to a body. For example, if two forces of equal magnitude act upon a rigid body along the same line of action but in opposite directions, they cancel and have no net effect. But if, instead, their lines of action are not identical, but merely parallel, then their effect is to create a moment on the body, which tends to rotate it. Calculation of torque For the simple geometry associated with the figure, there are three equivalent equations for the magnitude of the torque associated with a force \vec F directed at displacement \v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscoelasticity
In materials science and continuum mechanics, viscoelasticity is the property of materials that exhibit both viscous and elastic characteristics when undergoing deformation. Viscous materials, like water, resist both shear flow and strain linearly with time when a stress is applied. Elastic materials strain when stretched and immediately return to their original state once the stress is removed. Viscoelastic materials have elements of both of these properties and, as such, exhibit time-dependent strain. Whereas elasticity is usually the result of bond stretching along crystallographic planes in an ordered solid, viscosity is the result of the diffusion of atoms or molecules inside an amorphous material.Meyers and Chawla (1999): "Mechanical Behavior of Materials", 98-103. Background In the nineteenth century, physicists such as James Clerk Maxwell, Ludwig Boltzmann, and Lord Kelvin researched and experimented with creep and recovery of glasses, metals, and rubbers. Viscoel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure Distribution For Viscoelastic Rolling Cylinders
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and even by industry. Further, both spellings are often used ''within'' a particular industry or country. Industries in British English-speaking countries typically use the "gauge" spelling. is the pressure relative to the ambient pressure. Various units are used to express pressure. Some of these derive from a unit of force divided by a unit of area; the SI unit of pressure, the pascal (Pa), for example, is one newton per square metre (N/m2); similarly, the pound-force per square inch (psi, symbol lbf/in2) is the traditional unit of pressure in the imperial and US customary systems. Pressure may also be expressed in terms of standard atmospheric pressure; the unit atmosphere (atm) is equal to this pressure, and the torr is defined as of thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of aggregate bound together with a fluid cement that cures to a solid over time. It is the second-most-used substance (after water), the most–widely used building material, and the most-manufactured material in the world. When aggregate is mixed with dry Portland cement and water, the mixture forms a fluid slurry that can be poured and molded into shape. The cement reacts with the water through a process called hydration, which hardens it after several hours to form a solid matrix that binds the materials together into a durable stone-like material with various uses. This time allows concrete to not only be cast in forms, but also to have a variety of tooled processes performed. The hydration process is exothermic, which means that ambient temperature plays a significant role in how long it takes concrete to set. Often, additives (such as pozzolans or superplasticizers) are included in the mixture to improve the physical prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |