|
Rolling Code
A rolling code (or sometimes called a hopping code) is used in keyless entry systems to prevent a simple form of replay attack, where an eavesdropper records the transmission and replays it at a later time to cause the receiver to 'unlock'. Such systems are typical in garage door openers and keyless car entry systems. Techniques * Common PRNG (pseudorandom number generator) — preferably cryptographically secure — in both transmitter and receiver * Transmitter sends 'next' code in sequence * Receiver compares 'next' to its calculated 'next' code. * A typical implementation compares within the next 256 codes in case receiver missed some transmitted keypresses. HMAC-based one-time password employed widely in multi-factor authentication uses similar approach, but with pre-shared secret key and HMAC instead of PRNG and pre-shared random seed. Application in RF remote control A rolling code transmitter is useful in a security system for improving the security of r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keyless Entry
A remote keyless system (RKS), also known as remote keyless entry (RKE) or remote central locking, is an electronic lock that controls access to a building or vehicle by using an electronic remote control (activated by a handheld device or automatically by proximity). RKS largely and quickly superseded ''keyless entry'', a budding technology that restrictively bound locking and unlocking functions to vehicle-mounted keypads. Widely used in automobiles, an RKS performs the functions of a standard car key without physical contact. When within a few yards of the car, pressing a button on the remote can lock or unlock the doors, and may perform other functions. A remote keyless system can include both ''remote keyless entry'' (RKE), which unlocks the doors, and '' remote keyless ignition'' (RKI), which starts the engine. Numerous manufacturers have offered entry systems that use door- or pillar-mounted keypad entry systems; touchless passive entry / smart key systems that al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the upper limit of audio frequencies that humans can hear (though these are not electromagnetic) and the lower limit of infrared frequencies, and also encompasses the microwave range. These are the frequencies at which energy from an oscillating current can radiate off a conductor into space as radio waves, so they are used in radio technology, among other uses. Different sources specify different upper and lower bounds for the frequency range. Electric current Electric currents that oscillate at radio frequencies (RF currents) have special properties not shared by direct current or lower audio frequency alternating current, such as the 50 or 60 Hz current used in electrical power distribution. * Energy from RF currents in conduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DEF CON
DEF CON (also written as DEFCON, Defcon, or DC) is a Computer security conference, hacker convention held annually in Las Vegas Valley, Las Vegas, Nevada. The first DEF CON took place in June 1993 and today many attendees at DEF CON include computer security professionals, journalists, lawyers, federal government employees, security researchers, students, and Hacker (computer security), hackers with a general interest in source code, software, computer architecture, hardware modification, conference badges, and anything else that can be "hacked". The event consists of several tracks of speakers about computer and hacking-related subjects, as well as cyber-security challenges and competitions (known as hacking Wargame (hacking), wargames). Contests held during the event are extremely varied and can range from creating the longest Wi-Fi connection to finding the most effective way to cool a beer in the Nevada heat. Other contests, past and present, include lockpicking, Defcon Robot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tech Insider
''Business Insider'' (stylized in all caps: BUSINESS INSIDER; known from 2021 to 2023 as INSIDER) is a New York City–based multinational financial and business news website founded in 2007. Since 2015, a majority stake in ''Business Insider''s parent company Insider Inc. has been owned by the international publishing house Axel Springer. It operates several international editions, including one in the United Kingdom. ''Insider'' publishes original reporting and aggregates material from other outlets. it maintained a liberal policy on the use of anonymous sources. It has also published native advertising and granted sponsors editorial control of its content. The outlet has been nominated for several awards, but has also been criticized for using factually incorrect clickbait headlines to attract viewership. In 2015, Axel Springer SE acquired 88 percent of the stake in Insider Inc. for $343 million (€306 million), implying a total valuation of $442 million. From Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samy Kamkar
Samy Kamkar (born December 10, 1985) is an American privacy and security researcher, computer hacker and entrepreneur. At the age of 16, he dropped out of high school. One year later, he co-founded Fonality, a unified communications company based on open-source software, which raised over $46 million in private funding. In 2005, he created and released the fastest spreading Computer virus#Cross-site scripting virus, virus of all time, the MySpace worm Samy (XSS), Samy, and was subsequently raided by the United States Secret Service under the Patriot Act. He also created SkyJack, a custom drone which hacks into any nearby Parrot AR.Drone, Parrot drones allowing them to be controlled by its operator and created the Evercookie, which appeared in a top-secret National Security Agency, NSA document revealed by Edward Snowden and on the front page of ''The New York Times''. He has also worked with ''The Wall Street Journal'', and discovered the illicit mobile phone tracking where the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broken (cryptography)
In cryptography, security level is a measure of the strength that a cryptographic primitive — such as a cipher or hash function — achieves. Security level is usually expressed as a number of "bits of security" (also security strength), where ''n''-bit security means that the attacker would have to perform 2''n'' operations to break it, but other methods have been proposed that more closely model the costs for an attacker. This allows for convenient comparison between algorithms and is useful when combining multiple primitives in a hybrid cryptosystem, so there is no clear weakest link. For example, AES-128 (key size 128 bits) is designed to offer a 128-bit security level, which is considered roughly equivalent to a RSA using 3072-bit key. In this context, security claim or target security level is the security level that a primitive was initially designed to achieve, although "security level" is also sometimes used in those contexts. When attacks are found that have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
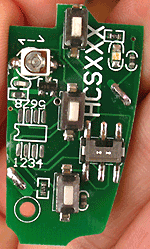
KeeLoq
KeeLoq is a proprietary hardware-dedicated block cipher that uses a non-linear feedback shift register (NLFSR). The uni-directional command transfer protocol was designed by Frederick Bruwer of Nanoteq (Pty) Ltd., the cryptographic algorithm was created by Gideon Kuhn at the University of Pretoria, and the silicon implementation was by Willem Smit at Nanoteq (Pty) Ltd (South Africa) in the mid-1980s. KeeLoq was sold to Microchip Technology Inc in 1995 for $10 million. It is used in ' hopping code' encoders and decoders such as NTQ105/106/115/125D/129D, HCS101/2XX/3XX/4XX/5XX and MCS31X2. KeeLoq has been used in many remote keyless entry systems by such companies like Chrysler, Daewoo, Fiat, Ford,Researchers Crack KeeLoq Code for Car Keys |
Random Seed
A random seed (or seed state, or just seed) is a number (or vector) used to initialize a pseudorandom number generator. A pseudorandom number generator's number sequence is completely determined by the seed: thus, if a pseudorandom number generator is later reinitialized with the same seed, it will produce the same sequence of numbers. For a seed to be used in a pseudorandom number generator, it does not need to be random. Because of the nature of number generating algorithms, so long as the original seed is ignored, the rest of the values that the algorithm generates will follow probability distribution in a pseudorandom manner. However, a non-random seed will be cryptographically insecure, as it can allow an adversary to predict the pseudorandom numbers generated. The choice of a good random seed is crucial in the field of computer security. When a secret encryption key is pseudorandomly generated, having the seed will allow one to obtain the key. High entropy is importan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Replay Attack
A replay attack (also known as a repeat attack or playback attack) is a form of network attack in which valid data transmission is maliciously or fraudulently repeated or delayed. This is carried out either by the originator or by an adversary who intercepts the data and re-transmits it, possibly as part of a spoofing attack by IP packet substitution. This is one of the lower-tier versions of a man-in-the-middle attack. Replay attacks are usually passive in nature. Another way of describing such an attack is: "an attack on a security protocol using a replay of messages from a different context into the intended (or original and expected) context, thereby fooling the honest participant(s) into thinking they have successfully completed the protocol run." Example Suppose Alice wants to prove her identity to Bob. Bob requests her password as proof of identity, which Alice dutifully provides (possibly after some transformation like hashing, or even salting, the password); meanwh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMAC
In cryptography, an HMAC (sometimes expanded as either keyed-hash message authentication code or hash-based message authentication code) is a specific type of message authentication code (MAC) involving a cryptographic hash function and a secret cryptographic key. As with any MAC, it may be used to simultaneously verify both the data integrity and authenticity of a message. An HMAC is a type of keyed hash function that can also be used in a key derivation scheme or a key stretching scheme. HMAC can provide authentication using a shared secret instead of using digital signatures with asymmetric cryptography. It trades off the need for a complex public key infrastructure by delegating the key exchange to the communicating parties, who are responsible for establishing and using a trusted channel to agree on the key prior to communication. Details Any cryptographic hash function, such as SHA-2 or SHA-3, may be used in the calculation of an HMAC; the resulting MAC algori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA; two-factor authentication, or 2FA) is an electronic authentication method in which a user is granted access to a website or application only after successfully presenting two or more distinct types of evidence (or factors) to an authentication mechanism. MFA protects personal data—which may include personal identification or financial assets—from being accessed by an unauthorized third party that may have been able to discover, for example, a single password. Usage of MFA has increased in recent years. Security issues which can cause the bypass of MFA are fatigue attacks, phishing and SIM swapping. Accounts with MFA enabled are significantly less likely to be compromised. Authentication factors Authentication takes place when someone tries to log into a computer resource (such as a computer network, device, or application). The resource requires the user to supply the identity by which the user is known to the resource, along wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |