|
Rigid Belt Actuator
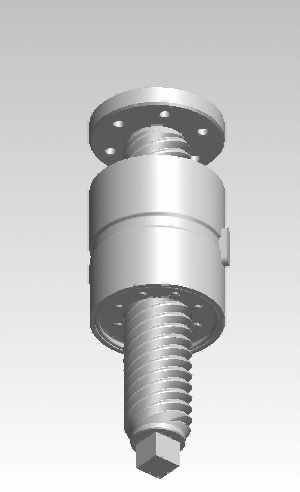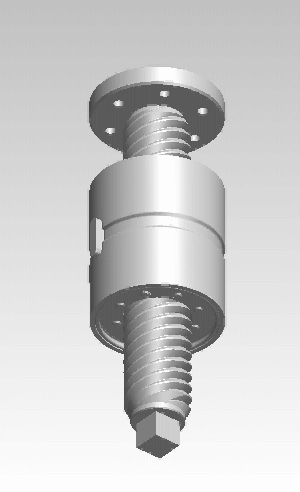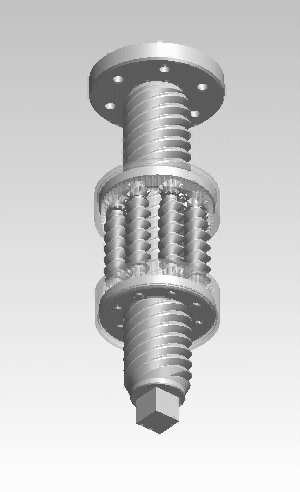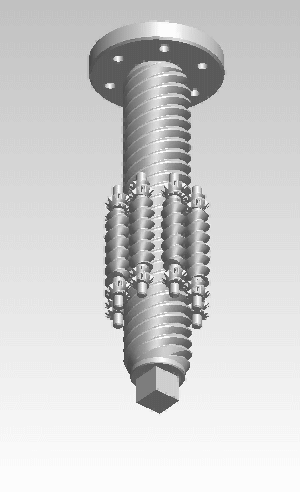
A rigid belt actuator, also known as a push-pull belt actuator or zipper belt actuator, is a specialized mechanical linear actuator used in push-pull and lift applications. The actuator is a Belt (mechanical), belt and pinion device that forms a telescoping beam or column member to transmit traction and thrust. Rigid belt actuators can move dynamic loads up to approximately 230 pounds over about 3 feet of travel. Principle of operation Rigid belt actuators can be thought of as rack and pinion devices that use a flexible rack. Rigid belt actuators use two reinforced plastic Belt (mechanical)#Ribbed belt, ribbed belts, that engage with pinions mounted on drive shafts within a housing. The belts have evenly spaced load bearing blocks on the non-ribbed face. As the pinions spin, the belts are rotated 90 degrees through the housing, which interlocks the blocks like a zipper into a rigid linear form. The resulting beam or column is effective at resisting tension and compression (buckli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Actuator
A linear actuator is an actuator that creates linear motion (i.e., in a straight line), in contrast to the circular motion of a conventional electric motor. Linear actuators are used in machine tools and industrial machinery, in computer peripherals such as disk drives and printers, in valves and Damper (flow), dampers, and in many other places where linear motion is required. Hydraulics, Hydraulic or Pneumatics, pneumatic cylinders inherently produce linear motion. Many other mechanisms are used to generate linear motion from a rotating motor. Types Mechanical actuators Machine, Mechanical linear actuators typically operate by conversion of rotary motion into linear motion. Conversion is commonly made via a few simple types of mechanism: * Screw (simple machine), Screw: leadscrew, screw jack, ball screw and roller screw actuators all operate on the principle of the simple machine known as the screw. By rotating the actuator's nut, the screw shaft moves in a line. * Whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belt (mechanical)
A belt is a loop of flexible material used to link two or more rotating shafts mechanically, most often parallel. Belts may be used as a source of motion, to transmit power efficiently or to track relative movement. Belts are looped over pulleys and may have a twist between the pulleys, and the shafts need not be parallel. In a two pulley system, the belt can either drive the pulleys normally in one direction (the same if on parallel shafts), or the belt may be crossed, so that the direction of the driven shaft is reversed (the opposite direction to the driver if on parallel shafts). The belt drive can also be used to change the speed of rotation, either up or down, by using different sized pulleys. As a source of motion, a conveyor belt is one application where the belt is adapted to carry a load continuously between two points. History The mechanical belt drive, using a pulley machine, was first mentioned in the text of the ''Dictionary of Local Expressions'' by the Han ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinion
A pinion is a round gear—usually the smaller of two meshed gears—used in several applications, including drivetrain and rack and pinion systems. Applications Drivetrain Drivetrains usually feature a gear known as the pinion, which may vary in different systems, including * the typically smaller gear in a gear drive train (although in the first commercially successful steam locomotive—the ''Salamanca''—the ''pinion'' was rather large). In many cases, such as remote controlled toys, the pinion is also the drive gear for a reduction in speed, since electric motors operate at higher speed and lower torque than desirable at the wheels. However the reverse is true in watches, where gear trains commence with a high-torque, low-speed spring and terminate in the fast-and-weak escapement. * the smaller gear that drives in a 90-degree angle towards a crown gear in a differential drive. * the small front sprocket on a chain driven motorcycle. *the clutch bell gear when pai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rack And Pinion
rack and pinion is a type of linear actuator that comprises a circular gear (the '' pinion'') engaging a linear gear (the ''rack''). Together, they convert between rotational motion and linear motion: rotating the pinion causes the rack to be driven in a line. Conversely, moving the rack linearly will cause the pinion to rotate. The rack and pinion mechanism is used in rack railways, where the pinion mounted on a locomotive or a railroad car engages a rack usually placed between the rails, and helps to move the train up a steep gradient. It is also used in arbor presses and drill presses, where the pinion is connected to a lever and displaces a vertical rack (the ram). In pipelines and other industrial piping systems, a rack displaced by a linear actuator turns a pinion to open or close a valve. Stairlifts, lock gates, electric gates, and the mechanical steering mechanism of cars are other notable applications. The term "rack and pinion" may be used also when the rac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zipper
A zipper (N. America), zip, zip fastener (UK), formerly known as a clasp locker, is a commonly used device for binding together two edges of textile, fabric or other flexible material. Used in clothing (e.g. jackets and jeans), luggage and other bags, camping gear (e.g. tents and sleeping bags), and many other items, zippers come in a wide range of sizes, shapes, and colors. In 1892, Whitcomb L. Judson, an American inventor from Chicago, patented the original design from which the modern device evolved. The zipper gets its name from a brand of rubber boots (or galoshes) it was used on in 1923. The galoshes could be fastened with a single zip of the hand, and soon the hookless fasteners came to be called "Zippers". Description A zipper consists of a slider mounted on two rows of metal or plastic teeth that are designed to interlock and thereby join the material to which the rows are attached. The slider, usually operated by hand, contains a Y-shaped channel that, by moving alon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Actuator
A linear actuator is an actuator that creates linear motion (i.e., in a straight line), in contrast to the circular motion of a conventional electric motor. Linear actuators are used in machine tools and industrial machinery, in computer peripherals such as disk drives and printers, in valves and Damper (flow), dampers, and in many other places where linear motion is required. Hydraulics, Hydraulic or Pneumatics, pneumatic cylinders inherently produce linear motion. Many other mechanisms are used to generate linear motion from a rotating motor. Types Mechanical actuators Machine, Mechanical linear actuators typically operate by conversion of rotary motion into linear motion. Conversion is commonly made via a few simple types of mechanism: * Screw (simple machine), Screw: leadscrew, screw jack, ball screw and roller screw actuators all operate on the principle of the simple machine known as the screw. By rotating the actuator's nut, the screw shaft moves in a line. * Whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
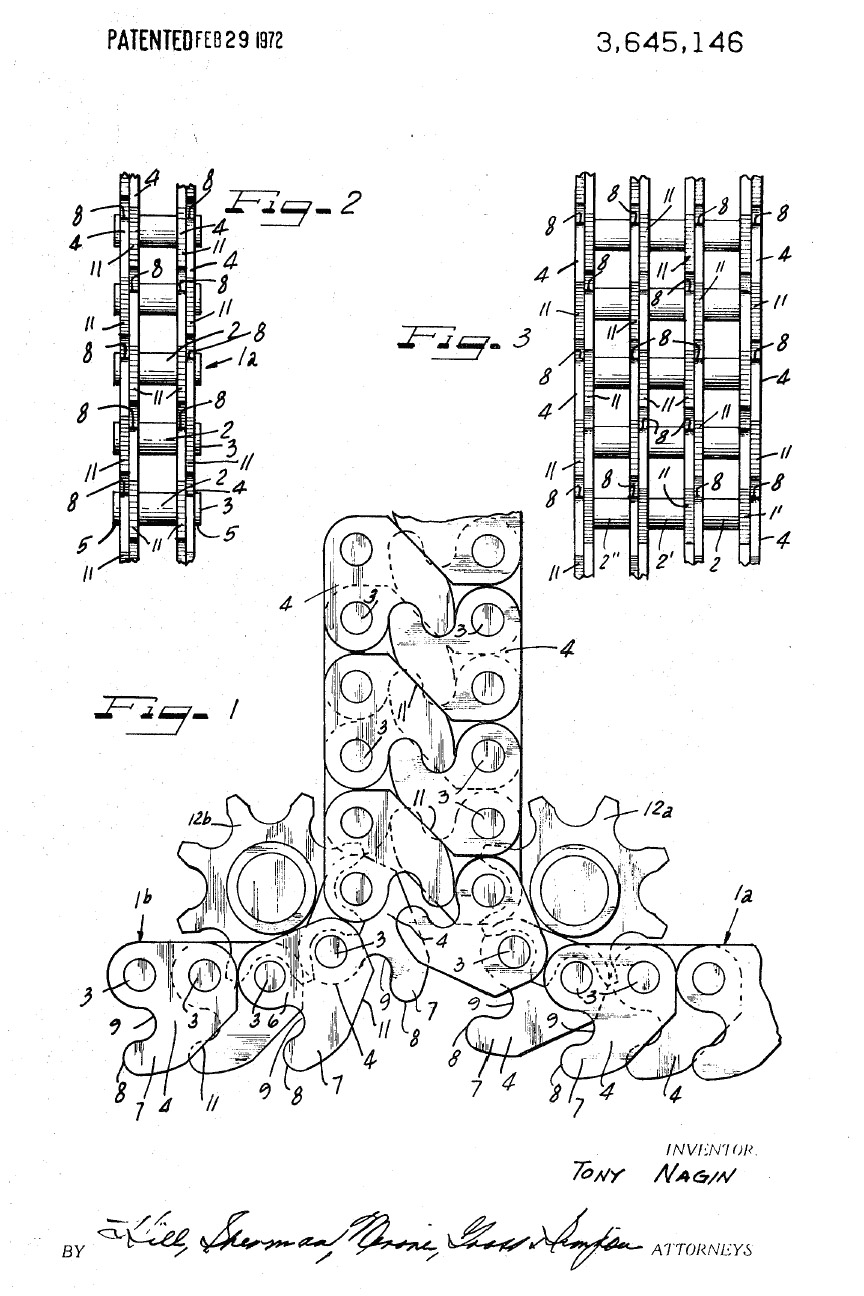
Rigid Chain Actuator
A rigid chain actuator, known variously as a linear chain actuator, push-pull chain actuator, electric chain actuator or column-forming chain actuator, is a specialized mechanical linear actuator used in window operating, push-pull material handling and lift applications. The actuator is a chain and pinion device that forms an articulated telescoping member to transmit traction and thrust. High-capacity rigid chain lifting columns ( jacks) can move dynamic loads exceeding over more than of travel. Principle of operation Rigid chain actuators function as rack and pinion linear actuators that use articulated racks. Rigid chain actuators use limited-articulation chains, usually resembling a roller chain, that engage with pinions mounted on a drive shaft within a housing. The links of the actuating member, the “rigid chain”, are articulated in a manner that they deflect from a straight line to one side only. As the pinions spin, the links of the chain are rotated 90 degree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |