|
Ribavirin
Ribavirin, also known as tribavirin, is an antiviral medication used to treat illness caused by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections, as well as some viral hemorrhagic fevers. For HCV, it is used in combination with other medications, such as simeprevir, sofosbuvir, peginterferon alfa-2b or peginterferon alfa-2a. It can also be used for viral hemorrhagic fevers—specifically, for Lassa fever, Crimean–Congo hemorrhagic fever, and Hantavirus infections (with exceptions for Ebola or Marburg virus diseases). Ribavirin is usually taken orally (by mouth) or inhaled. Despite widespread usage, it has faced scrutiny in the 21st century because of lack of proven efficacy in treating viral infections for which it has been prescribed in the past. Its common side effects include fatigue, headache, nausea, fever, muscle pains, and an irritable mood. Serious side effects include red blood cell breakdown, liver problems, and allergic reacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sofosbuvir
Sofosbuvir, sold under the brand name Sovaldi among others, is a medication used to treat hepatitis C. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include fatigue, headache, nausea, and trouble sleeping. Side effects are generally more common in interferon-containing regimens. Sofosbuvir may reactivate hepatitis B in those who have been previously infected. In combination with ledipasvir, daclatasvir or simeprevir, it is not recommended with amiodarone due to the risk of an abnormally slow heartbeat. Sofosbuvir is in the nucleotide analog family of medications and works by blocking the hepatitis C NS5B protein. Sofosbuvir was discovered in 2007 and approved for medical use in the United States in 2013. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses Initial HCV treatment In 2016, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the Infectious Diseases Society of America jointly published a recommendation for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simeprevir
Simeprevir, sold under the brand name Olysio among others, is a medication used in combination with other medications for the treatment of hepatitis C. It is specifically used for hepatitis C genotype 1 and 4. Medications it is used with include sofosbuvir or ribavirin and peginterferon-alfa. Cure rates are in 80s to 90s percent. It may be used in those who also have HIV/AIDS. It is taken by mouth once daily for typically 12 weeks. Common side effects include feeling tired, headache, rash, itchiness, and sensitivity to sunlight. In those with previous hepatitis B infection, active disease may recur. It is not recommended in those with significant liver problems. During pregnancy when used with ribavirin it may cause harm to the baby while when used with sofosbuvir its safety is unclear. Simeprevir is a HCV protease inhibitor. Simeprevir was developed by Medivir AB and Janssen Pharmaceutica. It was approved for medical use in the United States in 2013. It was removed from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lassa Fever
Lassa fever, also known as Lassa hemorrhagic fever, is a type of viral hemorrhagic fever caused by the Lassa virus. Many of those infected by the virus asymptomatic, do not develop symptoms. When symptoms occur they typically include fever, weakness, headaches, vomiting, and myalgia, muscle pains. Less commonly there may be bleeding from the mouth or gastrointestinal tract. The risk of death once infected is about one percent and frequently occurs within two weeks of the onset of symptoms. Of those who survive, about a quarter have hearing loss, which improves within three months in about half of these cases. The disease is usually initially spread to people via contact with the urine or feces of an infected multimammate mouse. Spread can then occur via direct contact between people. Diagnosis based on symptoms is difficult. Confirmation is by laboratory testing to detect the Virus classification#RNA viruses, virus's RNA, antibodies for the virus, or the virus itself in cell cul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection period, people often have mild or no symptoms. Early symptoms can include fever, dark urine, abdominal pain, and jaundice, yellow tinged skin. The virus persists in the liver, becoming Chronic condition, chronic, in about 70% of those initially infected. Early on, chronic infection typically has no symptoms. Over many years however, it often leads to liver disease and occasionally cirrhosis. In some cases, those with cirrhosis will develop serious complications such as liver failure, hepatocellular carcinoma, liver cancer, or esophageal varices, dilated blood vessels in the esophagus and gastric varices, stomach. HCV is spread primarily by blood-to-blood contact associated with injection drug use, poorly sterilized medical equipment, needlestick injuries in healthcare, and blood transfusions, transfusions. In r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peginterferon Alfa-2b
Pegylated interferon alfa-2b is a drug used to treat melanoma, as an adjuvant therapy to surgery. Also used to treat hepatitis C (typically, in combination with ribavirin), it is no longer recommended due to poor efficacy and adverse side-effects. Subcutaneous injection is the preferred delivery method. Belonging to the alpha interferon family of medications, the molecule is PEGylated to prevent breakdown. Approval for medical use in the United States was granted in 2001. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines as a therapy for chronic hepatitis C. Medical uses Hepatitis Till around 2010, PEGylated interferon alfa-2b in combination with ribavirin, was part of the standard regimen used in management of hepatitis C. Ribivarin helped in increasing the Sustained Virologic Response (SVR) even more. Developed by Schering-Plough, the drug was approved by Food and Drug Administration (FDA) of the United States in 2001, and has been on the World Health ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peginterferon Alfa-2a
Pegylated interferon alfa-2a, sold under the brand name Pegasys among others, is medication used to treat hepatitis C and hepatitis B. For hepatitis C it is typically used together with ribavirin and cure rates are between 24 and 92%. For hepatitis B it may be used alone. It is given by injection under the skin. Side effects are common. They may include headache, feeling tired, depression, trouble sleeping, hair loss, nausea, pain at the site of injection, and fever. Severe side effects may include psychosis, autoimmune disorders, blood clots, or infections. Use with ribavirin is not recommended during pregnancy. Pegylated interferon alfa-2a is in the alpha interferon family of medications. It is pegylated to protect the molecule from breakdown. Pegylated interferon alfa-2a was approved for medical use in the United States in 2002. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses This drug is approved around the world for the treatment of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
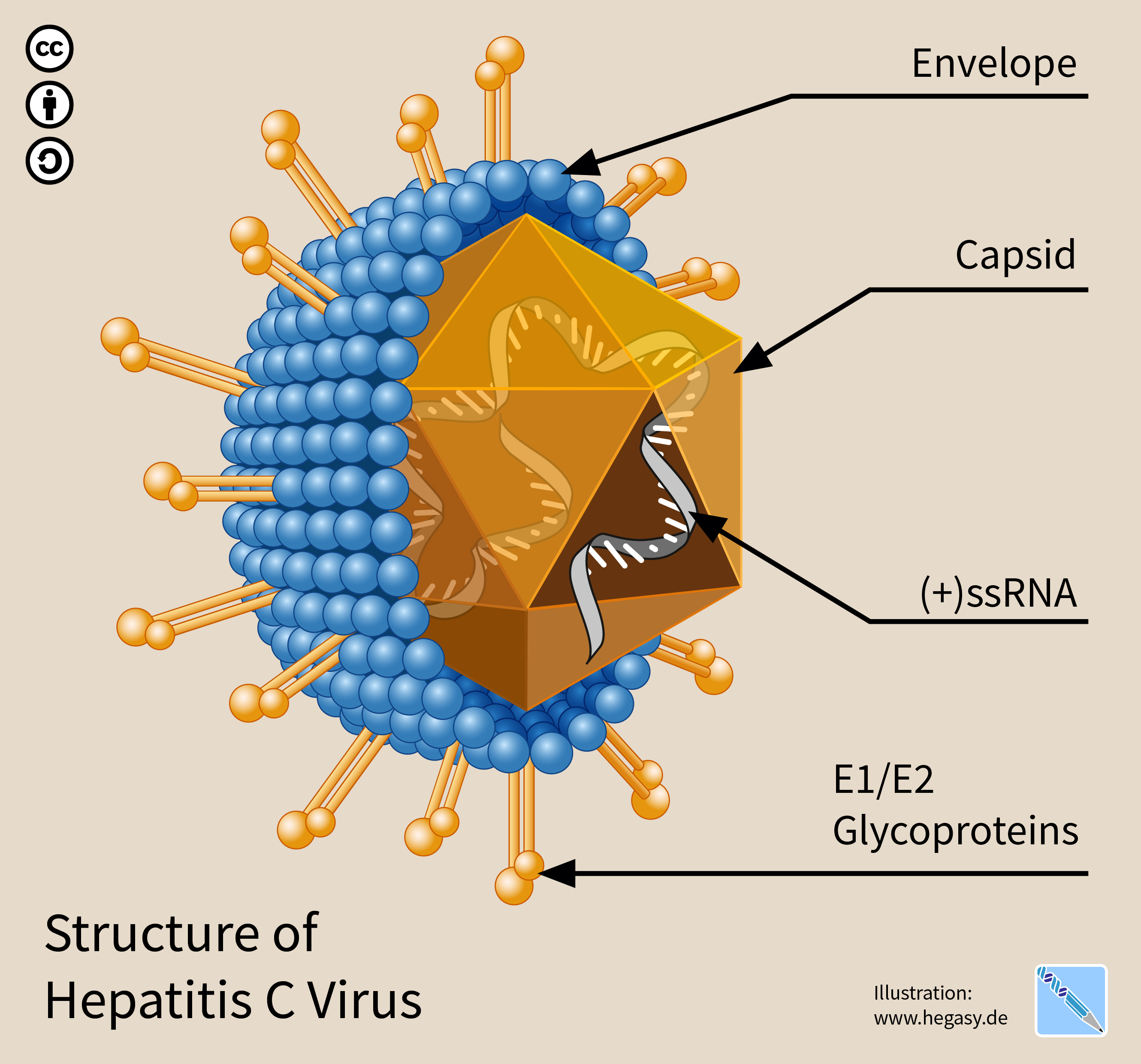
Hepatitis C Virus
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a small (55–65 nm in size), enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus of the family ''Flaviviridae''. The hepatitis C virus is the cause of hepatitis C and some cancers such as liver cancer ( hepatocellular carcinoma, abbreviated HCC) and lymphomas in humans. Taxonomy The hepatitis C virus belongs to the genus '' Hepacivirus'', a member of the family ''Flaviviridae''. Before 2011, it was considered to be the only member of this genus. However a member of this genus has been discovered in dogs: canine hepacivirus. There is also at least one virus in this genus that infects horses. Several additional viruses in the genus have been described in bats and rodents. Structure The hepatitis C virus particle consists of a lipid membrane envelope that is 55 to 65 nm in diameter. Two viral envelope glycoproteins, E1 and E2, are embedded in the lipid envelope. They take part in viral attachment and entry into the cell. Within the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiratory Syncytial Virus
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), also called human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) and human orthopneumovirus, is a virus that causes infections of the respiratory tract. It is a negative-sense, single-stranded RNA virus. Its name is derived from the large cells known as ''syncytia'' that form when infected cells fuse. RSV is a common cause of respiratory hospitalization in infants, and reinfection remains common in later life, though often with less severity. It is a notable pathogen in all age groups. Infection rates are typically higher during the cold winter months, causing bronchiolitis in infants, common colds in adults, and more serious respiratory illnesses, such as pneumonia, in the elderly and Immunodeficiency, immunocompromised. RSV can cause outbreaks both in the community and in hospital settings. Following initial infection via the eyes or nose, the virus infects the Epithelium, epithelial cells of the upper and lower airway, causing inflammation, cell damage, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Hemorrhagic Fever
Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) are a diverse group of diseases. "Viral" means a health problem caused by infection from a virus, " hemorrhagic" means to bleed, and "fever" means an unusually high body temperature. Bleeding and fever are common signs of VHFs, which is how the group of infections got its common name. There are five known families of RNA viruses which cause VHFs: '' Arenaviridae'', '' Filoviridae'', '' Flaviviridae'', '' Hantaviridae'', and ''Rhabdoviridae''. Some VHFs are usually mild, such as nephropathia epidemica (within the family ''Hantaviridae''). But some are usually severe and have a high death rate, such as Ebola virus (within the family ''Filoviridae''). All VHFs can potentially cause severe blood loss, high fever, and death. Both humans and non human animals can be infected. Signs and symptoms The following are signs and symptoms of most or all VHFs. * Circulatory shock *Diarrhea (feces which resemble more liquid than solid) *Headache *Hypotens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiviral Medication
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials, a larger group which also includes antibiotic (also termed antibacterial), antifungal and antiparasitic drugs, or antiviral drugs based on monoclonal antibodies. Most antivirals are considered relatively harmless to the host, and therefore can be used to treat infections. They should be distinguished from virucides, which are not medication but deactivate or destroy virus particles, either inside or outside the body. Natural virucides are produced by some plants such as eucalyptus and Australian tea trees. Medical uses Most of the antiviral drugs now available are designed to help deal with HIV, herpes viruses, the hepatitis B and C viruses, and influenza A and B viruses. Viruses use the host's cells to replicate and this make ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, Prescription drug, prescription and Over-the-counter drug, over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, Animal feed, animal foods & feed and Veterinary medicine, veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C). However, the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WHO Model List Of Essential Medicines
The WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (aka Essential Medicines List or EML), published by the World Health Organization (WHO), contains the medications considered to be most effective and safe to meet the most important needs in a health system. The list is frequently used by countries to help develop their own local lists of essential medicines. , more than 155 countries have created national lists of essential medicines based on the World Health Organization's model list. This includes both Developed country, developed and Developing country, developing countries. The list is divided into core items and complementary items. The core items are deemed to be the most cost-effective options for key health problems and are usable with little additional health care resources. The complementary items either require additional infrastructure such as specially trained health care providers or diagnostic equipment or have a lower cost–benefit ratio. About 25% of items are in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |