|
Retinol Isomerase
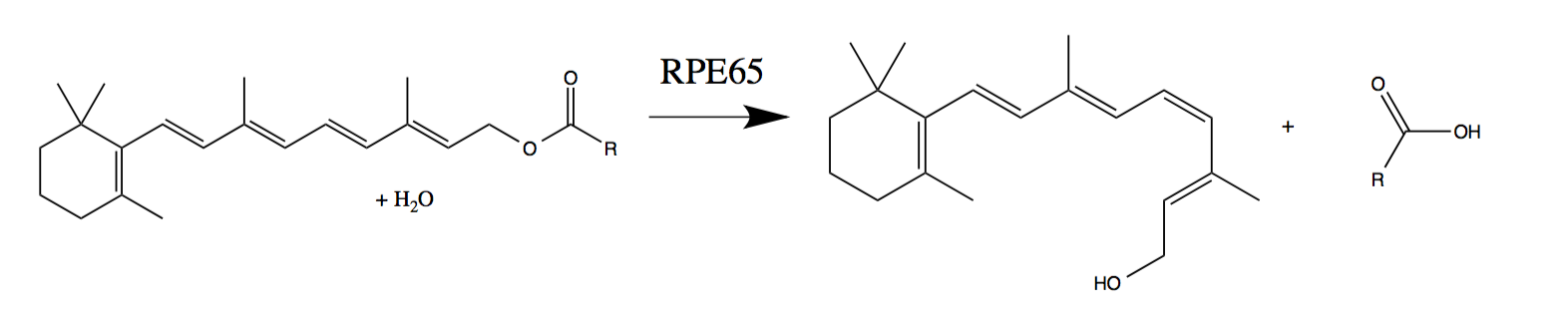
In enzymology, a retinol isomerase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :all-trans-retinol \rightleftharpoons 11-cis-retinol Hence, this enzyme has one substrate, all-trans-retinol, and one product, 11-cis-retinol. These enzymes are alternatively referred to as retinoid isomerases. This enzyme belongs to the family of isomerases, specifically cis-trans isomerases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is all-trans-retinol 11-cis-trans-isomerase. This enzyme is also called all-trans-retinol isomerase. This enzyme participates in retinol metabolism. In vertebrates, RPE65 is the active retinol isomerase in the visual cycle. A lack of RPE65 function results in congenital blindness in children (specifically Leber congenital amaurosis). Emixustat, a partial inhibitor of RPE65, is currently in FDA clinical trials for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD), is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzymology
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinol Metabolism
Retinol, also called vitamin A1, is a fat-soluble vitamin in the vitamin A family that is found in food and used as a dietary supplement. Retinol or other forms of vitamin A are needed for vision, cellular development, maintenance of skin and mucous membranes, immune function and reproductive development. Dietary sources include fish, dairy products, and meat. As a supplement it is used to treat and prevent vitamin A deficiency, especially that which results in xerophthalmia. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a muscle. As an ingredient in skin-care products, it is used to reduce wrinkles and other effects of skin aging. Retinol at normal doses is well tolerated. High doses may cause enlargement of the liver, dry skin, and hypervitaminosis A. High doses during pregnancy may harm the fetus. The body converts retinol to retinal and retinoic acid, through which it acts. Retinol was discovered in 1909, isolated in 1931, and first made in 1947. It is on the World Health ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macular Degeneration
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD), is a medical condition which may result in blurred vision, blurred or vision loss, no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no symptoms. Some people experience a gradual worsening of vision that may affect one or both eyes. While it does not result in complete blindness, loss of central vision can make it hard to recognize faces, drive, read, or perform other activities of daily life. Visual release hallucinations, Visual hallucinations may also occur. Macular degeneration typically occurs in older people, and is caused by damage to the macula of retina, macula of the retina. Genetic factors and smoking may play a role. The condition is diagnosed through a complete eye exam. Severity is divided into early, intermediate, and late types. The late type is additionally divided into "dry" and "wet" forms, with the dry form making up 90% of cases. The difference between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, Prescription drug, prescription and Over-the-counter drug, over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, Animal feed, animal foods & feed and Veterinary medicine, veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C). However, the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emixustat Hydrochloride
Emixustat is a small molecule notable for its establishment of a new class of compounds known as visual cycle modulators (VCMs). Formulated as the hydrochloride salt, emixustat hydrochloride, it is the first synthetic medicinal compound shown to affect retinal disease processes when taken by mouth. Emixustat was invented by the British-American chemist, Ian L. Scott, and is currently in Phase 3 trials for dry, age-related macular degeneration (AMD). The compound is also being investigated as a potential therapy for proliferative diabetic retinopathy, diabetic macular edema and Stargardt disease. In 2008, Acucela Inc. partnered with Otsuka Pharmaceutical Company for the development of emixustat (ACU-4429) in an agreement totaling $263 million in cash and milestone payments. Emixustat hydrochloride is a non-retinoid small molecule inhibitor of RPE65 (retinal pigment epithelium-specific 65 kDa protein, also known as retinoid isomerohydrolase). It is thought to reduce visual chromop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leber's Congenital Amaurosis
Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA) is a rare inherited eye disease that appears at birth or in the first few months of life. It affects about 1 in 40,000 newborns. LCA was first described by Theodor Leber in the 19th century. It should not be confused with Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy, which is a different disease also described by Theodor Leber. One form of LCA was successfully treated with gene therapy in 2008. Signs and symptoms LCA symptoms typically begin in the first few months of life, most commonly with involuntary twitching of the eye (nystagmus). Affected infants may show misaligned eyes when looking at something (strabismus), aversion to light (photophobia), and poke or rub at their eyes (Franceschetti’s oculodigital sign). Those with LCA invariably experience vision problems. Affected infants show decreased visual response to objects. Loss of visual acuity is severe, with affected individuals' vision ranging from 20/200 to 20/400. Around a third of thos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Disorder
A birth defect is an abnormal condition that is present at childbirth, birth, regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disability, disabilities that may be physical disability, physical, intellectual disability, intellectual, or developmental disability, developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which problems are seen with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which problems exist with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic disorder, metabolic and degenerative disease, degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders. Birth defects may result from genetic disorder, genetic or chromosome abnormality, chromosomal disorders, exposure to certain medications or chemicals, or certain vertically transmitted infection, infections during pregnancy. Risk factors include folate deficiency, alcohol drink, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RPE65
Retinal pigment epithelium-specific 65 kDa protein (also known as RPE65) is a retinoid isomerohydrolase enzyme of the vertebrate visual cycle. RPE65 is expressed in the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE, a layer of epithelial cells that nourish the photoreceptor cells) and is responsible for the conversion of all-trans-Retinoids, retinyl esters to 11-cis-retinol during phototransduction. 11-cis-retinol is then used in visual pigment regeneration in photoreceptor cells. RPE65 belongs to the carotenoid oxygenase family of enzymes. Function RPE65 is a critical enzyme in the vertebrate Visual phototransduction, visual cycle found in the retinal pigmented epithelium. It is also found in Rod cell, rods and cones. The photoisomerization of 11-cis-retinal to all-trans-retinal initiates the Visual phototransduction, phototransduction pathway through which the brain detects light. All-trans-retinol is not Photochemistry, photoactive and therefore must be reconverted to 11-cis-retinal before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Enzymes
Enzymes are listed here by their classification in the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology's Enzyme Commission (EC) numbering system: :Oxidoreductases (EC 1) ( Oxidoreductase) * Dehydrogenase * Luciferase * DMSO reductase :EC 1.1 (act on the CH-OH group of donors) * :EC 1.1.1 (with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NAD) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NADP) ** Homoserine dehydrogenase ** Aminopropanol oxidoreductase ** Diacetyl reductase ** Glycerol dehydrogenase ** Propanediol-phosphate dehydrogenase ** glycerol-3-phoshitiendopene dehydrogenase (NAD+) ** D-xylulose reductase ** L-xylulose reductase ** Lactate dehydrogenase ** Malate dehydrogenase ** Isocitrate dehydrogenase ** HMG-CoA reductase * :EC 1.1.2 (with a cytochrome as acceptor) * :EC 1.1.3 (with oxygen as acceptor) ** Glucose oxidase ** L-gulonolactone oxidase ** Thiamine oxidase ** Xanthine oxidase * EC 1.1.4 (with a disulfide as accep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isomerase
In biochemistry, isomerases are a general class of enzymes that convert a molecule from one isomer to another. Isomerases facilitate intramolecular rearrangements in which chemical bond, bonds are Bond cleavage, broken and formed. The general form of such a reaction is as follows: :\ce \quad \xrightarrow[\text] \quad \ce There is only one Enzyme substrate (biology), substrate yielding one product. This product has the same chemical formula, molecular formula as the substrate but differs in bond connectivity or spatial arrangement. Isomerases catalyze reactions across many biological processes, such as in glycolysis and carbohydrate metabolism. Isomerization Isomerases catalysis, catalyze changes within one molecule. They convert one isomer to another, meaning that the end product has the same molecular formula but a different physical structure. Isomers themselves exist in many varieties but can generally be classified as structural isomers or stereoisomerism, stereoisomers. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |