|
Retinal Ganglion Cells
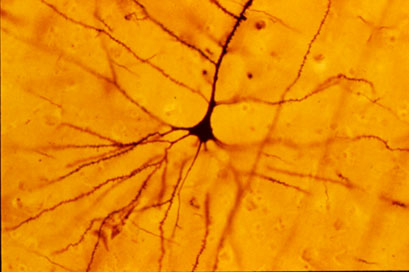
A retinal ganglion cell (RGC) is a type of neuron located near the inner surface (the ganglion cell layer) of the retina of the eye. It receives visual information from photoreceptors via two intermediate neuron types: bipolar cells and retina amacrine cells. Retina amacrine cells, particularly narrow field cells, are important for creating functional subunits within the ganglion cell layer and making it so that ganglion cells can observe a small dot moving a small distance. Retinal ganglion cells collectively transmit image-forming and non-image forming visual information from the retina in the form of action potential to several regions in the thalamus, hypothalamus, and mesencephalon, or midbrain. Retinal ganglion cells vary significantly in terms of their size, connections, and responses to visual stimulation but they all share the defining property of having a long axon that extends into the brain. These axons form the optic nerve, optic chiasm, and optic tract. A small p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural network in the nervous system. They are located in the nervous system and help to receive and conduct impulses. Neurons communicate with other cells via synapses, which are specialized connections that commonly use minute amounts of chemical neurotransmitters to pass the electric signal from the presynaptic neuron to the target cell through the synaptic gap. Neurons are the main components of nervous tissue in all Animalia, animals except sponges and placozoans. Plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Molecular evidence suggests that the ability to generate electric signals first appeared in evolution some 700 to 800 million years ago, during the Tonian period. Predecessors of neurons were the peptidergic secretory cells. They eventually ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
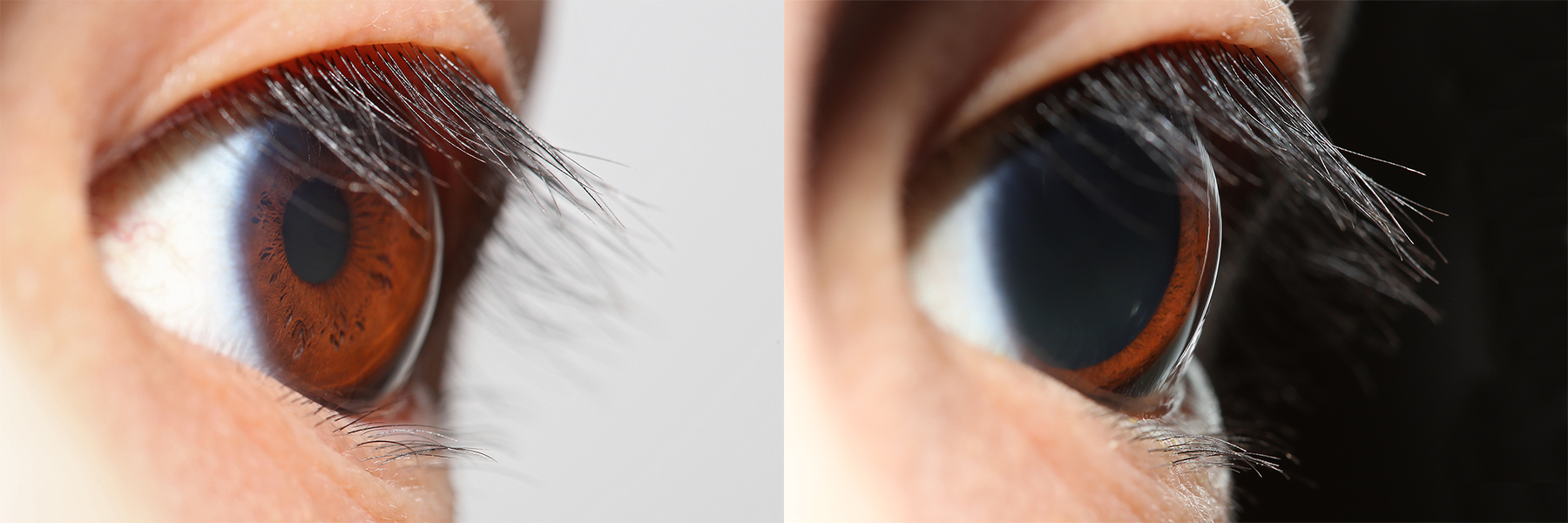
Pupillary Light Reflex
The pupillary light reflex (PLR) or photopupillary reflex is a reflex that controls the diameter of the pupil, in response to the intensity ( luminance) of light that falls on the retinal ganglion cells of the retina in the back of the eye, thereby assisting in adaptation of vision to various levels of lightness/darkness. A greater intensity of light causes the pupil to constrict ( miosis/myosis; thereby allowing less light in), whereas a lower intensity of light causes the pupil to dilate ( mydriasis, expansion; thereby allowing more light in). Thus, the pupillary light reflex regulates the intensity of light entering the eye. Light shone into one eye will cause both pupils to constrict. Terminology The pupil is the dark circular opening in the center of the iris and is where light enters the eye. By analogy with a camera, the pupil is equivalent to aperture, whereas the iris is equivalent to the diaphragm. It may be helpful to consider the ''Pupillary reflex'' as an Iris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koniocellular Cell
In neuroscience, koniocellular cells, also called K-cells, are relatively small neurons located in the koniocellular layer of the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) within the thalamus of primates, including humans. The term 'koniocellular' is derived . Koniocellular layers are located ventral to each parvocellular and magnocellular layer of the LGN. Even if the quantity of neurons is approximately equal to the number of magnocellular cells, the koniocellular layers are much thinner due to their size. In comparison to the parvocellular and magnocellular system, fewer studies have been conducted to investigate the koniocellular system. Koniocellular cells are a heterogeneous population differing in many aspects, such as response properties and connectivity. Structure K cells are neurochemically and anatomically distinct from M and P cells. There are three proteins by which K cells can be clearly distinguished: * Calbindin (28kDa calcium binding protein, CALB) * The alpha subun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bistratified Cell
Bistratified cell or bistratified ganglion cell can refer to either of two kinds of retinal ganglion cells whose cell body is located in the ganglion cell layer of the retina: * the small bistratified cell (SBC), also known as small-field bistratified ganglion cell * the large bistratified cell (LBC) or large-field bistratified ganglion cell Bistratified cells receive their input from bipolar cells and amacrine cells. The bistratified cells project their axons through the optic nerve and optic tract to the koniocellular layers in the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), synapsing with koniocellular cells. Koniocellular means "cells as small as dust"; their small size made them hard to find. About 8 to 10% of retinal ganglion cells are bistratified cells. They receive inputs from intermediate numbers of rods and cones. They have moderate spatial resolution, moderate conduction velocity, and can respond to moderate-contrast stimuli. They may be involved in color vision. See also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnocellular Cell
Magnocellular cells, also called M-cells, are neurons located within the magnocellular layer of the lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus. The cells are part of the visual system. They are termed "magnocellular" since they are characterized by their relatively large size compared to parvocellular cells. Structure The full details of the flow of signaling from the eye to the visual cortex of the brain that result in the experience of Visual perception, vision are incompletely understood. Many aspects are subject to active controversy and the disruption of new evidence. In the visual system, signals mostly travel from the retina to the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) and then to the visual cortex. In humans the LGN is normally described as having six distinctive layers. The inner two layers, (1 and 2) are magnocellular cell (M cell) layers, while the outer four layers, (3,4,5 and 6), are parvocellular cell (P cell) layers. An additional set of neurons, known as the konio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
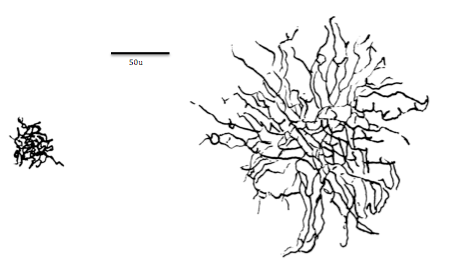
Parasol Cell
A parasol cell, sometimes called an M cell or M ganglion cell, is one type of retinal ganglion cell (RGC) located in the ganglion cell layer of the retina. These cells project to magnocellular cells in the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) as part of the magnocellular pathway in the visual system. They have large cell bodies as well as extensive branching dendrite networks and as such have large receptive fields. Relative to other RGCs, they have fast conduction velocities. While they do show clear center-surround antagonism (known as spatial opponency), they receive no information about color (absence of chromatic opponency). Parasol ganglion cells contribute information about the motion and depth of objects to the visual system. Parasol ganglion cells in the Magnocellular pathway Parasol ganglion cells are the first step in the magnocellular pathway of the visual system. They project from the retina via the optic nerve to the two most ventral layers of the LGN, which is a nuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parvocellular Cell
In neuroscience, parvocellular cells, also called P-cells, are neurons located within the parvocellular layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) of the thalamus. Their name comes , due to the small size of the cell compared to the larger magnocellular cells. Phylogenetically, parvocellular neurons are more modern than magnocellular ones. Function The parvocellular neurons of the visual system receive their input from midget cells, a type of retinal ganglion cell, whose axons comprise the optic tract. These synapses occur in one of the four dorsal parvocellular layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The information from each eye is kept separate at this point, and continues to be segregated until processing in the visual cortex. The electrically-encoded visual information leaves the parvocellular cells via relay cells in the optic radiations, traveling to the primary visual cortex layer 4C-β. The parvocellular neurons are sensitive to colour, and are more ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midget Cell
A midget cell, sometimes called a P cell or P ganglion cell, is one type of retinal ganglion cell (RGC). Midget cells originate in the ganglion cell layer of the retina, and project to the parvocellular layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN). The axons of midget cells travel through the optic nerve and optic tract, ultimately synapsing with parvocellular cells in the LGN. These cells are known as midget retinal ganglion cells due to the small sizes of their dendritic trees and cell bodies. About 80% of RGCs are midget cells. They receive inputs from relatively few rods and cones. In many cases, they are connected to midget bipolar cells, which are linked to one cone each. These neurons show roughly circular receptive fields with antagonistic center and surround; this property is known as spatial opponency and these neurons are typically divided into ON- or OFF-center, depending on whether they are excited or inhibited by photons falling on the center of their rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuromorphology
Neuromorphology (from Greek νεῦρον, neuron, "nerve"; μορφή, morphé, "form"; -λογία, -logia, “study of”) is the study of nervous system form, shape, and structure. The study involves looking at a particular part of the nervous system from a molecular and cellular level and connecting it to a physiological and anatomical point of view. The field also explores the communications and interactions within and between each specialized section of the nervous system. Morphology is distinct from morphogenesis. Morphology is the study of the shape and structure of biological organisms, while morphogenesis is the study of the biological development of the shape and structure of organisms. Therefore, neuromorphology focuses on the specifics of the structure of the nervous system and not the process by which the structure was developed. Neuromorphology and morphogenesis, while two different entities, are nonetheless closely linked. History Progress in defining the morpho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christina Enroth-Cugell
Christina Alma Elisabeth Enroth-Cugell (1919 – June 15, 2016), was a vision scientist who was a professor at Northwestern University for 31 years, was a founding faculty member and one of the first women to teach at the McCormick School of Engineering and chaired the Department of Neurobiology at the Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences from 1984 to 1986. Her husband David Cugell was a professor at the Feinberg School of Medicine for 58 years, the longest tenure in the school’s history. Enroth-Cugell was born in Helsinki, Finland. She earned a joint M.D./Ph.D. from the Karolinska Institute in Sweden and did post-doctorate work at Harvard University Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyma .... Enroth-Cugell was one of the first female interns at Passavant Memorial Hospi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
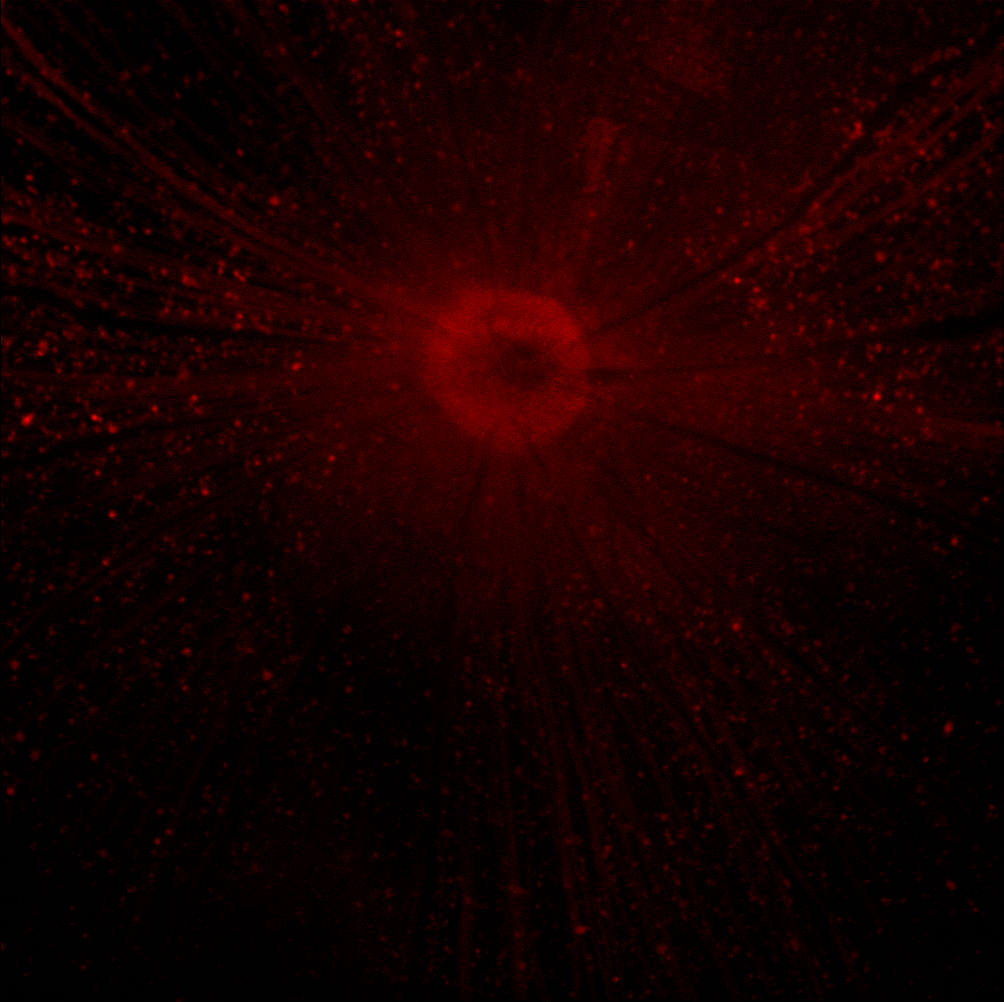
50x RGC Axotomy 1 Day
5 (five) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number, and cardinal number, following 4 and preceding 6, and is a prime number. Humans, and many other animals, have 5 digits on their limbs. Mathematics 5 is a Fermat prime, a Mersenne prime exponent, as well as a Fibonacci number. 5 is the first congruent number, as well as the length of the hypotenuse of the smallest integer-sided right triangle, making part of the smallest Pythagorean triple ( 3, 4, 5). 5 is the first safe prime and the first good prime. 11 forms the first pair of sexy primes with 5. 5 is the second Fermat prime, of a total of five known Fermat primes. 5 is also the first of three known Wilson primes (5, 13, 563). Geometry A shape with five sides is called a pentagon. The pentagon is the first regular polygon that does not tile the plane with copies of itself. It is the largest face any of the five regular three-dimensional regular Platonic solid can have. A conic is determined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fovea Centralis
The ''fovea centralis'' is a small, central pit composed of closely packed Cone cell, cones in the eye. It is located in the center of the ''macula lutea'' of the retina. The ''fovea'' is responsible for sharp central visual perception, vision (also called foveal vision), which is necessary in humans for activities for which visual detail is of primary importance, such as reading (activity), reading and driving. The fovea is surrounded by the ''parafovea'' belt and the ''perifovea'' outer region. The ''parafovea'' is the intermediate belt, where the Retinal ganglion cell, ganglion cell layer is composed of more than five layers of cells, as well as the highest density of cones; the ''perifovea'' is the outermost region where the ganglion cell layer contains two to four layers of cells, and is where visual acuity is below the optimum. The ''perifovea'' contains an even more diminished density of cones, having 12 per 100 micrometres versus 50 per 100 micrometres in the most centra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |