|
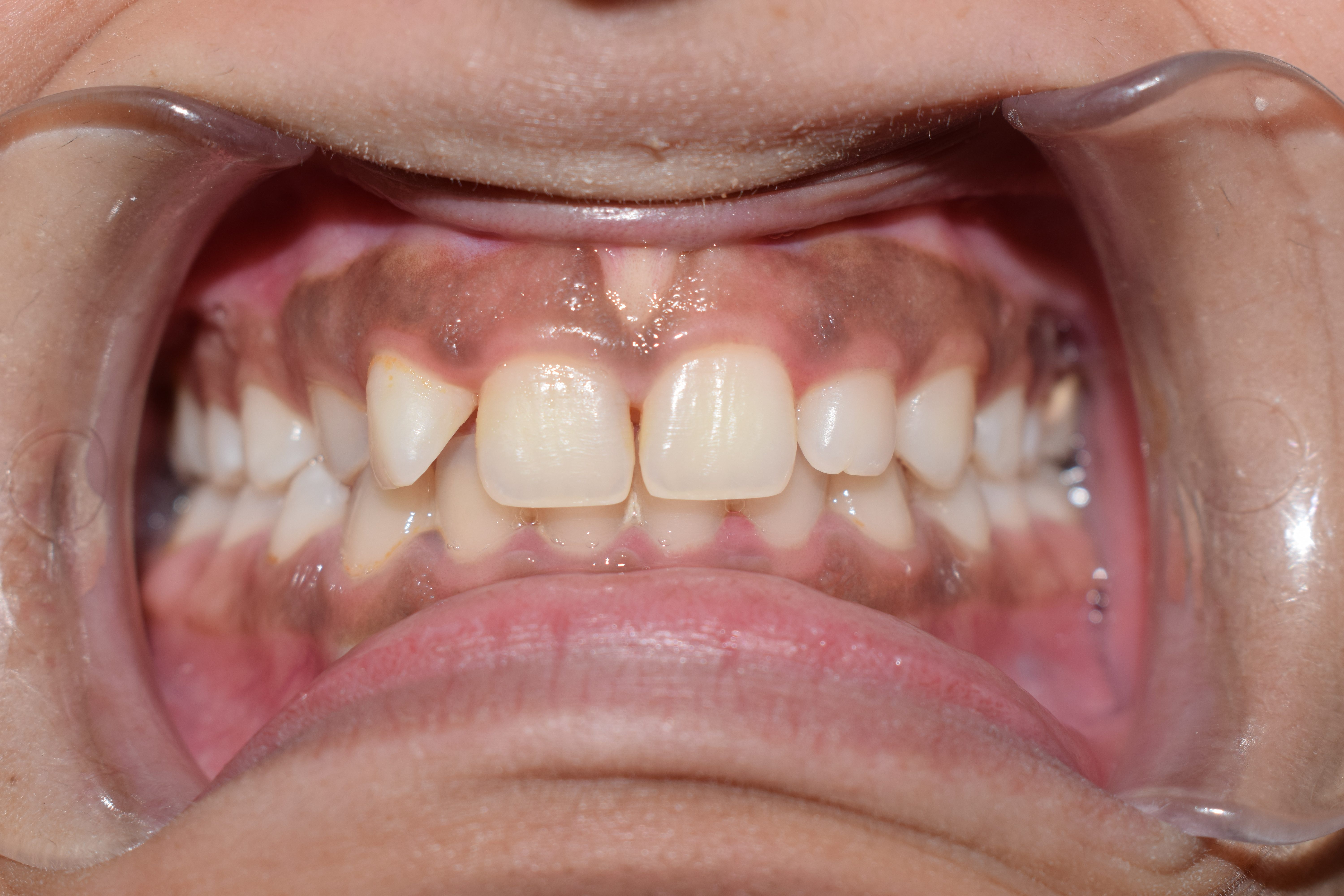
Rete Pegs
Rete pegs (also known as rete processes or rete ridges) are the epithelial extensions that project into the underlying connective tissue in both skin and mucous membranes. In the epithelium of the mouth, the attached gingiva exhibit rete pegs, while the sulcularItoiz, ME; Carranza, FA: The Gingiva. In Newman, MG; Takei, HH; Carranza, FA; editors: ''Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology'', 9th Edition. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company, 2002. pages 23. and junctional epithelia do not.Page, RC; Schroeder, HE. "Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Periodontal Disease: A Summary of Current Work." ''Lab Invest'' 1976;34(3):235-249 Scar tissue lacks rete pegs and scars tend to shear off more easily than normal tissue as a result. Also known as ''papillae'', they are downward thickenings of the epidermis The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and Subcutaneous tissue, hypodermis. The epidermal layer provides a barrie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Epidermis And Dermis With Intradermal Nevus 10x
Normal(s) or The Normal(s) may refer to: Film and television * ''Normal'' (2003 film), starring Jessica Lange and Tom Wilkinson * ''Normal'' (2007 film), starring Carrie-Anne Moss, Kevin Zegers, Callum Keith Rennie, and Andrew Airlie * ''Normal'' (2009 film), an adaptation of Anthony Neilson's 1991 play ''Normal: The Düsseldorf Ripper'' * '' Normal!'', a 2011 Algerian film * ''The Normals'' (film), a 2012 American comedy film * "Normal" (''New Girl''), an episode of the TV series Mathematics * Normal (geometry), an object such as a line or vector that is perpendicular to a given object * Normal basis (of a Galois extension), used heavily in cryptography * Normal bundle * Normal cone, of a subscheme in algebraic geometry * Normal coordinates, in differential geometry, local coordinates obtained from the exponential map (Riemannian geometry) * Normal distribution In probability theory and statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of many internal organs, the corresponding inner surfaces of body cavities, and the inner surfaces of blood vessels. Epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. These tissues also lack blood or lymph supply. The tissue is supplied by nerves. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either simple squamous, simple columnar, or simple cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and Subcutaneous tissue, hypodermis. The epidermal layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss. The epidermis is composed of stratified squamous epithelium, multiple layers of flattened cells that overlie a base layer (stratum basale) composed of Epithelium#Cell types, columnar cells arranged perpendicularly. The layers of cells develop from stem cells in the basal layer. The thickness of the epidermis varies from 31.2μm for the penis to 596.6μm for the Sole (foot), sole of the foot with most being roughly 90μm. Thickness does not vary between the sexes but becomes thinner with age. The human epidermis is an example of epithelium, particularly a stratified squamous epithelium. The word epidermis is derived through Latin , itself and . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucous Membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at body openings such as the eyes, eyelids, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lips, the genital areas, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated. Structure The mucosa is composed of one or more layers of epithelial cells that secrete mucus, and an underlying lamina propria of loose connective tissue. The type of cells and type of mucus secreted vary from organ to organ and each can differ along a given tract. Mucous membranes line the digestive, respiratory and rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gingiva
The gums or gingiva (: gingivae) consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health. Structure The gums are part of the soft tissue lining of the mouth. They surround the teeth and provide a seal around them. Unlike the soft tissue linings of the lips and cheeks, most of the gums are tightly bound to the underlying bone which helps resist the friction of food passing over them. Thus when healthy, it presents an effective barrier to the barrage of periodontal insults to deeper tissue. Healthy gums are usually coral pink in light skinned people, and may be naturally darker with melanin pigmentation. Changes in color, particularly increased redness, together with swelling and an increased tendency to bleed, suggest an inflammation that is possibly due to the accumulation of bacterial plaque. Overall, the clinical appearance of the tissue reflects the underlying histology, both in hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulcular Epithelium
In dental anatomy, the sulcular epithelium is that epithelium Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ... which lines the gingival sulcus.Carranza's Clinical Periodontology, W.B. Saunders, 2002, page 23. It is apically bounded by the junctional epithelium and meets the epithelium of the oral cavity at the height of the free gingival margin. The sulcular epithelium is nonkeratinized. References Dental anatomy {{dentistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junctional Epithelium
In dental anatomy, the junctional epithelium (JE) is that epithelium which lies at, and in health also defines, the base of the gingival sulcus (i.e. where the gums attach to a tooth). The probing depth of the gingival sulcus is measured by a calibrated periodontal probe. In a healthy-case scenario, the probe is gently inserted, slides by the sulcular epithelium (SE), and is stopped by the epithelial attachment (EA). However, the probing depth of the gingival sulcus may be considerably different from the true histological gingival sulcus depth. Location The junctional epithelium, a nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium, lies immediately apical to the sulcular epithelium, which lines the gingival sulcus from the base to the free gingival margin, where it interfaces with the epithelium of the oral cavity. The gingival sulcus is bounded by the enamel of the crown of the tooth and the sulcular epithelium. Immediately apical to the base of the pocket, and coronal to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
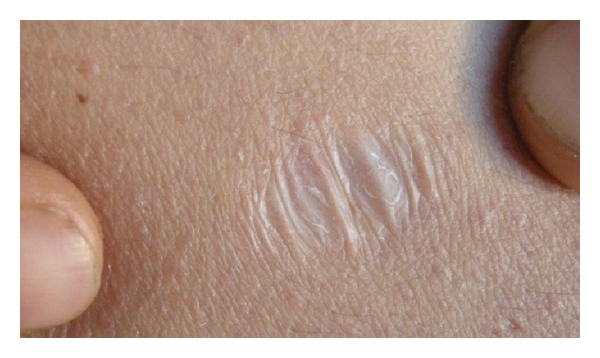
Scar
A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrosis, fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other Organ (anatomy), organs, and biological tissue, tissues of the body. Thus, scarring is a natural part of the healing process. With the exception of very minor lesions, every wound (e.g., after accident, disease, or surgery) results in some degree of scarring. An exception to this are animals with complete Regeneration (biology), regeneration, which regrow tissue without scar formation. Scar tissue is composed of the same protein (collagen) as the tissue that it replaces, but the fiber composition of the protein is different; instead of a random basketweave formation of the collagen fibers found in normal tissue, in fibrosis the collagen cross-links and forms a pronounced alignment in a single direction. This collagen scar tissue alignment is usually of inferior functional quality to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermal Papillae
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided into two layers, the superficial area adjacent to the epidermis called the papillary region and a deep thicker area known as the reticular dermis.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology'' (10th ed.). Saunders. Pages 1, 11–12. . The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis through a basement membrane. Structural components of the dermis are collagen, elastic fibers, and extrafibrillar matrix.Marks, James G; Miller, Jeffery (2006). ''Lookingbill and Marks' Principles of Dermatology'' (4th ed.). Elsevier Inc. Page 8–9. . It also contains mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and thermoreceptors that provide the sense of heat. In addition, hair fol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |