|
Religion In Bhutan
Bhutan is a Buddhist country culturally, socially, politically, and constitutionally, and Buddhism plays a vital role in the cultural and spiritual heritage of the nation. The official religion in Bhutan is Buddhism, which is practiced by 74.7% of the population. Hinduism is followed by 22.6% of the Population. The freedom of religion is guaranteed by the King. In the past, approximately 75% of the population of 770,000 followed either the Drukpa Lineage of the Kagyu school, the Nyingma school of Tibetan Buddhism or another school of Buddhism. Almost 22% of citizens (mainly Lhotshampas) practiced Hinduism.Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project: Bhutan |
Ngalop People
The Ngalop ( ; "earliest risen people" or "first converted people" according to folk etymology) are people of Tibetan origin who migrated to Bhutan as early as the ninth century. Orientalists adopted the term "Bhote" or Bhotiya, meaning "people of Bod (Tibet)", a term also applied to the Tibetan people, leading to confusion, and now is rarely used in reference to the Ngalop. The Ngalop introduced Tibetan culture and Buddhism to Bhutan and comprise the dominant political and cultural element in modern Bhutan. Furthermore, cultural, ethnic, and linguistic identity in Bhutan are not always mutually exclusive. For these reasons, Ngalops are often simply identified as Bhutanese. Their language, Dzongkha, is the national language and is descended from Old Tibetan. The Ngalop are dominant in western and northern Bhutan, including Thimphu and the Dzongkha-speaking region. The term Ngalop may subsume several related linguistic and cultural groups, such as the Kheng people and speakers of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaman
Shamanism is a spiritual practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with the spirit world through altered states of consciousness, such as trance. The goal of this is usually to direct spirits or spiritual energies into the physical world for the purpose of healing, divination, or to aid human beings in some other way. Beliefs and practices categorized as shamanic have attracted the interest of scholars from a variety of disciplines, including anthropologists, archeologists, historians, religious studies scholars, philosophers, and psychologists. Hundreds of books and academic papers on the subject have been produced, with a peer-reviewed academic journal being devoted to the study of shamanism. Terminology Etymology The Modern English word ''shamanism'' derives from the Russian word , , which itself comes from the word from a Tungusic language – possibly from the southwestern dialect of the Evenki spoken by the Sym Evenki peoples, or from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
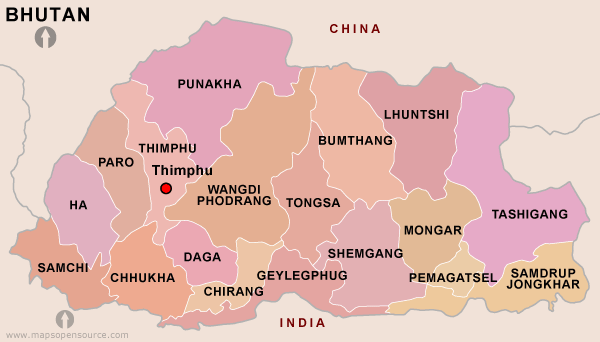
Thimphu
Thimphu (; ) is the capital and largest city of Bhutan. It is situated in the western central part of Bhutan, and the surrounding valley is one of Bhutan's '' dzongkhags'', the Thimphu District. The ancient capital city of Punakha was replaced by Thimphu as the capital in 1955, and in 1961 Thimphu was officially declared the capital of the Kingdom of Bhutan by the 3rd Druk Gyalpo Jigme Dorji Wangchuck. The city extends in a north–south direction on the west bank of the valley formed by the Wang Chhu, which flows out into India as the Raidāk River. Thimphu is the sixth highest capital in the world by altitude, ranging from to . Unlike many capitals, Thimphu does not have its own airport, instead relying on the Paro Airport, accessible by road away. Thimphu, as the political and economic center of Bhutan, has a dominant agriculture and livestock base, contributing to about 45% of the country's GNP. Tourism, though a contributor to the economy, is strictly regulated, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a place of worship, a building used for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. By convention, the specially built places of worship of some religions are commonly called "temples" in English, while those of other religions are not, even though they fulfill very similar functions. The religions for which the terms are used include the great majority of ancient religions that are now extinct, such as the Ancient Egyptian religion and the Ancient Greek religion. Among religions still active: Hinduism (whose temples are called Mandir or Kovil), Buddhism (whose temples are called Vihar), Sikhism (whose temples are called gurudwara), Jainism (whose temples are sometimes called derasar), Zoroastrianism (whose temples are sometimes called Agiary), the Baháʼí Faith (which are often simply referred to as Baháʼí House of Worship), Taoism (which are sometimes called Daoguan), Shinto (which are often called Jinja), C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vedic
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''. The Vedas ( or ; ), sometimes collectively called the Veda, are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the oldest layer of Sanskrit literature and the oldest scriptures of Hinduism. There are four Vedas: the Rigveda, the Yajurveda, the Samaveda and the Atharvaveda. Each Veda has four subdivisions – the Samhitas ( mantras and benedictions), the Brahmanas (commentaries on and explanation of rituals, ceremonies and sacrifices – Yajñas), the Aranyakas (text on rituals, ceremonies, sacrifices and symbolic-sacrifices), and the Upanishads (texts discussing meditation, philosophy and spiritual knowledge).Gavin Flood (1996), ''An Introduction to Hinduism'', Cambridge University Press, , pp. 35–39A Bhattacharya (2006), ''Hindu Dharma: Introduction to Scriptures and Theology'', , pp. 8–14; George ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shakta
Shaktism () is a major Hindu denomination in which the deity or metaphysical reality is considered metaphorically to be a woman. Shaktism involves a galaxy of goddesses, all regarded as different aspects, manifestations, or personifications of the divine feminine energy called ''Shakti''. It includes various modes of worship, ranging from those focused on the most worshipped Durga, to gracious Parvati, and the fierce Kali. After the decline of Buddhism in India, various Hindu and Buddhist goddesses were combined to form the Mahavidya, a pantheon of ten goddesses. The most common forms of the Mahadevi worshipped in Shaktism include: Durga, Kali, Saraswati, Lakshmi, Parvati, and Tripura Sundari. Also worshipped are the various Gramadevatas across the Indian villages. Shaktism also encompasses various tantric sub-traditions, including Vidyapitha and Kulamārga. Shaktism emphasizes that intense love of the deity is more important than simple obedience, thus showing an inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaishnavite
Vaishnavism () ), also called Vishnuism, is one of the major Hindu denominations, Hindu traditions, that considers Vishnu as the sole Para Brahman, supreme being leading all other Hindu deities, that is, ''Mahavishnu''. It is one of the major Hindu denominations along with Shaivism, Shaktism, and Smartism. Its followers are called Vaishnavites or ''Vaishnava''s (), and it includes sub-sects like Krishnaism and Ramanandi Sampradaya, Ramaism, which consider Krishna and Rama as the supreme beings respectively. According to a 2020 estimate by The World Religion Database (WRD), hosted at Boston University’s Institute on Culture, Religion and World Affairs (CURA), Vaishnavism is the largest Hindu sect, constituting about 399 million Hindus. The ancient emergence of Vaishnavism is unclear, and broadly hypothesized as a History of Hinduism, fusion of various regional non-Vedic religions with worship of Vishnu. It is considered a merger of several popular non-Vedic theistic traditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaivite
Shaivism (, , ) is one of the major Hindu traditions, which worships Shiva as the supreme being. It is the second-largest Hindu sect after Vaishnavism, constituting about 385 million Hindus, found widely across South Asia (predominantly in Southern India), Sri Lanka, and Nepal.Keay, p.xxvii. The followers of Shaivism are called Shaivas or Shaivites. According to Chakravarti, Shaivism developed as an amalgam of pre-Aryan religions and traditions, Vedic Rudra, and post-Vedic traditions, accommodating local traditions and Yoga, puja and bhakti. According to Bisschop, early shaivism is rooted in the worship of vedic deity Rudra. The earliest evidence for sectarian Rudra-Shiva worship appears with the Pasupata (early CE), possibly owing to the Hindu synthesis, when many local traditions were aligned with the Vedic-Brahmanical fold. The Pāśupata movement rapidly expanded throughout North India, giving rise to different forms of Shaivism, which led to the emergence of variou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lhotshampa
The Lhotshampa or Lhotsampa (; ) people are a heterogeneous Bhutanese people of Nepali descent. The Lhotshampa were estimated to comprise around 35% of the Bhutan's population by the U.S. Department of State as of 2008. The Lhotshampa are predominantly Hindu and Buddhist, who speak the Nepali language. People of Nepali origin started to settle in uninhabited areas of southern Bhutan in the 19th century. The term "Lhotshampa", which means "southern borderlanders" in Dzongkha, began to be used by the Bhutanese state in the second half of the twentieth century to refer to the population of Nepali origin in the south of the country. By the 1990s, over 100,000 Lhotshampa had been forcibly displaced and removed from Bhutan. After being displaced as a result of the state-run ethnic cleansing and living in refugee camps in eastern parts of Nepal, starting in 2007 most of the Bhutanese refugees were resettled to various countries, such as the United States, Canada, Australia, the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |