|
Rectified Truncated Icosahedron
In geometry, the rectified truncated icosahedron is a convex polyhedron. It has 92 faces: 60 isosceles triangles, 12 regular pentagons, and 20 regular hexagons. It is constructed as a rectification (geometry), rectified, truncated icosahedron, rectification truncating vertices down to mid-edges. As a near-miss Johnson solid, under icosahedral symmetry, the pentagons are always regular, although the hexagons, while having equal edge lengths, do not have the same edge lengths with the pentagons, having slightly different but alternating angles, causing the triangles to be Isosceles triangle, isosceles instead. The shape is a symmetrohedron with notation ''I(1,2,*,[2])'' Images Dual By Conway polyhedron notation, the dual polyhedron can be called a ''joined truncated icosahedron'', jtI, but it is topologically equivalent to the rhombic enneacontahedron with all rhombic faces. Related polyhedra The ''rectified truncated icosahedron'' can be seen in sequence of rectification (geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Near-miss Johnson Solid
In geometry, a near-miss Johnson solid is a strictly convex set, convex polyhedron whose face (geometry), faces are close to being regular polygons but some or all of which are not precisely regular. Thus, it fails to meet the definition of a Johnson solid, a polyhedron whose faces are all regular, though it "can often be physically constructed without noticing the discrepancy" between its regular and irregular faces.. The precise number of near-misses depends on how closely the faces of such a polyhedron are required to approximate regular polygons. Some near-misses with high symmetry are also symmetrohedron, symmetrohedra with some truly regular polygon faces. Some near-misses are also zonohedron, zonohedra. Examples Coplanar misses Some failed Johnson solid candidates have coplanar faces. These polyhedra can be perturbed to become convex with faces that are arbitrarily close to regular polygons. These cases use 4.4.4.4 vertex figures of the square tiling, 3.3.3.3.3.3 vertex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
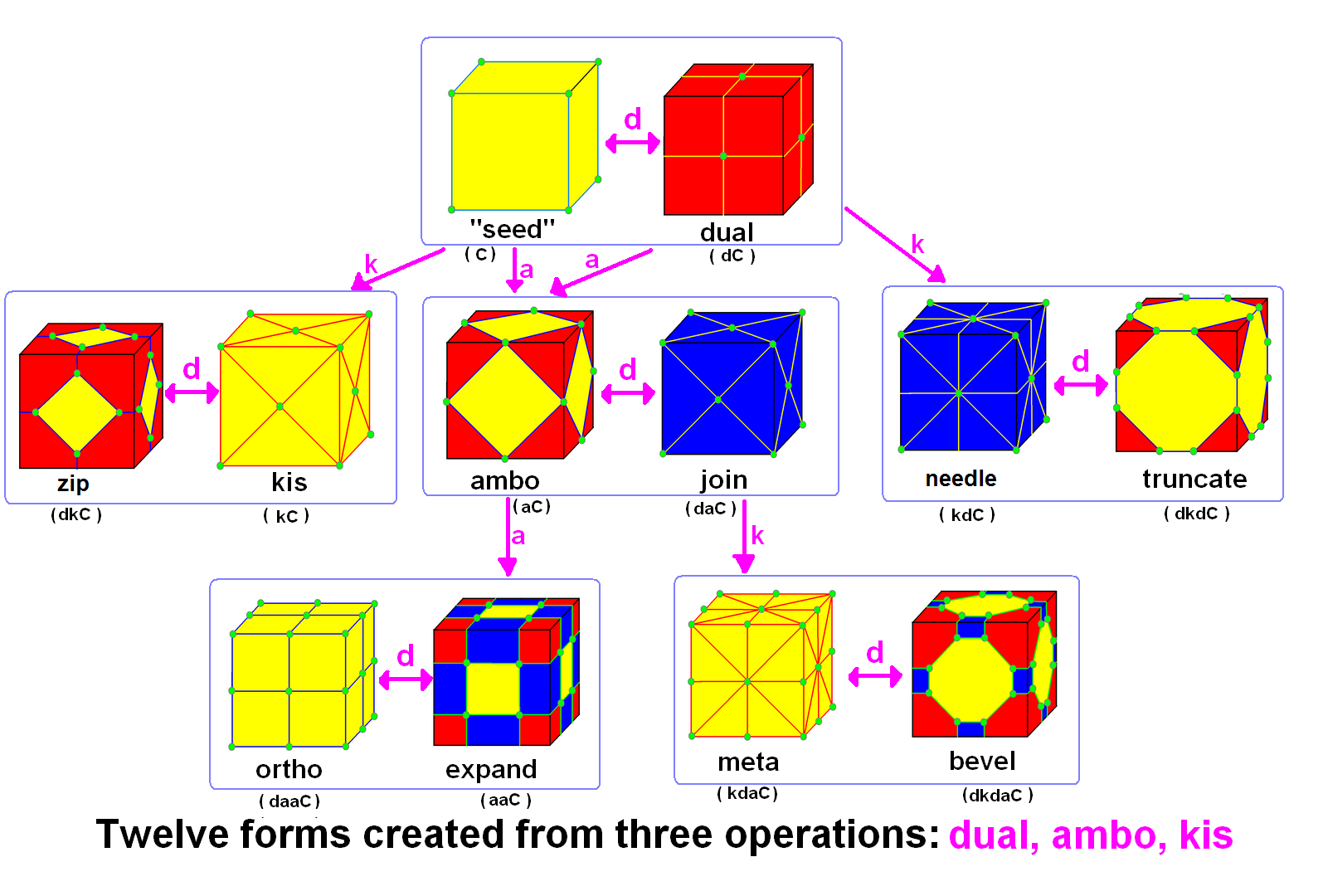
Conway Polyhedron Notation
In geometry and topology, Conway polyhedron notation, invented by John Horton Conway and promoted by George W. Hart, is used to describe polyhedra based on a seed polyhedron modified by various prefix operations. Conway and Hart extended the idea of using operators, like truncation as defined by Kepler, to build related polyhedra of the same symmetry. For example, represents a truncated cube, and , parsed as , is ( topologically) a truncated cuboctahedron. The simplest operator dual swaps vertex and face elements; e.g., a dual cube is an octahedron: . Applied in a series, these operators allow many higher order polyhedra to be generated. Conway defined the operators (ambo), (bevel), ( dual), (expand), (gyro), (join), (kis), (meta), (ortho), ( snub), and ( truncate), while Hart added ( reflect) and (propellor). Later implementations named further operators, sometimes referred to as "extended" operators. Conway's basic operations are sufficient to generate the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rectified Truncated Icosahedron Net
Rectification has the following technical meanings: Mathematics * Rectification (geometry), truncating a polytope by marking the midpoints of all its edges, and cutting off its vertices at those points * Rectifiable curve, in mathematics * Rectifiable set, in mathematics Science * GHK flux equation#Rectification, in biology, a process in cell membranes Technology * Image rectification, adjustment of images to simplify stereo vision or to map images to a map coordinate system (GIS) * The function of a rectifier, a device that converts alternating electrical current to direct current * Rectified airspeed, a means of displaying the airspeed of high-speed aircraft * Rectification (chemical/process engineering), countercurrent distillation, a unit operation also used for the production of rectified spirit (see Distillation#Fractional distillation) Other uses * Rectification (law), an equitable legal remedy whereby a court orders a change in a written document to reflect what it s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Truncated Truncated Icosahedron Net
In mathematics and computer science, truncation is limiting the number of numerical digit, digits right of the decimal point. Truncation and floor function Truncation of positive real numbers can be done using the floor function. Given a number x \in \mathbb_+ to be truncated and n \in \mathbb_0, the number of elements to be kept behind the decimal point, the truncated value of x is :\operatorname(x,n) = \frac. However, for negative numbers truncation does not round in the same direction as the floor function: truncation always rounds toward zero, the \operatorname function rounds towards negative infinity. For a given number x \in \mathbb_-, the function \operatorname is used instead :\operatorname(x,n) = \frac. Causes of truncation With computers, truncation can occur when a decimal number is type conversion, typecast as an integer; it is truncated to zero decimal digits because integers cannot store non-integer real numbers. In algebra An analogue of truncation ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Truncated Icosahedron Flat
In mathematics and computer science, truncation is limiting the number of digits right of the decimal point. Truncation and floor function Truncation of positive real numbers can be done using the floor function. Given a number x \in \mathbb_+ to be truncated and n \in \mathbb_0, the number of elements to be kept behind the decimal point, the truncated value of x is :\operatorname(x,n) = \frac. However, for negative numbers truncation does not round in the same direction as the floor function: truncation always rounds toward zero, the \operatorname function rounds towards negative infinity. For a given number x \in \mathbb_-, the function \operatorname is used instead :\operatorname(x,n) = \frac. Causes of truncation With computers, truncation can occur when a decimal number is typecast as an integer; it is truncated to zero decimal digits because integers cannot store non-integer real numbers. In algebra An analogue of truncation can be applied to polynomials. In th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Snub Rectified Truncated Icosahedron
A snub, cut, or slight is a refusal to recognise an acquaintance by ignoring them, avoiding them or pretending not to know them. For example, a failure to greet someone may be considered a snub. In awards and lists For awards, the term "snub" is usually used to refer to a work or person that fails to be nominated or win award, with whether or not a person or work was legitimately snubbed for an award has often been subject for public debate. The term "snub" has also been used in relation to lists, such as the NBA 75th Anniversary Team. Many notable people and works have failed to be nominated or win a major award. For example, Alfred Hitchcock and Stanley Kubrick never won best director at the Oscars despite being nominated five and four times respectively, and Glenn Close, Peter O'Toole, Deborah Kerr, Sigourney Weaver and Cicely Tyson have never won an Oscar related to acting despite each having multiple nominations. Among films, ''Citizen Kane,'' ''E.T. the Extra-Terrestrial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Truncated Rectified Truncated Icosahedron
In mathematics and computer science, truncation is limiting the number of digits right of the decimal point. Truncation and floor function Truncation of positive real numbers can be done using the floor function. Given a number x \in \mathbb_+ to be truncated and n \in \mathbb_0, the number of elements to be kept behind the decimal point, the truncated value of x is :\operatorname(x,n) = \frac. However, for negative numbers truncation does not round in the same direction as the floor function: truncation always rounds toward zero, the \operatorname function rounds towards negative infinity. For a given number x \in \mathbb_-, the function \operatorname is used instead :\operatorname(x,n) = \frac. Causes of truncation With computers, truncation can occur when a decimal number is typecast as an integer; it is truncated to zero decimal digits because integers cannot store non-integer real numbers. In algebra An analogue of truncation can be applied to polynomials. In th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Expanded Truncated Icosahedron
Expansion may refer to: Arts, entertainment and media * ''L'Expansion'', a French monthly business magazine * ''Expansion'' (album), by American jazz pianist Dave Burrell, released in 2004 * ''Expansions'' (McCoy Tyner album), 1970 * ''Expansions'' (Lonnie Liston Smith album), 1975 * ''Expansión'' (Mexico), a Mexican news portal linked to CNN * Expansion (sculpture) (2004) Bronze sculpture illuminated from within * ''Expansión'' (Spanish newspaper), a Spanish economic daily newspaper published in Spain * Expansion pack in gaming, extra content for games, often simply "expansion" Science, technology, and mathematics * Expansion (geometry), stretching of geometric objects with flat sides * Expansion (model theory), in mathematical logic, a mutual converse of a reduct * Expansion card, in computing, a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an expansion slot * Expansion chamber, on a two-stroke engine, a tuned exhaust system that enhances power output * Expansion joint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rectified Truncated Icosahedron
In geometry, the rectified truncated icosahedron is a convex polyhedron. It has 92 faces: 60 isosceles triangles, 12 regular pentagons, and 20 regular hexagons. It is constructed as a rectification (geometry), rectified, truncated icosahedron, rectification truncating vertices down to mid-edges. As a near-miss Johnson solid, under icosahedral symmetry, the pentagons are always regular, although the hexagons, while having equal edge lengths, do not have the same edge lengths with the pentagons, having slightly different but alternating angles, causing the triangles to be Isosceles triangle, isosceles instead. The shape is a symmetrohedron with notation ''I(1,2,*,[2])'' Images Dual By Conway polyhedron notation, the dual polyhedron can be called a ''joined truncated icosahedron'', jtI, but it is topologically equivalent to the rhombic enneacontahedron with all rhombic faces. Related polyhedra The ''rectified truncated icosahedron'' can be seen in sequence of rectification (geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Truncated Truncated Icosahedron
In mathematics and computer science, truncation is limiting the number of digits right of the decimal point. Truncation and floor function Truncation of positive real numbers can be done using the floor function. Given a number x \in \mathbb_+ to be truncated and n \in \mathbb_0, the number of elements to be kept behind the decimal point, the truncated value of x is :\operatorname(x,n) = \frac. However, for negative numbers truncation does not round in the same direction as the floor function: truncation always rounds toward zero, the \operatorname function rounds towards negative infinity. For a given number x \in \mathbb_-, the function \operatorname is used instead :\operatorname(x,n) = \frac. Causes of truncation With computers, truncation can occur when a decimal number is typecast as an integer; it is truncated to zero decimal digits because integers cannot store non-integer real numbers. In algebra An analogue of truncation can be applied to polynomials. In th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Uniform Polyhedron-53-t12
A uniform is a variety of costume worn by members of an organization while usually participating in that organization's activity. Modern uniforms are most often worn by armed forces and paramilitary organizations such as police, emergency services, security guards, in some workplaces and schools, and by inmates in prisons. In some countries, some other officials also wear uniforms in their duties; such is the case of the Commissioned Corps of the United States Public Health Service or the French prefects. For some organizations, such as police, it may be illegal for non-members to wear the uniform. Etymology From the Latin ''unus'' (meaning one), and ''forma'' (meaning form). Variants Corporate and work uniforms Workers sometimes wear uniforms or corporate clothing of one nature or another. Workers required to wear a uniform may include retail workers, bank and post-office workers, public-security and health-care workers, blue-collar employees, personal trainers in he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Truncated Icosahedron
In geometry, the truncated icosahedron is a polyhedron that can be constructed by Truncation (geometry), truncating all of the regular icosahedron's vertices. Intuitively, it may be regarded as Ball (association football), footballs (or soccer balls) that are typically patterned with white hexagons and black pentagons. It can be found in the application of geodesic dome structures such as those whose architecture Buckminster Fuller pioneered are often based on this structure. It is an example of an Archimedean solid, as well as a Goldberg polyhedron. Construction The truncated icosahedron can be constructed from a regular icosahedron by cutting off all of its vertices, known as Truncation (geometry), truncation. Each of the 12 vertices at the one-third mark of each edge creates 12 pentagonal faces and transforms the original 20 triangle faces into regular hexagons. Therefore, the resulting polyhedron has 32 faces, 90 edges, and 60 vertices. A Goldberg polyhedron is one whose f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |