|
Rapidly Dividing Cells
In cellular biology, labile cells are cells that continuously multiply and divide throughout life . Labile cells replace the cells that are lost from the body. When injured, labile cells are repaired rapidly due to an aggressive TR response. This continual division of labile cells allows them to reproduce new stem cells and replace functional cells that are lost in the body. Functional cells may be lost through necrosis, which is the premature death of cells caused by environmental disturbances, such as diseases or injuries. Functional cells may also need to be replaced after undergoing apoptosis, which is the programmed death of cells that occurs normally as part of an organism's development. Labile cells continually regenerate by undergoing mitosis and are one of three types of cells that are involved in cell division, classified by their regenerative capacity. The other two cell types include stable cells and permanent cells. Each of these three cell types respond to injuries t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellular Biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the Anatomy, structure, Physiology, function, and behavior of cell (biology), cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and functioning of organisms. Cell biology is the study of the structural and functional units of cells. Cell biology encompasses both Prokaryote, prokaryotic and Eukaryote, eukaryotic cells and has many subtopics which may include the study of Metabolism, cell metabolism, Signaling pathway, cell communication, cell cycle, biochemistry, and Cell (biology), cell composition. The study of cells is performed using several microscopy techniques, cell culture, and cell fractionation. These have allowed for and are currently being used for discoveries and research pertaining to how cells function, ultimately giving insight into understanding larger organisms. Knowing the components of cells and how cells work is f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. The term "necrosis" came about in the mid-19th century and is commonly attributed to German pathologist Rudolf Virchow, who is often regarded as one of the founders of modern pathology. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated digestion of cell components. In contrast, ''apoptosis'' is a naturally occurring programmed and targeted cause of cellular death. While apoptosis often provides beneficial effects to the organism, necrosis is almost always detrimental and can be fatal. Cellular death due to necrosis does not follow the apoptotic signal transduction pathway, but rather various receptors are activated and result in the loss of cell membrane integrity and an uncontrolled release of products of cell death into the extracellular space. This initiates an inflammatory response in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrointestinal Tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. The GI tract contains all the major organ (biology), organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digestion, digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Nephrozoa, Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores (ostium (sponges), ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore (osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
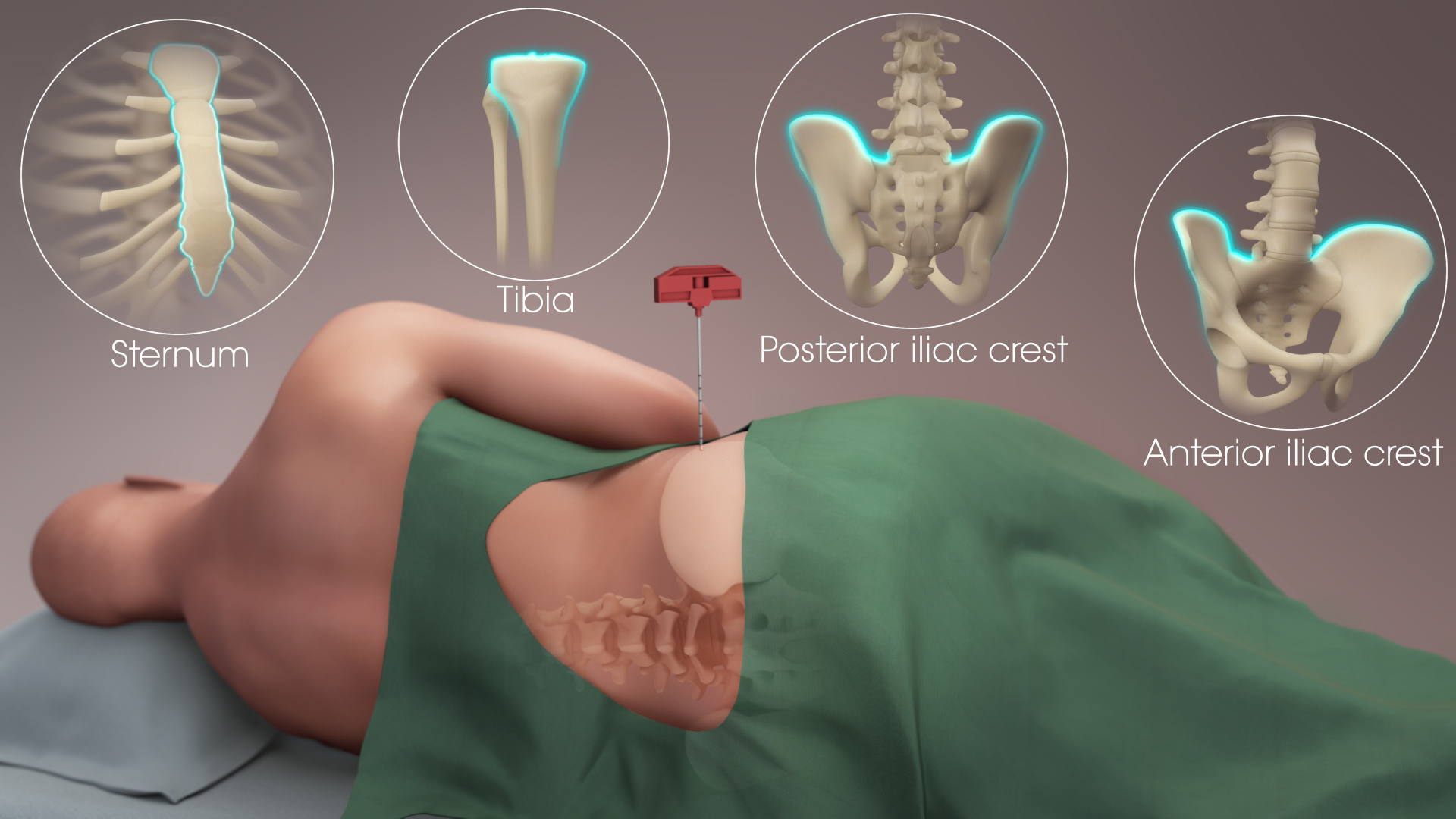
Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of Blood cell, hematopoietic cells, marrow adipose tissue, and supportive stromal cells. In adult humans, bone marrow is primarily located in the Rib cage, ribs, vertebrae, sternum, and Pelvis, bones of the pelvis. Bone marrow comprises approximately 5% of total body mass in healthy adult humans, such that a person weighing 73 kg (161 lbs) will have around 3.7 kg (8 lbs) of bone marrow. Human marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day, which join the Circulatory system, systemic circulation via permeable vasculature sinusoids within the medullary cavity. All types of Hematopoietic cell, hematopoietic cells, including both Myeloid tissue, myeloid and Lymphocyte, lymphoid lineages, are create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytotoxic Drugs
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs), or it may aim only to prolong life or to reduce symptoms (palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called '' medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' now means the non-specific use of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or to induce DNA damage (so that DNA repair can augment chemotherapy). This meaning excludes the more-selective agents that block extracellular signals (signal transduction). Therapies with specific molecular or genetic targets, which inhibit growth-promoting signals from classic endocrine hormones (primarily estrogens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stable Cell
In cellular biology, stable cells are cells that multiply only when needed. They spend most of the time in the quiescent G0 phase of the cell cycle but can be stimulated to enter the cell cycle when needed. Examples include the liver, the proximal tubules of the kidney and endocrine gland The endocrine system is a network of glands and organs located throughout the body. Along with the nervous system, it makes the neuroendocrine system, which controls and regulates many of the body's functions. Endocrine glands are ductless gland ...s. See also * Labile cells, which multiply constantly throughout life * Permanent cells, which don't have the ability to divide Cell biology {{cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permanent Cell
Permanent cells are cells that are incapable of regeneration. These cells are considered to be terminally differentiated and non-proliferative in postnatal life. This includes neurons, heart cells, skeletal muscle cells. Although these cells are considered permanent in that they neither reproduce nor transform into other cells, this does not mean that the body cannot create new versions of these cells. For instance, structures in the bone marrow produce new red blood cells constantly, while skeletal muscle damage can be repaired by underlying satellite cells, which fuse to become a new skeletal muscle cell. Disease and virology studies can use permanent cells to maintain cell count and accurately quantify the effects of vaccines. Some embryology studies also use permanent cells to avoid harvesting embryonic cells from pregnant animals; since the cells are permanent, they may be harvested at a later age when an animal is fully developed. See also * Labile cells, which multi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |