|
Rapid Automatized Naming
Rapid automatized naming (RAN) is a task that measures how quickly individuals can name aloud objects, pictures, colors, or symbols (letters or digits). Variations in rapid automatized naming time in children provide a strong predictor of their later ability to read, and is independent from other predictors such as phonological awareness, verbal IQ, and existing reading skills. Importantly, rapid automatized naming of pictures and letters can predict later reading abilities for pre-literate children. History The concept of rapid automatized naming began with a study by Geshwind and Fusillo in 1966. They found some adults who had had a stroke were later unable to name colors despite being able to color match and having no evidence of color blindness. These individuals however were able to spell and write, indicating that their brain structures were intact and that they could generate the pathway from spoken words to visual and kinaesthetic representations. This visual-verbal discon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbol
A symbol is a mark, Sign (semiotics), sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, physical object, object, or wikt:relationship, relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise different concepts and experiences. All communication is achieved through the use of symbols: for example, a red octagon is a common symbol for "Stop sign, STOP"; on maps, blue lines often represent rivers; and a red rose often symbolizes love and compassion. Numerical digit, Numerals are symbols for numbers; Letter (alphabet), letters of an alphabet may be symbols for certain phonemes; and personal names are symbols representing individuals. The academic study of symbols is called semiotics. In the arts, Artistic symbol, symbolism is the use of a abstract and concrete, concrete element to represent a more abstract idea. In cartography, an organized collection of symbols forms a map layout, legend for a ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Language
Dutch ( ) is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken by about 25 million people as a first language and 5 million as a second language and is the List of languages by total number of speakers, third most spoken Germanic language. In Europe, Dutch is the native language of most of the population of the Netherlands and Flanders (which includes 60% of the population of Belgium). "1% of the EU population claims to speak Dutch well enough in order to have a conversation." (page 153). Dutch was one of the official languages of South Africa until 1925, when it was replaced by Afrikaans, a separate but partially Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible daughter language of Dutch. Afrikaans, depending on the definition used, may be considered a sister language, spoken, to some degree, by at least 16 million people, mainly in South Africa and Namibia, and evolving from Cape Dutch dialects. In South America, Dutch is the native l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reading Disability
A reading disability is a condition in which a person displays difficulty reading. Examples of reading disabilities include developmental dyslexia and alexia (acquired dyslexia). Definition The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke defines reading disability or dyslexia as follows: "Dyslexia is a brain-based type of learning disability that specifically impairs a person's ability to read. These individuals typically read at levels significantly lower than expected despite having normal intelligence. Although the disorder varies from person to person, common characteristics among people with dyslexia are difficulty with spelling, phonological processing (the manipulation of sounds), and rapid visual-verbal responding. In adults, dyslexia usually occurs after a brain injury or in the context of dementia. It can also be inherited in some families, and recent studies have identified a number of genes that may predispose an individual to developing dyslexia." The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered, it would be impossible for language, relationships, or personal identity to develop. Memory loss is usually described as forgetfulness or amnesia. Memory is often understood as an informational processing system with explicit and implicit functioning that is made up of a sensory processor, short-term (or working) memory, and long-term memory. This can be related to the neuron. The sensory processor allows information from the outside world to be sensed in the form of chemical and physical stimuli and attended to various levels of focus and intent. Working memory serves as an encoding and retrieval processor. Information in the form of stimuli is encoded in accordance with explicit or implicit functions by the working memory p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonology
Phonology (formerly also phonemics or phonematics: "phonemics ''n.'' [''obsolescent''] 1. Any procedure for identifying the phonemes of a language from a corpus of data. 2. (formerly also phonematics) A former synonym for phonology, often preferred by the American Structuralists and reflecting the importance in structuralist work of phonemics in sense 1.": "phonematics ''n.'' 1. [''obsolete''] An old synonym for phonemics (sense 2).") is the branch of linguistics that studies how languages systematically organize their phonemes or, for sign languages, their constituent parts of signs. The term can also refer specifically to the sound or sign system of a particular language variety. At one time, the study of phonology related only to the study of the systems of phonemes in spoken languages, but now it may relate to any Linguistic description, linguistic analysis either: Sign languages have a phonological system equivalent to the system of sounds in spoken languages. The buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccade
In vision science, a saccade ( ; ; ) is a quick, simultaneous movement of both Eye movement (sensory), eyes between two or more phases of focal points in the same direction. In contrast, in Smooth pursuit, smooth-pursuit movements, the eyes move smoothly instead of in jumps. Controlled cortically by the frontal eye fields (FEF), or subcortically by the superior colliculus, saccades serve as a mechanism for focal points, rapid eye movement, and the fast phase of optokinetic reflex, optokinetic nystagmus. The word appears to have been coined in the 1880s by French ophthalmologist Louis Émile Javal, Émile Javal, who used a mirror on one side of a page to observe eye movement in silent reading, and found that it involves a succession of discontinuous individual movements. Function Humans and many organisms do not look at a scene in steadiness; instead, the eyes move around, locating interesting parts of the scene and building up a three-dimensional 'map' corresponding to the scen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
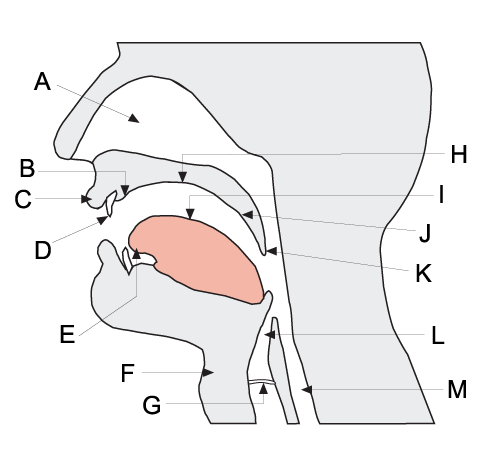
Articulation (phonetics)
The field of articulatory phonetics is a subfield of phonetics that studies articulation and ways that humans produce speech. Articulatory phoneticians explain how humans produce speech sounds via the interaction of different physiological structures. Generally, articulatory phonetics is concerned with the transformation of aerodynamic energy into acoustic energy. Aerodynamic energy refers to the airflow through the vocal tract. Its potential form is air pressure; its kinetic form is the actual dynamic airflow. Acoustic energy is variation in the air pressure that can be represented as sound waves, which are then perceived by the human auditory system as sound. Respiratory sounds can be produced by expelling air from the lungs. However, to vary the sound quality in a way useful for speaking, two speech organs normally move towards each other to contact each other to create an obstruction that shapes the air in a particular fashion. The point of maximum obstruction is called t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reading Disability
A reading disability is a condition in which a person displays difficulty reading. Examples of reading disabilities include developmental dyslexia and alexia (acquired dyslexia). Definition The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke defines reading disability or dyslexia as follows: "Dyslexia is a brain-based type of learning disability that specifically impairs a person's ability to read. These individuals typically read at levels significantly lower than expected despite having normal intelligence. Although the disorder varies from person to person, common characteristics among people with dyslexia are difficulty with spelling, phonological processing (the manipulation of sounds), and rapid visual-verbal responding. In adults, dyslexia usually occurs after a brain injury or in the context of dementia. It can also be inherited in some families, and recent studies have identified a number of genes that may predispose an individual to developing dyslexia." The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyslexia
Dyslexia (), previously known as word blindness, is a learning disability that affects either reading or writing. Different people are affected to different degrees. Problems may include difficulties in spelling words, reading quickly, writing words, "sounding out" words in the head, pronouncing words when reading aloud and understanding what one reads. Often these difficulties are first noticed at school. The difficulties are involuntary, and people with this disorder have a normal desire to learn. People with dyslexia have higher rates of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), developmental language disorders, and difficulties with numbers. Dyslexia is believed to be caused by the interaction of genetic and environmental factors. Some cases run in families. Dyslexia that develops due to a traumatic brain injury, stroke, or dementia is sometimes called "acquired dyslexia" or alexia. The underlying mechanisms of dyslexia result from differences within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthography Of French
French orthography encompasses the spelling and punctuation of the French language. It is based on a combination of phonemic and historical principles. The spelling of words is largely based on the pronunciation of Old French –1200 AD, and has stayed more or less the same since then, despite enormous changes to the pronunciation of the language in the intervening years. Even in the late 17th century, with the publication of the Dictionnaire de l'Académie française">first French dictionary by the Académie française, there were attempts to reform French orthography. This has resulted in a complicated relationship between spelling and sound, especially for vowels; a multitude of silent letters; and many homophones, e.g. ''/////'' (all pronounced ) and ''//'' (all pronounced ). This is conspicuous in verbs: ' (you speak), ' (I speak / one speaks) and ' (they speak) all sound like . Later attempts to respell some words in accordance with their Latin etymologies further increased ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonemic Orthography
A phonemic orthography is an orthography (system for writing a language) in which the graphemes (written symbols) correspond consistently to the language's phonemes (the smallest units of speech that can differentiate words), or more generally to the language's diaphonemes. Natural languages rarely have perfectly phonemic orthographies; a high degree of grapheme–phoneme correspondence can be expected in orthographies based on alphabetic writing systems, but they differ in how complete this correspondence is. English orthography, for example, is alphabetic but highly nonphonemic. In less formally precise terms, a language with a highly phonemic orthography may be described as having regular spelling or phonetic spelling. Another terminology is that of deep and shallow orthographies, in which the depth of an orthography is the degree to which it diverges from being truly phonemic. The concept can also be applied to nonalphabetic writing systems like syllabaries. Ideal phonemic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |