|
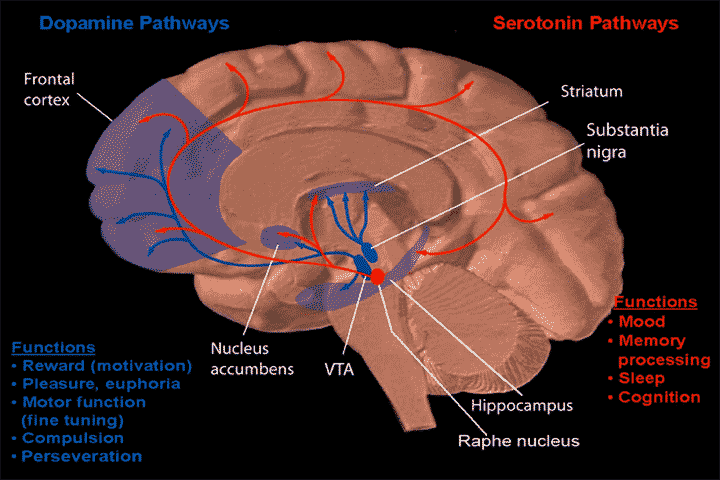
Raphe
Raphe ( ; from ;Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented throughout by Sir Henry Stuart Jones. with the assistance of. Roderick McKenzie.'' Oxford: Clarendon Press. : raphae or raphes) has several different meanings in scientific terminology. In botany and planktology, it is commonly used when describing a seam or ridge on diatoms or seeds. In animal anatomy, it is used to describe a ridged union of continuous biological tissue. There are several different significant anatomical raphes: * The raphe nucleus is a moderate-size cluster of nuclei found in the brain stem that releases serotonin to the rest of the brain. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressants are believed to act at these nuclei. * The buccal raphe, which is on the cheek and evidence of the fusion of the maxillary and mandibular processes * The lingual raphe on the tongue. Obvious physical evidence of the lingual raphe includes the frenulum (also c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raphe Nucleus
The raphe nuclei (, "seam") are a moderate-size cluster of nuclei found in the brain stem. They have 5-HT1 receptors which are coupled with Gi/Go-protein-inhibiting adenyl cyclase. They function as autoreceptors in the brain and decrease the release of serotonin. The anxiolytic drug Buspirone acts as partial agonist against these receptors. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressants are believed to act in these nuclei, as well as at their targets. Anatomy The raphe nuclei are traditionally considered to be the medial portion of the reticular formation, and appear as a ridge of cells in the center and most medial portion of the brain stem. In order from caudal to rostral, the raphe nuclei are known as the '' nucleus raphe obscurus'', the '' nucleus raphe pallidus'', the ''nucleus raphe magnus'', the '' nucleus raphe pontis'', the '' median raphe nucleus'', ''dorsal raphe nucleus'', ''caudal linear nucleus''. In the first systematic examination of the raphe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin
Serotonin (), also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is a monoamine neurotransmitter with a wide range of functions in both the central nervous system (CNS) and also peripheral tissues. It is involved in mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction. In the CNS, serotonin regulates mood, appetite, and sleep. Most of the body's serotonin—about 90%—is synthesized in the gastrointestinal tract by enterochromaffin cells, where it regulates intestinal movements. It is also produced in smaller amounts in the brainstem's raphe nuclei, the skin's Merkel cells, pulmonary neuroendocrine cells, and taste receptor cells of the tongue. Once secreted, serotonin is taken up by platelets in the blood, which release it during clotting to promote vasoconstriction and platelet aggregation. Around 8% of the body's serotonin is stored in platelets, and 1–2% is found in the CNS. Serotonin acts as both a vasoconstrictor and vas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
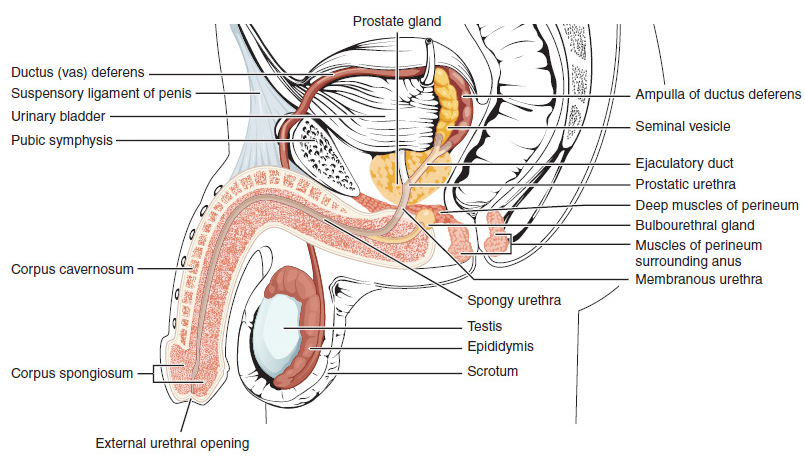
Penile Raphe
The penile raphe is a visible line or ridge of tissue that runs on the ventral (urethral) side of the human penis beginning from the base of the shaft and ending in the prepuce between the penile frenulum. The line is typically darker than the rest of the shaft skin, even though its shape and pigmentation may vary greatly among males. The penile raphe is part of a broader line in the male reproductive organs, that runs from the anus through the perineum (perineal raphe) and continues to the scrotum and penis, collectively referred to as median raphe. The penile raphe along with the skin between it are homologous to the female labia minora. The line consists of a subcutaneous fibrous plate, which may vary in prominence and thickness in various areas of the genitals. In the scrotum, the line is located over the internal scrotal septum that divides the two sides of the sac and is densely occupied by nerve fibers. The raphe may become more prominent and darker when the scrotal s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterygomandibular Raphe
The pterygomandibular raphe (pterygomandibular fold or pterygomandibular ligament) is a thin tendinous band of buccopharyngeal fascia. It is attached superiorly to the pterygoid hamulus of the medial pterygoid plate, and inferiorly to the posterior end of the mylohyoid line of the mandible. It gives attachment to the buccinator muscle (in front), and the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle (behind). Structure The pterygomandibular raphe is a tendinous band formed by the buccopharyngeal fascia. It is a paired structure, with one on each side of the mouth. Superiorly, it is attached to the pterygoid hamulus of the medial pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone; inferiorly, it is attached to the posterior end of the mylohyoid line of the mandible. Relations *Its ''medial surface'' is covered by the mucous membrane of the mouth. * Its ''lateral surface'' is separated from the ramus of the mandible by adipose tissue. * Its ''posterior border'' gives attachment to the superior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatine Raphe
The palatine raphe (also median palatine raphe) is a raphe of the oral cavity. It is a narrow, slight midline ridge extending anteroposteriorly across the palate, from the incisive papilla anteriorly to the palatine uvula posteriorly. Beneath the raphe, the submucosa is absent. Anatomy The palatine raphe is a midline tendinous band of the palate. Relations and attachments The raphe is a surface feature overlying - and indicating - the intermaxillary suture, and median palatine suture. The greater palatine foramen may be palpated on either side about half way between the palatine raphe, and the palatal gingival margin of the 2nd or 3rd upper molar tooth. The palatine raphe serves as an attachment for multiple muscles: the palatoglossus muscle The palatoglossal muscle is a muscle of the soft palate and an extrinsic muscle of the tongue. Its surface is covered by oral mucosa and forms the visible palatoglossal arch. Structure From its origin, it passes anteroinferio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perineal Raphe
The perineal raphe is a visible line or ridge of tissue on the body that extends from the anus through the perineum to the scrotum (male) or the vulva (female). It is found in both males and females, arises from the fusion of the urogenital folds, and is visible running medial through anteroposterior, to the anus where it resolves in a small knot of skin of varying size. In males, this structure continues through the midline of the scrotum (scrotal raphe) and upwards through the posterior midline aspect of the penis ( penile raphe). It also exists deeper through the scrotum where it is called the scrotal septum. It is the result of a fetal developmental phenomenon whereby the scrotum and penis close toward the midline and fuse. See also * Embryonic and prenatal development of the male reproductive system in humans * Frenulum of penis * Linea nigra * Raphe Raphe ( ; from ;Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented throughout by Sir He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Palpebral Raphe
The lateral palpebral raphe is a ligamentous band near the eye. Its existence is contentious, and many sources describe it as the continuation of nearby muscles. It is formed from the lateral ends of the orbicularis oculi muscle. It connects the orbicularis oculi muscle, the frontosphenoidal process of the zygomatic bone, and the tarsi of the eyelids. Structure The lateral palpebral raphe is formed from the lateral ends of the orbicularis oculi muscle. It may also be formed from the pretarsal muscles of the eyelids. It is attached to the margin of the frontosphenoidal process of the zygomatic bone. It passes towards the midline to the lateral commissure of the eyelids. Here, it divides into two slips, which are attached to the margins of the respective tarsi of the eyelids. The lateral palpebral ligament has a tensile strength of around 12 newtons. Relations The lateral palpebral raphe is a much weaker structure than the medial palpebral ligament on the other side of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diatom
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma'') is any member of a large group comprising several Genus, genera of algae, specifically microalgae, found in the oceans, waterways and soils of the world. Living diatoms make up a significant portion of Earth's Biomass (ecology), biomass. They generate about 20 to 50 percent of the oxygen produced on the planet each year, take in over 6.7 billion tonnes of silicon each year from the waters in which they live, and constitute nearly half of the organic material found in the oceans. The Protist shell, shells of dead diatoms are a significant component of marine sediment, and the entire Amazon basin is fertilized annually by 27 million tons of diatom shell dust transported by transatlantic winds from the African Sahara, much of it from the Bodélé Depression, which was once made up of a system of fresh-water lakes. Diatoms are unicellular organisms: they occur either as solitary cells or in Colony (biology), colonies, which can take the shape of ribb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharyngeal Raphe
The pharyngeal raphe is a raphe that serves as the posterior attachment for several of the pharyngeal constrictors (thyropharyngeal part of the inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle, middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle, superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle The superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle is a quadrilateral muscle of the pharynx. It is the uppermost and thinnest of the three pharyngeal constrictors. The muscle is divided into four parts according to its four distincts origins: a pterygop ...). Two sides of the pharyngeal wall are joined posteriorly in the midline by the raphe. Superiorly, it attaches to the pharyngeal tubercle; inferiorly, it extends to the level of vertebra C6 where it blends with the posterior wall of the esophagus. References External links * * Illustration (#32) Human head and neck {{anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iliococcygeal Raphe
The iliococcygeal raphe is a raphe Raphe ( ; from ;Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented throughout by Sir Henry Stuart Jones. with the assistance of. Roderick McKenzie.'' Oxford: Clarendon Press. : raphae or raphes) has several differe ... representing the midline location where the levatores ani converge. See also * Anococcygeal body References Pelvis {{anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anococcygeal Body
The anococcygeal body (anococcygeal ligament or anococcygeal raphe) is a fibrous median raphe in the floor of the pelvis, which extends between the coccyx and the margin of the anus. It is composed of fibers of the levator ani muscle that unite with the muscle of the opposite side, muscle fibres from external anal sphincter, and fibrous connective tissue.Daftary, Shirish; Chakravarti, Sudip (2011). Manual of Obstetrics, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1-16. . The fibers of the levator ani pass downward and backward to the middle line of the floor of the pelvis; the most posterior are inserted into the side of the last two segments of the coccyx The coccyx (: coccyges or coccyxes), commonly referred to as the tailbone, is the final segment of the vertebral column in all apes, and analogous structures in certain other mammals such as horse anatomy, horses. In tailless primates (e.g. hum ...; those placed more anteriorly unite with the muscle of the opposite side, in the anococcygeal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Penis
In Human body, human anatomy, the penis (; : penises or penes; from the Latin ''pēnis'', initially 'tail') is an external sex organ (intromittent organ) through which males urination, urinate and ejaculation, ejaculate, as Penis, on other animals. Together with the testes and surrounding structures, the penis functions as part of the male reproductive system. The main parts of the penis are the Root of penis, root, Body of penis, body, the epithelium of the penis, including the shaft skin, and the foreskin covering the glans penis, glans. The body of the penis is made up of three columns of tissue (biology), tissue: two Corpus cavernosum penis, corpora cavernosa on the dorsal side and corpus spongiosum penis, corpus spongiosum between them on the ventral side. The Urethra#Male, urethra passes through the prostate gland, where it is joined by the ejaculatory ducts, and then through the penis. The urethra goes across the corpus spongiosum and ends at the tip of the glans as the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |