|
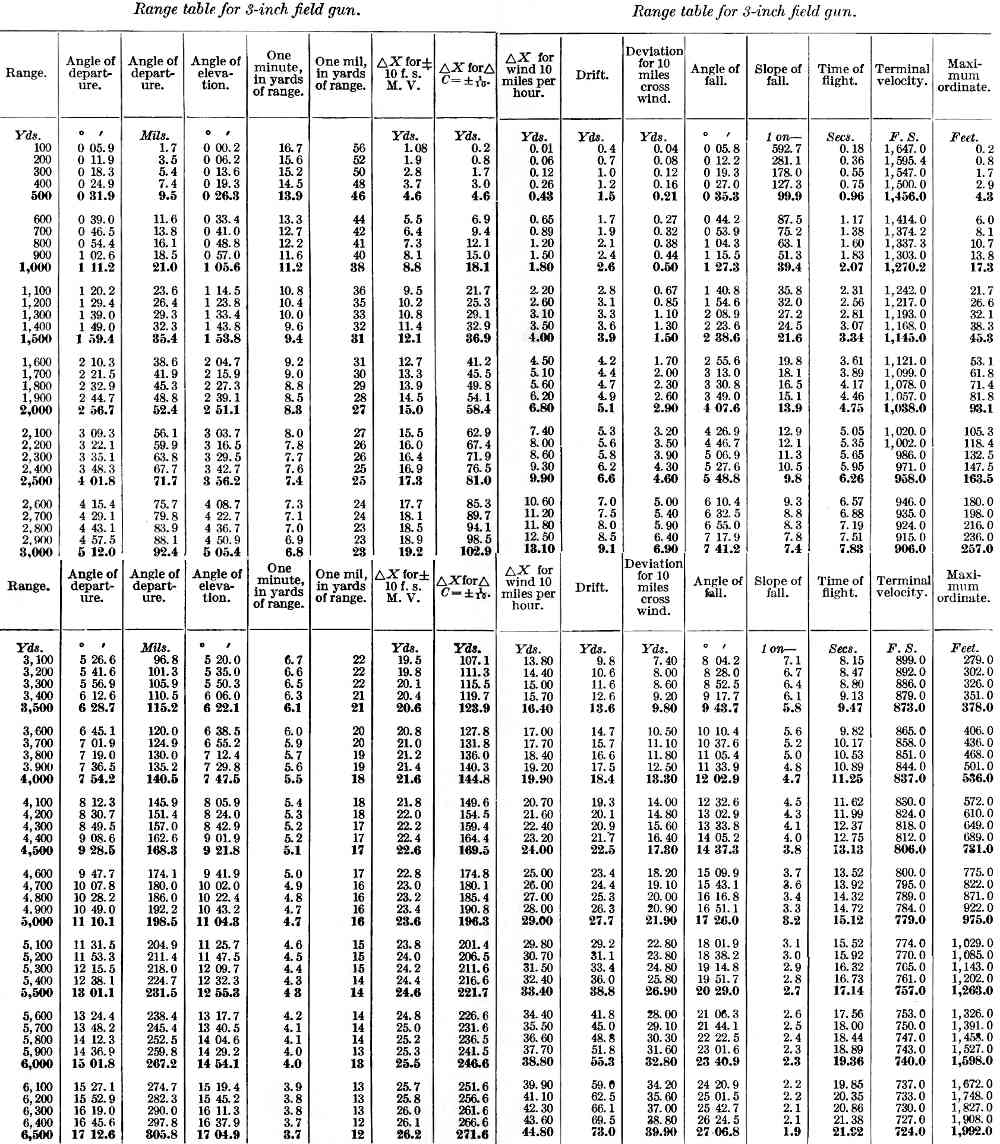
Range Table
A range table was a list of angles of elevation a particular artillery gun barrel needed to be set to, to strike a target at a particular distance with a projectile of a particular weight using a propellant cartridge of a particular weight. They were used for several centuries by field and naval gunners of all countries until gradually replaced by computerised fire-control systems beginning in World War II (1939–1945). Range table for US 3-inch (76.2 mm) field gun, models 1902-1905 This gun used a standard "fixed" cartridge with shell, hence a single set of tables applied to all its ammunition. Range table for British 3 inch (76.2 mm) Stokes Mortar, 1917 Different propellant charges were used to achieve required range, angle of descent and flight time. This is typical of mortars and howitzers. (Provisional) Range Table For 3-Inch Stokes Mortar, Printed in September 1917.Range Tables transcribed and supplied courtesy of John Reed Cartridge : ballistite, reinforced with Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US 3 Inch Field Gun Range Tables 1917
US or Us most often refers to: * ''Us'' (pronoun), the objective case of the English first-person plural pronoun ''we'' * US, an abbreviation for the United States US, U.S., Us, us, or u.s. may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Albums * ''Us'' (Brother Ali album) or the title song, 2009 * ''Us'' (Empress Of album), 2018 * ''Us'' (Mull Historical Society album), 2003 * ''Us'' (Peter Gabriel album), 1992 * ''Us'' (EP), by Moon Jong-up, 2021 * ''Us'', by Maceo Parker, 1974 * ''Us'', mini-album by Peakboy, 2019 Songs * "Us" (James Bay song), 2018 * "Us" (Jennifer Lopez song), 2018 * "Us" (Regina Spektor song), 2004 * "Us" (Gracie Abrams song), 2024 * "Us", by Azealia Banks from '' Fantasea'', 2012 * "Us", by Celine Dion from ''Let's Talk About Love'', 1997 * "Us", by Gucci Mane from ''Delusions of Grandeur'', 2019 * "Us", by Spoon from '' Hot Thoughts'', 2017 Other media * US Festival, two 1980s California music festivals organized by Steve Wozniak * ''Us'' (1991 f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stokes Mortar
The Stokes mortar was a British trench mortar designed by Sir Wilfred Stokes KBE that was issued to the British and U.S. armies, as well as the Portuguese Expeditionary Corps, during the latter half of the First World War. The 3-inch trench mortar is a smooth-bore, muzzle-loading weapon for high angles of fire. Although it is called a 3-inch mortar, its bore is actually 3.2 inches or 81 mm. Design The Stokes mortar was a simple weapon, consisting of a smoothbore metal tube fixed to a base plate (to absorb recoil) with a lightweight bipod mount. When a mortar bomb was dropped into the tube, an impact sensitive primer in the base of the bomb would make contact with a firing pin at the base of the tube, and ignite the propellant charge in the base, launching the bomb towards the target. The warhead itself was detonated by an impact fuse on reaching the target. The barrel is a seamless drawn-steel tube necked down at the breech or base end. To the breech end is fitted a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballistite
Ballistite is a smokeless propellant made from two high explosives, nitrocellulose and nitroglycerine. It was developed and patented by Alfred Nobel in the late 19th century. Military adoption Alfred Nobel patented Ballistite in 1887 while living in Paris. His formulation was composed of 10% camphor and equal parts nitroglycerine and collodion. The camphor reacted with any acidic products of the chemical breakdown of the two explosives. This both stabilized the explosive against further decomposition and prevented spontaneous explosions. However, camphor tends to evaporate over time, leaving a potentially unstable mixture. Nobel's patent specified that the nitrocellulose should be "of the well-known soluble kind". He offered to sell the rights of the new explosive to the French government, but was declined. Modern research shows that Vieille already discovered it in 1884-1885, about the same time as his Poudre B, and noted its high flame temperatures leading to bore erosion. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guncotton
Nitrocellulose (also known as cellulose nitrate, flash paper, flash cotton, guncotton, pyroxylin and flash string, depending on form) is a highly flammable compound formed by nitrating cellulose through exposure to a mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid. One of its first major uses was as guncotton, a replacement for gunpowder as propellant in firearms. It was also used to replace gunpowder as a low-order explosive in mining and other applications. In the form of collodion, it was also a critical component in an early photographic emulsion, the use of which revolutionized photography in the 1860s. In the 20th century, it was adapted to automobile lacquer and adhesives. Production The process uses a mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid to convert cellulose into nitrocellulose. The quality of the cellulose is important. Hemicellulose, lignin, pentosans, and mineral salts give inferior nitrocelluloses. In organic chemistry, nitrocellulose is a nitrate ester, not a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cordite
Cordite is a family of smokeless propellants developed and produced in Britain since 1889 to replace black powder as a military firearm propellant. Like modern gunpowder, cordite is classified as a low explosive because of its slow burning rates and consequently low brisance. These produce a subsonic deflagration wave rather than the supersonic detonation wave produced by brisants, or high explosives. The hot gases produced by burning gunpowder or cordite generate sufficient pressure to propel a bullet or shell to its target, but not so quickly as to routinely destroy the barrel of the gun. Cordite was used initially in the .303 British, Mark I and II, standard rifle cartridge between 1891 and 1915. Shortages of cordite in World War I led to the creation of the "Devil's Porridge" munitions factory ( HM Factory, Gretna) on the English–Scottish border, which produced around 800 tonnes of cordite per week. The UK also imported some United States–developed smokeless ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |