|
Ralfinamide
Ralfinamide (INN; development codes NW-1029, FCE-26742A, and PNU-0154339E) is a multimodal drug which is under investigation by Newron Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of neuropathic pain and other pain conditions such as post-operative dental pain. It has a relatively complex pharmacology, acting as a mixed voltage-gated sodium channel blocker (including Nav1.7), N-type calcium channel blocker, noncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonist, and monoamine oxidase B inhibitor. As of 2020, it was in phase III clinical trials. In 2010 it failed a phase II trial for lower back pain. Encouraging Phase II results have been announced for neuropathic pain. See also * List of investigational analgesics * Safinamide, different fluorine position * Evenamide, structurally-related antipsychotic in development * Lacosamide, used for partial-onset seizures and diabetic neuropathic pain * Ziconotide, FDA approved peptide Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Investigational Analgesics
This is a list of investigational analgesics, or analgesics that are currently under development for clinical use but are not yet approved. ''Chemical/generic names are listed first, with developmental code names, synonyms, and brand names in parentheses.'' This list was last comprehensively updated in June 2017. It is likely to become outdated with time. Opioid receptor modulators * Axelopran/oxycodone – combination of a centrally active μ-opioid receptor agonist and a peripherally selective μ-, κ-, and δ-opioid receptor antagonist. * Cebranopadol (GRT-6005) – non-selective μ-opioid receptor, nociceptin receptor, and δ-opioid receptor full agonist and κ-opioid receptor partial agonist * Desmetramadol (''O''-desmethyltramadol; Omnitram) – μ-opioid receptor agonist, norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (NRI), and 5-HT2C receptor antagonist. * Deumitragynine (KUR-101) – atypical μ-opioid receptor agonist related to mitragynine (found in kratom) * (GRT-6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
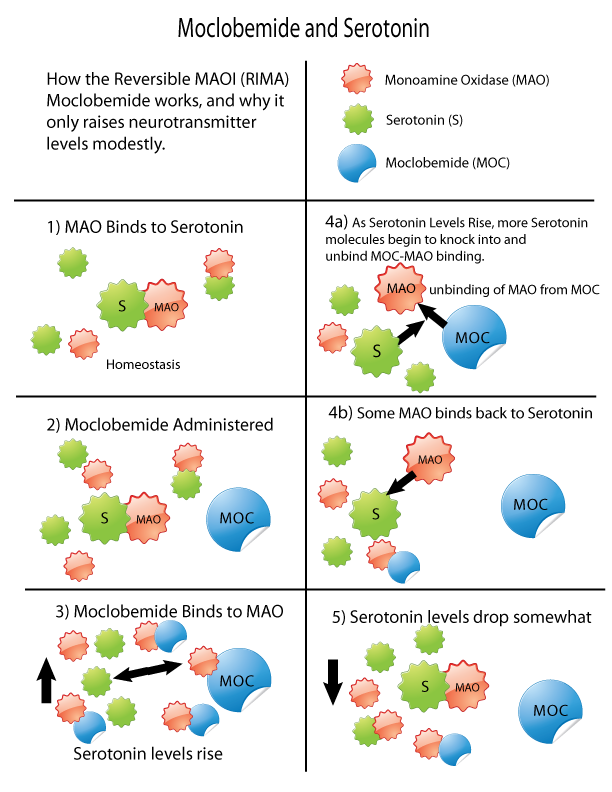
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a drug class, class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders. Reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs) are a subclass of MAOIs that binding selectivity, selectively and Enzyme inhibitor#Reversible inhibitors, reversibly enzyme inhibitor, inhibit the MAO-A enzyme. RIMAs are used clinically in the medication, treatment of major depressive disorder, depression and dysthymia. Due to their reversibility, they are safer in single-drug overdose than the older, irreversible MAOIs, and weaker in increasing the monoamines important in depressive disorder. RIMAs have not gained widespread market share in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NMDA Receptor Antagonists
NMDA receptor antagonists are a class of drugs that work to antagonize, or inhibit the action of, the ''N''-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor ( NMDAR). They are commonly used as anesthetics for humans and animals; the state of anesthesia they induce is referred to as dissociative anesthesia. Several synthetic opioids function additionally as NMDAR-antagonists, such as pethidine, levorphanol, methadone, dextropropoxyphene, tramadol, and ketobemidone. Some NMDA receptor antagonists, such as ketamine, dextromethorphan (DXM), phencyclidine (PCP), methoxetamine (MXE), and nitrous oxide (N2O), are sometimes used as recreational drugs, for their dissociative, hallucinogenic, and euphoriant properties. When used recreationally, they are classified as dissociative drugs. Uses and effects NMDA receptor antagonists induce a state called dissociative anesthesia, marked by catalepsy, amnesia, and analgesia. Ketamine is a favored anesthetic for emergency patients with unknown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders. Reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs) are a subclass of MAOIs that selectively and reversibly inhibit the MAO-A enzyme. RIMAs are used clinically in the treatment of depression and dysthymia. Due to their reversibility, they are safer in single-drug overdose than the older, irreversible MAOIs, and weaker in increasing the monoamines important in depressive disorder. RIMAs have not gained widespread market share in the United States. Medical uses MAOIs have been found to be effective in the treatment of panic disorder with agoraphob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Channel Blockers
Calcium channel blockers (CCB), calcium channel antagonists or calcium antagonists are a group of medications that disrupt the movement of calcium () through calcium channels. Calcium channel blockers are used as antihypertensive drugs, i.e., as medications to decrease blood pressure in patients with hypertension. CCBs are particularly effective against large vessel stiffness, one of the common causes of elevated systolic blood pressure in elderly patients. Calcium channel blockers are also frequently used to alter heart rate (especially from atrial fibrillation), to prevent peripheral and cerebral vasospasm, and to reduce chest pain caused by angina pectoris. N-type, L-type, and T-type voltage-dependent calcium channels are present in the zona glomerulosa of the human adrenal gland, and CCBs can directly influence the biosynthesis of aldosterone in adrenocortical cells, with consequent impact on the clinical treatment of hypertension with these agents. CCBs have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analgesics
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic, antalgic, pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used for pain management. Analgesics are conceptually distinct from anesthetics, which temporarily reduce, and in some instances eliminate, sensation, although analgesia and anesthesia are neurophysiologically overlapping and thus various drugs have both analgesic and anesthetic effects. Analgesic choice is also determined by the type of pain: For neuropathic pain, recent research has suggested that classes of drugs that are not normally considered analgesics, such as tricyclic antidepressants and anticonvulsants may be considered as an alternative. Various analgesics, such as many NSAIDs, are available over the counter in most countries, whereas various others are prescription drugs owing to the substantial risks and high chances of overdose, misuse, and addiction in the absence of medical supervision. Etymology The word ''analgesic'' derives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptide
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. Peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligands such as coenzymes and cofactors, to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. All peptides except cyclic peptides have an N-terminal (amine group) and C-terminal (carboxyl g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ziconotide
Ziconotide, sold under the brand name Prialt, also called intrathecal ziconotide (ITZ) because of its administration route, is an atypical analgesic agent for the amelioration of severe and chronic pain. Derived from '' Conus magus'', a cone snail, it is the synthetic form of an ω- conotoxin peptide. In December 2004 the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved ziconotide when delivered as an infusion into the cerebrospinal fluid using an intrathecal pump system. Medical uses Due to the profound side effects or lack of efficacy when delivered through more common routes, such as orally or intravenously, ziconotide must be administered intrathecally (i.e., directly into the spinal fluid). As this is the most expensive and invasive method of drug delivery and involves additional risks of its own, ziconotide therapy is generally considered appropriate (as evidenced by the range of use approved by the FDA in the US) only for "management of severe chronic pain in patient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacosamide
Lacosamide, sold under the brand name Vimpat among others, is a medication used for the treatment of partial-onset seizures and primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures. It is used by mouth or intravenously. It is available as a generic medication. Medical uses Lacosamide is indicated for the treatment of partial-onset seizures and adjunctive therapy in the treatment of primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Off-label use As with other anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs), lacosamide may have a variety of off-label uses, including for pain management and treatment of mental health disorders. Lacosamide and other AEDs have been used off-label in the management of bipolar disorder, cocaine addiction, dementia, depression, diabetic peripheral neuropathy, fibromyalgia, headache, hiccups, Huntington's disease, mania, migraine, obsessive-compulsive disorder, panic disorder, restless leg syndrome, and tinnitus. Combinations of AEDs are often employed for seizure reduction. Studies a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evenamide
Evenamide () (developmental code names NW-3509, NW-3509A) is a selective voltage-gated sodium channel blocker, including (and not limited to) subtypes Nav1.3, Nav1.7, and Nav1.8, which is described as an antipsychotic and is under development by Newron Pharmaceuticals as an add-on therapy for the treatment of schizophrenia. The drug has shown efficacy in animal models of psychosis, mania, depression, and aggression. It has completed phase I clinical trials, and phase II clinical trials will be commenced in the third quarter of 2015. The drug was discovered by Newron Pharmaceuticals SpA, a pharmaceutical company located in Italy and according to the company, it shows benefit to the management of schizophrenia to poorly responded treatment with antipsychotics. It acts exclusively through glutamatergic inhibition. Clinical studies In a randomized study with treatment-resistant schizophrenia patients, evenamide was added to the treatment regimen, with the psychological a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |