|
Radioulnar Synostosis
Radioulnar synostosis is a rare condition where there is an abnormal connection ( synostosis) between the radius and ulna bones of the forearm. This can be present at birth (congenital), when it is a result of a failure of the bones to form separately, or following an injury (post-traumatic). It typically causes restricted movement of the forearm, in particular rotation (pronation and supination), though is usually not painful unless it causes subluxation of the radial head. It can be associated with dislocation of the radial head which leads to limited elbow extension. Types Congenital Congenital radioulnar synostosis is rare, with approximately 350 cases reported in journals. It typically affects both sides (bilateral) and can be associated with other skeletal problems such as hip and knee abnormalities, finger abnormalities ( syndactyly or clinodactyly), or Madelung's deformity. It is sometimes part of known genetic syndromes such as Klinefelter syndrome (48,XXXY varian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synostosis
Synostosis (; plural: synostoses) is fusion of two or more bones. It can be normal in puberty (e.g. fusion of the epiphyseal plate to become the epiphyseal line), or abnormal. When synostosis is abnormal it is a type of dysostosis. Examples of synostoses include: * craniosynostosis – an abnormal fusion of two or more cranial bones; * radioulnar synostosis – the abnormal fusion of the radius and ulna bones of the forearm; * tarsal coalition – a failure to separately form all seven bones of the tarsus (the hind part of the foot) resulting in an amalgamation of two bones; and * syndactyly – the abnormal fusion of neighboring digits. Synostosis within joints can cause ankylosis. __TOC__ Clinical significance Radioulnar synostosis is one of the more common failures of separation of parts of the upper limb. There are two general types: one is characterized by fusion of the radius and ulna at their proximal borders and the other is fused distal to the proximal radial e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
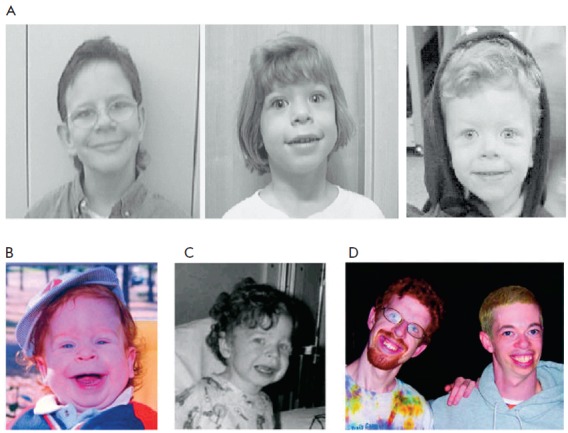
Klinefelter Syndrome
Klinefelter syndrome (KS), also known as 47,XXY, is a chromosome anomaly where a male has an extra X chromosome. These complications commonly include infertility and small, poorly functioning testicles (if present). These symptoms are often noticed only at puberty, although this is one of the most common chromosomal disorders. The birth prevalence of KS in the State of Victoria, Australia was estimated to be 223 per 100,000 males. It is named after American endocrinologist Harry Klinefelter, who identified the condition in the 1940s, along with his colleagues at Massachusetts General Hospital. The syndrome is defined by the presence of at least one extra X chromosome in addition to a Y chromosome, yielding a total of 47 or more chromosomes rather than the usual 46. Klinefelter syndrome occurs randomly. The extra X chromosome comes from the father and mother nearly equally. An older mother may have a slightly increased risk of a child with KS. The syndrome is diagnosed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haematoma
A hematoma, also spelled haematoma, or blood suffusion is a localized bleeding outside of blood vessels, due to either disease or trauma including injury or surgery and may involve blood continuing to seep from broken capillaries. A hematoma is benign and is initially in liquid form spread among the tissues including in sacs between tissues where it may coagulate and solidify before blood is reabsorbed into blood vessels. An ecchymosis is a hematoma of the skin larger than 10 mm. They may occur among and or within many areas such as skin and other organs, connective tissues, bone, joints and muscle. A collection of blood (or even a hemorrhage) may be aggravated by anticoagulant medication (blood thinner). Blood seepage and collection of blood may occur if heparin is given via an intramuscular route; to avoid this, heparin must be given intravenously or subcutaneously. Signs and symptoms Some hematomas are visible under the surface of the skin (commonly called bruise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
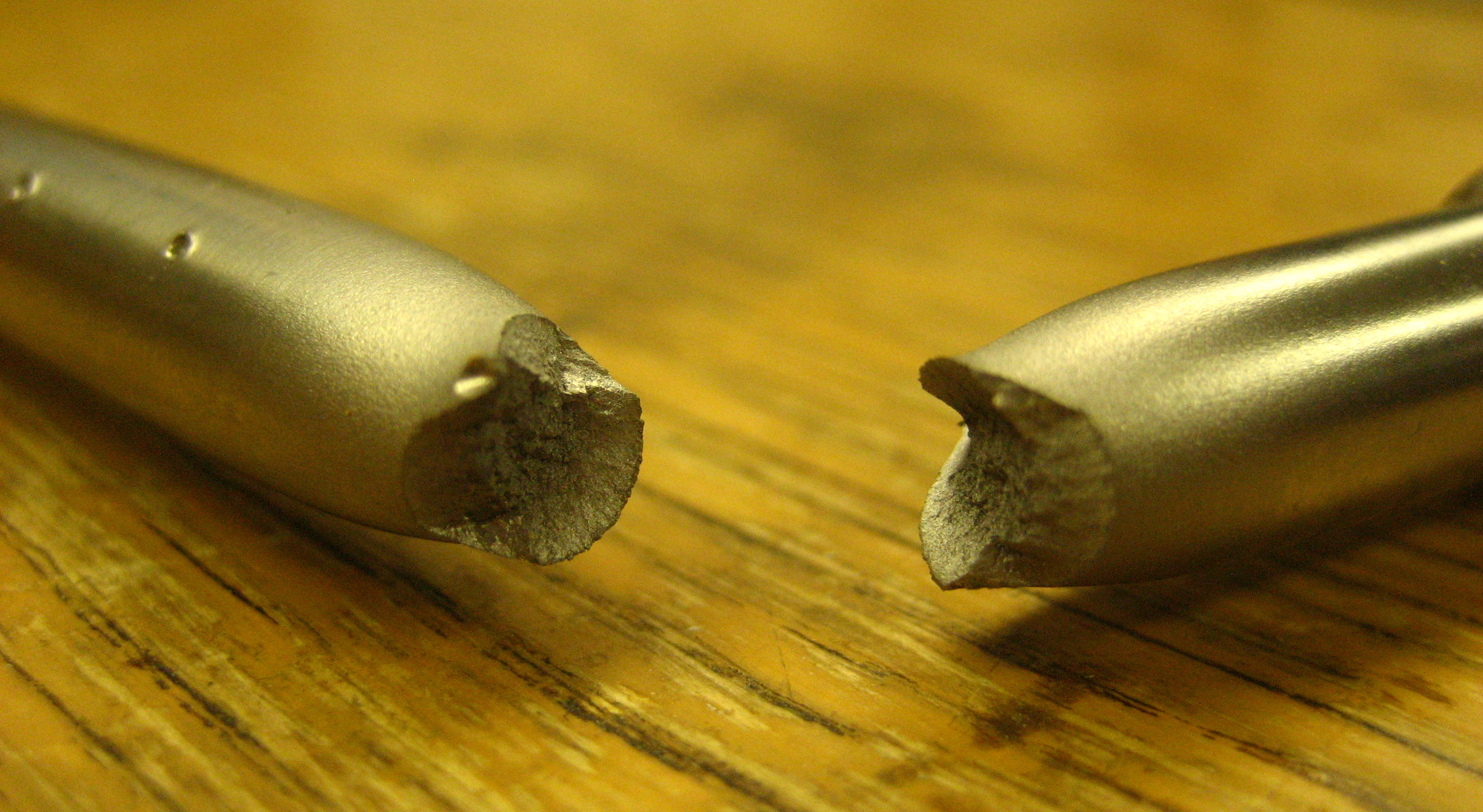
Bone Fracture
A bone fracture (abbreviated FRX or Fx, Fx, or #) is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of any bone in the body. In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several fragments, known as a ''comminuted fracture''. An open fracture (or compound fracture) is a bone fracture where the broken bone breaks through the skin. A bone fracture may be the result of high force Impact force, impact or Stress fracture, stress, or a minimal trauma injury as a result of certain medical conditions that weaken the bones, such as osteoporosis, osteopenia, bone cancer, or osteogenesis imperfecta, where the fracture is then properly termed a pathologic fracture. Most bone fractures require urgent medical attention to prevent further injury. Signs and symptoms Although bone tissue contains no nociceptors, pain receptors, a bone fracture is painful for several reasons: * Breaking in the continuity of the periosteum, with or without similar disconti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fracture
Fracture is the appearance of a crack or complete separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress (mechanics), stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displacement develops perpendicular to the surface, it is called a normal tensile crack or simply a crack; if a displacement develops tangentially, it is called a shear crack, slip band, or dislocation. #Brittle, Brittle fractures occur without any apparent deformation before fracture. #Ductile, Ductile fractures occur after visible deformation. Fracture strength, or breaking strength, is the stress when a specimen fails or fractures. The detailed understanding of how a fracture occurs and develops in materials is the object of fracture mechanics. Strength Fracture strength, also known as breaking strength, is the stress at which a specimen structural integrity and failure, fails via fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASDs) are a group of conditions that can occur in a person who is exposed to alcohol during gestation. FASD affects 1 in 20 Americans, but is highly misdiagnosed and underdiagnosed. The several forms of the condition (in order of most severe to least severe) are: fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS), partial fetal alcohol syndrome (pFAS), alcohol-related neurodevelopmental disorder (ARND), and neurobehavioral disorder associated with prenatal alcohol exposure (ND-PAE). Other terms used are fetal alcohol effects (FAE), partial fetal alcohol effects (PFAE), alcohol-related birth defects (ARBD), and static encephalopathy, but these terms have fallen out of favor and are no longer considered part of the spectrum. Not all infants exposed to alcohol in utero will have detectable FASD or pregnancy complications. The risk of FASD increases with the amount consumed, the frequency of consumption, and the longer duration of alcohol consumption during pregnanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HOXA11
Homeobox protein Hox-A11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HOXA11'' gene. Function In vertebrates, the genes encoding the class of transcription factors called homeobox genes are found in clusters named A, B, C, and D on four separate chromosomes. Expression of these proteins is spatially and temporally regulated during embryonic development. This gene is part of the A cluster on chromosome 7 and encodes a DNA-binding transcription factor which may regulate gene expression, morphogenesis, and differentiation. This gene is involved in the regulation of uterine development and is required for female fertility. Mutations in this gene can cause radioulnar synostosis with amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia. See also * Homeobox A homeobox is a Nucleic acid sequence, DNA sequence, around 180 base pairs long, that regulates large-scale anatomical features in the early stages of embryonic development. Mutations in a homeobox may change large-scale anatomical featu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amegakaryocytic Thrombocytopenia
Congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia (CAMT) is a rare autosomal recessive bone marrow failure syndrome characterized by severe thrombocytopenia, which can progress to aplastic anemia and leukemia. CAMT usually manifests as thrombocytopenia in the initial month of life or in the fetal phase. Typically CAMPT presents with petechiae, cerebral bleeds, recurrent rectal bleeding, or pulmonary hemorrhage. The cause of CAMT is believed to be mutations in the MPL gene coding for thrombopoietin receptor, which is expressed in pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells and cells of the megakaryocyte lineage. CAMT is diagnosed by a bone marrow biopsy and is often initially suspected to be fetal and neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia. Two types of Congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia have been identified with type I being more severe. Treatment is mostly supportive, consisting of multiple platelet transfusions. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is the only known cure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal Dominant
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the Phenotype, effect of a different variant of the same gene on Homologous chromosome, the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second is called recessive. This state of having Heterozygosity, two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or Heredity, inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes (autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holt–Oram Syndrome
Holt–Oram syndrome (also called atrio-digital syndrome, atriodigital dysplasia, cardiac-limb syndrome, heart-hand syndrome type 1, HOS, ventriculo-radial syndrome) is an autosomal dominant disorder that affects bones in the arms and hands (the upper limbs) and often causes heart problems. The syndrome may include an absent radial bone in the forearm, an atrial septal defect in the heart, or heart block. It affects approximately 1 in 100,000 people. Presentation All people with Holt-Oram syndrome have at least one abnormal wrist bone, which can often only be detected by X-ray. Other bone abnormalities are associated with the syndrome. These vary widely in severity, and include a missing thumb, a thumb that looks like a finger, upper arm bones of unequal length or underdeveloped, partial or complete absence of bones in the forearm, and abnormalities in the collar bone or shoulder blade. Bone abnormalities may affect only one side of the body or both sides; if both sides ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornelia De Lange Syndrome
Cornelia de Lange syndrome (CdLS) is a genetic disorder. People with Cornelia de Lange syndrome experience a range of physical, cognitive, and medical challenges ranging from mild to severe. Cornelia de Lange syndrome has a widely varied phenotype, meaning people with the syndrome have varied features and challenges. The typical features of CdLS include thick or long eyebrows, a small nose, small stature, developmental delay, long or smooth philtrum, thin upper lip and downturned mouth. The syndrome is named after Dutch pediatrician Cornelia Catharina de Lange, who described it in 1933. It is often termed Brachmann de Lange syndrome or Bushy syndrome and is also known as Amsterdam dwarfism. Its exact incidence is unknown, but it is estimated at 1 in 10,000 to 30,000. Signs and symptoms The phenotype of CdLS is highly varied and is described as a spectrum; from Classic CdLS (with a greater number of key features) to mild variations with only a few features. Some people will ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Williams Syndrome
Williams syndrome (WS), also Williams–Beuren syndrome (WBS), is a genetic disorder that affects many parts of the body. Facial features frequently include a broad forehead, underdeveloped chin, short nose, and full cheeks. Mild to moderate intellectual disability is observed, particularly challenges with visual spatial tasks such as drawing. Verbal skills are relatively unaffected. Many people have an outgoing personality, a happy disposition, an openness to engaging with other people, increased empathy and decreased aggression. Medical issues with teeth, heart problems (especially supravalvular aortic stenosis), and periods of hypercalcemia, high blood calcium are common. Williams syndrome is caused by a genetic abnormality, specifically a Deletion (genetics), deletion of about 27 genes from the long arm of one of the two chromosome 7s. Typically, this occurs as a random event during the formation of the egg or sperm from which a person develops. In a small number of cases, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |