|
Radiant Heater
Radiant heating and cooling is a category of HVAC technologies that exchange heat by both convection and radiation with the environments they are designed to heat or cool. There are many subcategories of radiant heating and cooling, including: "radiant ceiling panels",ISO. (2012). ''ISO 11855:2012—Building environment design-Design, dimensioning, installation and control of embedded radiant heating and cooling systems''. International Organization for Standardization. "embedded surface systems", "thermally active building systems", and infrared heaters. According to some definitions, a technology is only included in this category if radiation comprises more than 50% of its heat exchange with the environment; therefore technologies such as radiators and chilled beams (which may also involve radiation heat transfer) are usually not considered radiant heating or cooling. Within this category, it is practical to distinguish between high temperature radiant heating (devices with em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
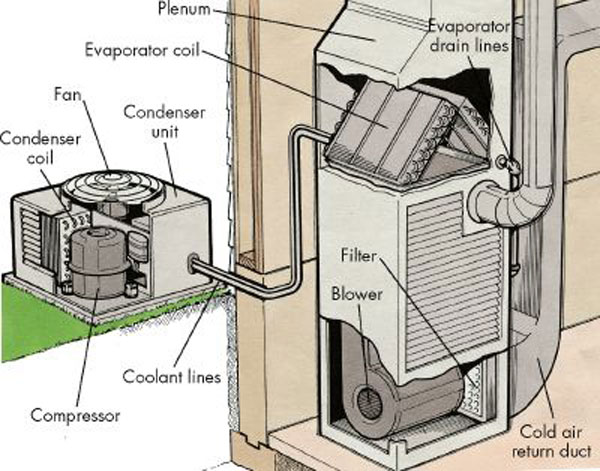
Heating, Ventilation, And Air Conditioning
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC ) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC system design is a subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer. "Refrigeration" is sometimes added to the field's abbreviation as HVAC&R or HVACR, or "ventilation" is dropped, as in HACR (as in the designation of HACR-rated circuit breakers). HVAC is an important part of residential structures such as single family homes, apartment buildings, hotels, and senior living facilities; medium to large industrial and office buildings such as skyscrapers and hospitals; vehicles such as cars, trains, airplanes, ships and submarines; and in marine environments, where safe and Sick building syndrome, healthy building conditions are regulated with respect to temperature and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IH - Frico Halogeninfravärmare (värmestrålare)
IH may refer to: In science and technology In medicine * Immune-histochemistry * intrauterine hypoxia * Hepatitis A (infectious hepatitis) * Idiopathic hypersomnia * Intracranial hypertension Other uses in science and technology * Hydrogen iodide * Induction heating :* Induction heater * Industrial hygiene, the control and prevention of hazards in a work environment * Ih, full icosahedral symmetry Other uses * ih, see List of Latin-script digraphs#I * Információs Hivatal, a Hungarian intelligence office * International House World Organisation * International Harvester, a manufacturer of agricultural machinery, construction equipment, trucks, and other products * IH, notation for intersection homology groups * Interstate Highway See also * HI (other) HI or Hi may refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''Hello Internet'', a podcast hosted by CGP Grey and Brady Haran * Hi (magazine), ''Hi'' (magazine), teen-lifestyle publication * Hi (Ofra Haza song), "Hi" (Ofra Haz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patio Heater
A patio heater, also called a mushroom heater or umbrella heater, is a radiant heating appliance for generating thermal radiation for outdoor use. Types of heater A burner on top of a pole, it burns natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), propane or butane, and directs the flames against a perforated metal screen. Heat is radiated from the surface of the screen in a circular pattern around the appliance. A reflector a top the burner reflects heat that would be otherwise lost upwards. This is because the reflecting hood is usually silvered which makes it a poor absorber of heat but excellent at reflecting infrared radiation back. This reduces the amount of heat lost by conduction as silvered surfaces will not absorb infrared light. The chimenea is an alternative to the patio heater for home use, which burns wood instead of gas. Some newer types of patio heaters are Electric heating#Radiative heaters, electrically powered radiative heaters that emit infrared energy onto nearby s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is the force exerted by a fluid opposing the weight of a partially or fully immersed object (which may be also be a parcel of fluid). In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus, the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. The pressure difference results in a net upward force on the object. The magnitude of the force is proportional to the pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the submerged volume of the object, i.e. the Displacement (fluid), displaced fluid. For this reason, an object with average density greater than the surrounding fluid tends to sink because its weight is greater than the weight of the fluid it displaces. If the objec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Source Heat Pump
An air source heat pump (ASHP) is a heat pump that can absorb heat from air outside a building and release it inside; it uses the same vapor-compression refrigeration process and much the same equipment as an air conditioner, but in the opposite direction. ASHPs are the most common type of heat pump and, usually being smaller, tend to be used to heat individual houses or flats rather than blocks, districts or industrial processes. ''Air-to-air'' heat pumps provide hot or cold air directly to rooms, but do not usually provide hot water. ''Air-to-water'' heat pumps use radiators or underfloor heating to heat a whole house and are often also used to provide domestic hot water. An ASHP can typically gain 4 kWh thermal energy from 1 kWh electric energy. They are optimized for flow temperatures between , suitable for buildings with heat emitters sized for low flow temperatures. With losses in efficiency, an ASHP can even provide full central heating with a flow tempera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Transfer
Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the generation, use, conversion, and exchange of thermal energy (heat) between physical systems. Heat transfer is classified into various mechanisms, such as thermal conduction, Convection (heat transfer), thermal convection, thermal radiation, and transfer of energy by phase changes. Engineers also consider the transfer of mass of differing chemical species (mass transfer in the form of advection), either cold or hot, to achieve heat transfer. While these mechanisms have distinct characteristics, they often occur simultaneously in the same system. Heat conduction, also called diffusion, is the direct microscopic exchanges of kinetic energy of particles (such as molecules) or quasiparticles (such as lattice waves) through the boundary between two systems. When an object is at a different temperature from another body or its surroundings, heat flows so that the body and the surroundings reach the same temperature, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chilled Beam
A chilled beam is a type of Thermal radiation, radiation/convection HVAC system designed to heat and cool large buildings through the use of water. This method removes most of the zone sensible local heat gains and allows the flow rate of pre-conditioned air from the air handling unit to be reduced, lowering by 60% to 80% the ducted design airflow rate and the equipment capacity requirements. There are two types of chilled beams, a Passive Chilled Beam (PCB) and an Active Chilled Beam (ACB). They both consist of pipes of water (fin-and-tube) that pass through a heat exchanger contained in a case suspended from, or recessed in, the ceiling.Price, 2011, ''Engineer's HVAC Handbook'', p. 1067, ''2012 ASHRAE Handbook HVAC Systems and Equipment'', ASHRAE, 2012, p. 20.9, As the beam cools the air around it, the air becomes denser and falls to the floor. It is replaced by warmer air moving up from below, causing a constant passive air movement called convection, to cool the room.Hamilton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydronic
Hydronics () is the use of liquid water or gaseous water (steam) or a water solution (usually glycol with water) as a heat-transfer medium in heating and cooling systems. The name differentiates such systems from oil and refrigerant systems. Historically, in large-scale commercial buildings such as high-rise and campus facilities, a hydronic system may include both a chilled and a heated water loop, to provide for both heating and air conditioning. Chillers and cooling towers are used either separately or together as means to provide water cooling, while boilers heat water. A recent innovation is the chiller boiler system, which provides an efficient form of HVAC for homes and smaller commercial spaces. District heating Many larger cities have a district heating system that provides, through underground piping, publicly available high temperature hot water and chilled water. A building in the service district may be connected to these on payment of a service fee. Types o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwell's equations. Common phenomena are related to electricity, including lightning, static electricity, electric heating, electric discharges and many others. The presence of either a positive or negative electric charge produces an electric field. The motion of electric charges is an electric current and produces a magnetic field. In most applications, Coulomb's law determines the force acting on an electric charge. Electric potential is the Work (physics), work done to move an electric charge from one point to another within an electric field, typically measured in volts. Electricity plays a central role in many modern technologies, serving in electric power where electric current is used to energise equipment, and in electronics dealing w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underfloor Heating
Underfloor heating and cooling is a form of Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning, central heating and cooling that achieves indoor climate control for thermal comfort using hydronics, hydronic or electrical heating elements embedded in a floor. Heating is achieved by Conduction (heat), conduction, radiation and convection. Use of underfloor heating dates back to the Neoglacial and Neolithic periods. History Underfloor heating has a long history back into the Neoglacial and Neolithic periods. Archeological digs in Asia and the Aleutian islands of Alaska reveal how the inhabitants drafted smoke from fires through stone covered trenches which were excavated in the floors of their subterranea (geography), subterranean dwellings. The hot smoke heated the floor stones and the heat then radiated into the living spaces. These early forms have evolved into modern systems using fluid filled pipes or electrical cables and mats. Below is a chronological overview of under floor heating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making up a substance. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), with the third being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convector Heater
A convection heater, also known as a convector heater, is a type of heater that utilizes convection currents to heat and circulate air. These currents move through the appliance and across its heating element, using thermal conduction to warm the air and decrease its density relative to colder air, causing it to rise. History Ancient heating systems, including hearths, furnaces, and stoves, operated primarily through convection. Fixed central hearths, which were first excavated and retrieved in Greece, date back to 2500BC, whereas crude fireplaces were used as early as the 800sAD and in the 13th century, when castles in Europe were built with fireplaces with a crude form of chimney. Developments in convection heating technology included the publication of the very first manual on fireplace design called ''Mechanique du Feu'' in 1713, the creation of stoves with thermostatic control in 1849, and the rise of numerous cast iron stove manufacturers during the American Civil War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |