|
Radequinil
Radequinil ( INN; AC-3933) is a cognitive enhancer which acts as a partial inverse agonist of the benzodiazepine site of the GABAA receptor. It was under development by Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and made it to phase II Phase II, Phase 2 or Phase Two may refer to: Media * Marvel Cinematic Universe: Phase Two, six American superhero films from 2013–2015 * ''Star Trek: Phase II'', an unrealized television series based on the characters of Gene Roddenberry's ''S ... clinical trials but development seems to have been halted and it was never marketed. See also * GABAA receptor negative allosteric modulator * GABAA receptor § Ligands References Nootropics Oxadiazoles Lactams GABAA receptor negative allosteric modulators Phenol ethers Naphthyridines {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GABAA Receptor Negative Allosteric Modulator
A GABAA receptor negative allosteric modulator is a negative allosteric modulator (NAM), or inhibitor, of the GABAA receptor, a ligand-gated ion channel of the major inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). They are closely related and similar to GABAA receptor antagonists. The effects of GABAA receptor NAMs are functionally the opposite of those of GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) like the benzodiazepines, barbiturates, and ethanol (alcohol). Non-selective GABAA receptor NAMs can produce a variety of effects including convulsions, neurotoxicity, and anxiety, among others. Flumazenil is a competitive antagonist of the benzodiazepine site of the GABAA receptor and hence is a GABAA receptor NAM of sorts. It is used to reverse benzodiazepine overdose. The drug can provoke seizures in those with benzodiazepine dependence. Selective NAMs (or "inverse agonists") of α5 subunit-containing GABAA receptors, such as basmisanil and α5IA, do no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Enhancer
Nootropics ( , or ) (colloquial: smart drugs and cognitive enhancers, similar to adaptogens) are a wide range of natural or synthetic supplements or drugs and other substances that are claimed to improve cognitive function or to promote relaxation, particularly boosting mood, executive functions, attention, memory, creativity, or motivation in healthy individuals. The use of cognition-enhancing supplements by healthy individuals in the absence of a medical indication spans numerous controversial issues, including the ethics and fairness of their use, concerns over adverse effects, and the diversion of prescription drugs for non-medical uses. Nonetheless, the international sales of cognitive- or mood-enhancing supplements have continued to grow over time and in 2012 reached 0.69 billion. With sales supported by global health trends, the market is expected to reach US$33.85 billion by the year 2030, at a CAGR of 14.8%. While most nootropics are not regulated, there are othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverse Agonist
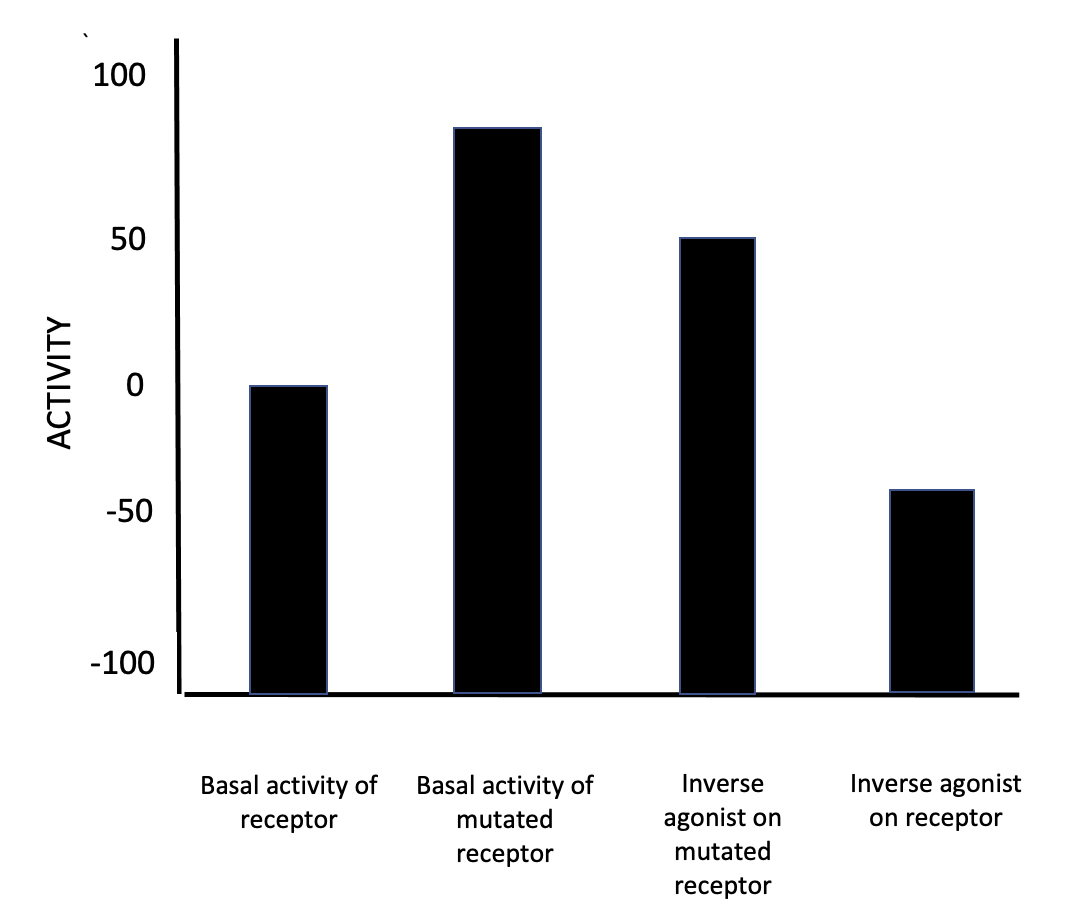
In pharmacology, an inverse agonist is a drug that binds to the same receptor as an agonist but induces a pharmacological response opposite to that of the agonist. A neutral antagonist has no activity in the absence of an agonist or inverse agonist but can block the activity of either. Inverse agonists have opposite actions to those of agonists but the effects of both of these can be blocked by antagonists. A prerequisite for an inverse agonist response is that the receptor must have a constitutive (also known as intrinsic or basal) level of activity in the absence of any ligand. An agonist increases the activity of a receptor above its basal level, whereas an inverse agonist decreases the activity below the basal level. The efficacy of a full agonist is by definition 100%, a neutral antagonist has 0% efficacy, and an inverse agonist has < 0% (i.e., negative) efficacy. Examples Receptors for which inverse agonists have been identified include the[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzodiazepine Site
The GABAA receptor (GABAAR) is an ionotropic receptor and ligand-gated ion channel. Its endogenous ligand is γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Upon opening, the GABAA receptor on the postsynaptic cell is selectively permeable to chloride ions (Cl−) and, to a lesser extent, bicarbonate ions (HCO3−). Depending on the membrane potential and the ionic concentration difference, this can result in ionic fluxes across the pore. If the membrane potential is higher than the equilibrium potential (also known as the reversal potential) for chloride ions, when the receptor is activated Cl− will flow into the cell. This causes an inhibitory effect on neurotransmission by diminishing the chance of a successful action potential occurring at the postsynaptic cell. The reversal potential of the GABAA-mediated inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) in normal solution is −70 mV, contrasting the GABAB IPSP (-100 mV). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GABAA Receptor
The GABAA receptor (GABAAR) is an ionotropic receptor and ligand-gated ion channel. Its endogenous ligand is γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Upon opening, the GABAA receptor on the postsynaptic cell is selectively permeable to chloride ions (Cl−) and, to a lesser extent, bicarbonate ions (HCO3−). Depending on the membrane potential and the ionic concentration difference, this can result in ionic fluxes across the pore. If the membrane potential is higher than the equilibrium potential (also known as the reversal potential) for chloride ions, when the receptor is activated Cl− will flow into the cell. This causes an inhibitory effect on neurotransmission by diminishing the chance of a successful action potential occurring at the postsynaptic cell. The reversal potential of the GABAA-mediated inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) in normal solution is −70 mV, contrasting the GABAB IPSP (-100 mV). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma
is a pharmaceutical company based in Japan. Its headquarters are in Chuo-ku, Osaka. The original Dainippon Pharmaceuticals (Dainippon Seiyaku) was established in 1885 by Nagayo Sensai, a graduate of Tekijuku – the first private medical school in Japan established by Ogata Kōan. It was set up as a wholly privately-owned company funded by individuals from Tokyo and Osaka, with the land and buildings lent by the government. Technical expertise for the enterprise was provided by Shibata Shokei and Nagai Nagayoshi. The company started its operation in 1885 with equipment imported from Germany. The main products were tincture and other similar drugs listed in the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. Among them was ephedrine, an anti-asthma drug invented by Nagai. In 1893, however, Nagai left the company and the business started to post operating losses. In 1898 it was acquired by Osaka Seiyaku (Osaka Pharmaceutical). Another origin of the company began as Sumitomo Pharmaceuticals, incorporated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in short-term memory, remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include primary progressive aphasia, problems with language, Orientation (mental), disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and challenging behaviour, behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the typical life expectancy following diagnosis is three to nine years. The cause of Alzheimer's disease is poorly understood. There are many environmental and genetic risk factors associated with its development. The strongest genetic risk factor is from an alle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phases Of Clinical Research
The phases of clinical research are the stages in which scientists conduct experiments with a health intervention to obtain sufficient evidence for a process considered effective as a medical treatment. For drug development, the clinical phases start with testing for safety in a few human subjects, then expand to many study participants (potentially tens of thousands) to determine if the treatment is effective. Clinical research is conducted on drug candidates, vaccine candidates, new medical devices, and new diagnostic assays. Summary Clinical trials testing potential medical products are commonly classified into four phases. The drug development process will normally proceed through all four phases over many years. If the drug successfully passes through Phases I, II, and III, it will usually be approved by the national regulatory authority for use in the general population. Phase IV trials are 'post-marketing' or 'surveillance' studies conducted to monitor safety over sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinical Trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human subject research, human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, pharmaceutical drug, drugs, medical nutrition therapy, dietary choices, dietary supplements, and medical devices) and known interventions that warrant further study and comparison. Clinical trials generate data on dosage, safety and efficacy. They are conducted only after they have received institutional review board, health authority/ethics committee approval in the country where approval of the therapy is sought. These authorities are responsible for vetting the risk/benefit ratio of the trial—their approval does not mean the therapy is 'safe' or effective, only that the trial may be conducted. Depending on product type and development stage, investigators initially enroll volunteers or patients into small Pilot experiment, pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nootropics
Nootropics ( , or ) (colloquial: smart drugs and cognitive enhancers, similar to adaptogens) are a wide range of natural or synthetic supplements or drugs and other substances that are claimed to improve cognitive function or to promote relaxation, particularly boosting mood, executive functions, attention, memory, creativity, or motivation in healthy individuals. The use of cognition-enhancing supplements by healthy individuals in the absence of a medical indication spans numerous controversial issues, including the ethics and fairness of their use, concerns over adverse effects, and the diversion of prescription drugs for non-medical uses. Nonetheless, the international sales of cognitive- or mood-enhancing supplements have continued to grow over time and in 2012 reached 0.69 billion. With sales supported by global health trends, the market is expected to reach US$33.85 billion by the year 2030, at a CAGR of 14.8%. While most nootropics are not regulated, there are oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxadiazoles
Oxadiazoles are a class of heterocyclic aromatic chemical compound of the azole family; with the molecular formula C2H2N2O. There are four isomers of oxadiazole: File:1,2,3-oxadiazole.svg, 1,2,3-oxadiazole File:1,2,4-oxadiazole.svg, 1,2,4-oxadiazole File:1,2,5-oxadiazole.svg, 1,2,5-oxadiazole(furazan) File:1,3,4-oxadiazole.svg, 1,3,4-oxadiazole 1,2,4-Oxadiazole, 1,2,5-oxadiazole, and 1,3,4-oxadiazole are all known and appear in a variety of pharmaceutical drugs including raltegravir, butalamine, fasiplon, oxolamine, and pleconaril. The 1,2,3-isomer is unstable and ring-opens to form the diazoketone tautomer; however, it does exist within the unusual sydnone motif. In 2018, a compound called bis(1,2,4-oxadiazole)bis(methylene) dinitrate which might have a 1.5 times the power of TNT was developed at the United States Army Research Laboratory (ARL) working with the Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos National Laboratory (often shortened as Los Alamos and LA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)