|
Queue (abstract Data Type)
In computer science, a queue is a collection of entities that are maintained in a sequence and can be modified by the addition of entities at one end of the sequence and the removal of entities from the other end of the sequence. By convention, the end of the sequence at which elements are added is called the back, tail, or rear of the queue, and the end at which elements are removed is called the head or front of the queue, analogously to the words used when people line up to wait for goods or services. The operation of adding an element to the rear of the queue is known as ''enqueue'', and the operation of removing an element from the front is known as ''dequeue''. Other operations may also be allowed, often including a '' peek'' or ''front'' operation that returns the value of the next element to be dequeued without dequeuing it. The operations of a queue make it a first-in-first-out (FIFO) data structure. In a FIFO data structure, the first element added to the queue will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FIFO (computing And Electronics)
Representation of a FIFO queue In computing and in systems theory, first in, first out (the first in is the first out), acronymized as FIFO, is a method for organizing the manipulation of a data structure (often, specifically a data buffer) where the oldest (first) entry, or "head" of the queue, is processed first. Such processing is analogous to servicing people in a queue area on a first-come, first-served (FCFS) basis, i.e. in the same sequence in which they arrive at the queue's tail. FCFS is also the jargon term for the FIFO operating system scheduling algorithm, which gives every process central processing unit (CPU) time in the order in which it is demanded. FIFO's opposite is LIFO, last-in-first-out, where the youngest entry or "top of the stack" is processed first. A priority queue is neither FIFO or LIFO but may adopt similar behaviour temporarily or by default. Queueing theory encompasses these methods for processing data structures, as well as interactions be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big O Notation
Big ''O'' notation is a mathematical notation that describes the asymptotic analysis, limiting behavior of a function (mathematics), function when the Argument of a function, argument tends towards a particular value or infinity. Big O is a member of a #Related asymptotic notations, family of notations invented by German mathematicians Paul Gustav Heinrich Bachmann, Paul Bachmann, Edmund Landau, and others, collectively called Bachmann–Landau notation or asymptotic notation. The letter O was chosen by Bachmann to stand for '':wikt:Ordnung#German, Ordnung'', meaning the order of approximation. In computer science, big O notation is used to Computational complexity theory, classify algorithms according to how their run time or space requirements grow as the input size grows. In analytic number theory, big O notation is often used to express a bound on the difference between an arithmetic function, arithmetical function and a better understood approximation; one well-known exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persistent Data Structure
In computing, a persistent data structure or not ephemeral data structure is a data structure that always preserves the previous version of itself when it is modified. Such data structures are effectively immutable, as their operations do not (visibly) update the structure in-place, but instead always yield a new updated structure. The term was introduced in Driscoll, Sarnak, Sleator, and Tarjan's 1986 article. A data structure is partially persistent if all versions can be accessed but only the newest version can be modified. The data structure is fully persistent if every version can be both accessed and modified. If there is also a meld or merge operation that can create a new version from two previous versions, the data structure is called confluently persistent. Structures that are not persistent are called ''ephemeral''. These types of data structures are particularly common in logical and functional programming, as languages in those paradigms discourage (or fully forbid) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amortized Analysis
In computer science, amortized analysis is a method for analyzing a given algorithm's complexity, or how much of a resource, especially time or memory, it takes to execute. The motivation for amortized analysis is that looking at the worst-case run time can be too pessimistic. Instead, amortized analysis averages the running times of operations in a sequence over that sequence. As a conclusion: "Amortized analysis is a useful tool that complements other techniques such as worst-case and average-case analysis." For a given operation of an algorithm, certain situations (e.g., input parametrizations or data structure contents) may imply a significant cost in resources, whereas other situations may not be as costly. The amortized analysis considers both the costly and less costly operations together over the whole sequence of operations. This may include accounting for different types of input, length of the input, and other factors that affect its performance. History Amortize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purely Functional Data Structure
In computer science, a purely functional data structure is a data structure that can be directly implemented in a purely functional language. The main difference between an arbitrary data structure and a purely functional one is that the latter is (strongly) immutable. This restriction ensures the data structure possesses the advantages of immutable objects: (full) persistency, quick copy of objects, and thread safety. Efficient purely functional data structures may require the use of lazy evaluation and memoization. Definition Persistent data structures have the property of keeping previous versions of themselves unmodified. On the other hand, non-persistent structures such as arrays admit a destructive update, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JavaScript
JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language and core technology of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. Ninety-nine percent of websites use JavaScript on the client side for webpage behavior. Web browsers have a dedicated JavaScript engine that executes the client code. These engines are also utilized in some servers and a variety of apps. The most popular runtime system for non-browser usage is Node.js. JavaScript is a high-level, often just-in-time–compiled language that conforms to the ECMAScript standard. It has dynamic typing, prototype-based object-orientation, and first-class functions. It is multi-paradigm, supporting event-driven, functional, and imperative programming styles. It has application programming interfaces (APIs) for working with text, dates, regular expressions, standard data structures, and the Document Object Model (DOM). The ECMAScript standard does not include any input/output (I/O), such as netwo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
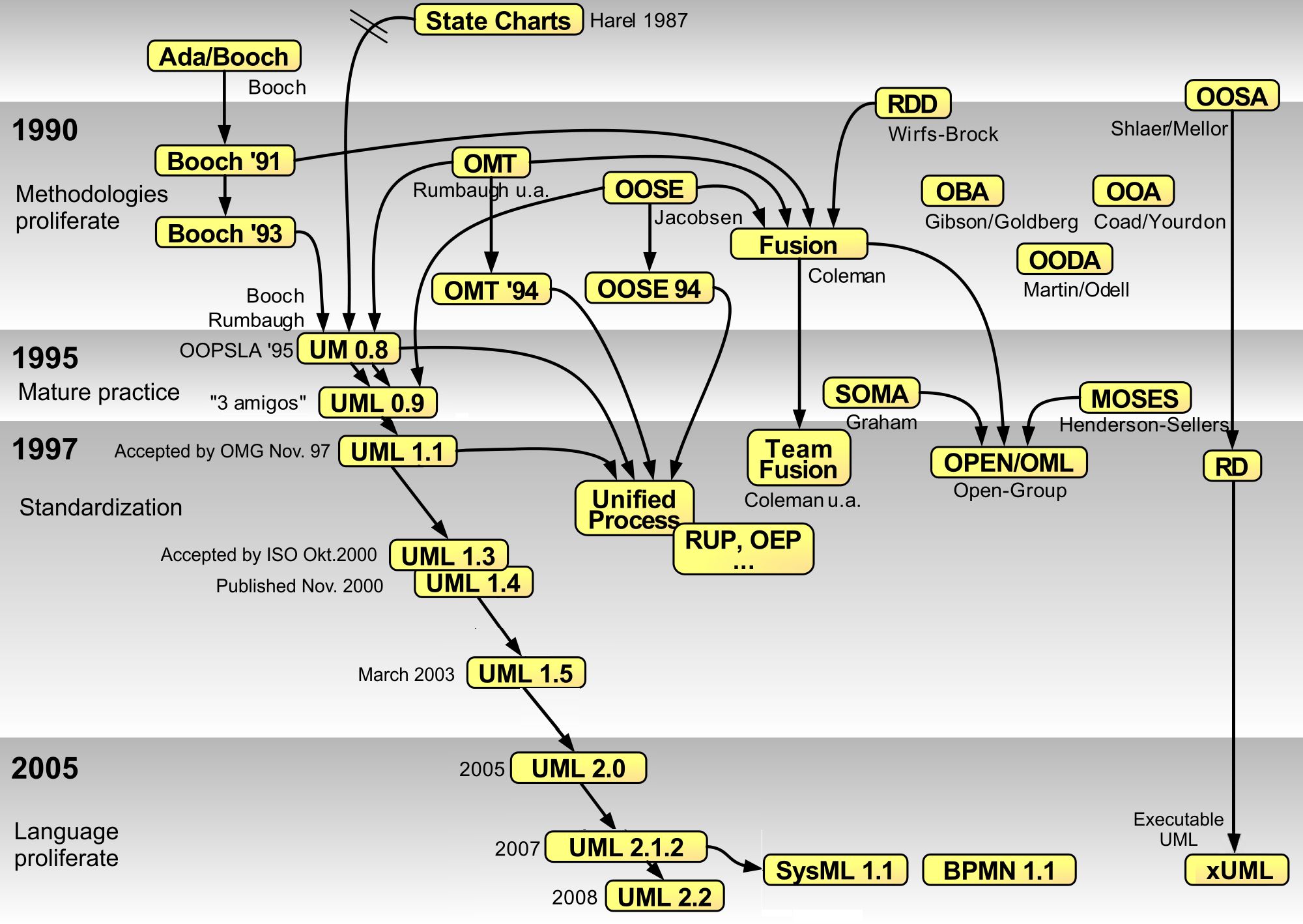
UML Queue Class
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose visual modeling language that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system. UML provides a standard notation for many types of diagrams which can be roughly divided into three main groups: behavior diagrams, interaction diagrams, and structure diagrams. The creation of UML was originally motivated by the desire to standardize the disparate notational systems and approaches to software design. It was developed at Rational Software in 1994–1995, with further development led by them through 1996. In 1997, UML was adopted as a standard by the Object Management Group (OMG) and has been managed by this organization ever since. In 2005, UML was also published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as the ISO/IEC 19501 standard. Since then the standard has been periodically revised to cover the latest revision of UML. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gearman
Gearman is an open-source application framework designed to distribute appropriate computer tasks to multiple computers, so large tasks can be done more quickly. In some cases, load balancing rather than raw speed may be the main goal; a Web server, for instance, could use Gearman to send tasks for which it is not optimized to another computer (which may be running on a different architecture, using another operating system, or loaded with a computer language better suited to a particular operation). It was originally written in Perl by Brad Fitzpatrick. Brian Aker and Eric Day rewrote the framework in C. How Gearman Works Gearman assigns each involved computer a role as client, job server, or worker. A worker machine can be assigned multiple instances of the worker role, which allows more powerful computers to complete more portions of a given task. Tasks originate on a client, are transmitted from the client to the job server, and performed on one or more workers. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Template Library
The Standard Template Library (STL) is a software library originally designed by Alexander Stepanov for the C++ programming language that influenced many parts of the C++ Standard Library. It provides four components called ''algorithms'', ''containers'', '' functors'', and ''iterators''. The STL provides a set of common classes for C++, such as containers and associative arrays, that can be used with any built-in type or user-defined type that supports some elementary operations (such as copying and assignment). STL algorithms are independent of containers, which significantly reduces the complexity of the library. The STL achieves its results through the use of templates. This approach provides compile-time polymorphism that is often more efficient than traditional run-time polymorphism. Modern C++ compilers are tuned to minimize abstraction penalties arising from heavy use of the STL. The STL was created as the first library of generic algorithms and data structures f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruby (programming Language)
Ruby is a general-purpose programming language. It was designed with an emphasis on programming productivity and simplicity. In Ruby, everything is an object (computer science), object, including primitive data types. It was developed in the mid-1990s by Yukihiro Matsumoto, Yukihiro "Matz" Matsumoto in Japan. Ruby is interpreted language, interpreted, high-level programming language, high-level, and Dynamic typing, dynamically typed; its interpreter uses garbage collection (computer science), garbage collection and just-in-time compilation. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including procedural programming, procedural, object-oriented programming, object-oriented, and functional programming. According to the creator, Ruby was influenced by Perl, Smalltalk, Eiffel (programming language), Eiffel, Ada (programming language), Ada, BASIC, and Lisp (programming language), Lisp. History Early concept According to Matsumoto, Ruby was conceived in 1993. In a 1999 post to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perl
Perl is a high-level, general-purpose, interpreted, dynamic programming language. Though Perl is not officially an acronym, there are various backronyms in use, including "Practical Extraction and Reporting Language". Perl was developed by Larry Wall in 1987 as a general-purpose Unix scripting language to make report processing easier. Since then, it has undergone many changes and revisions. Perl originally was not capitalized and the name was changed to being capitalized by the time Perl 4 was released. The latest release is Perl 5, first released in 1994. From 2000 to October 2019 a sixth version of Perl was in development; the sixth version's name was changed to Raku. Both languages continue to be developed independently by different development teams which liberally borrow ideas from each other. Perl borrows features from other programming languages including C, sh, AWK, and sed. It provides text processing facilities without the arbitrary data-length limits of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |