|
Queen (insect)
The gyne (, from Greek γυνή, "woman") is the primary reproductive female Caste (biology), caste of social insects (especially ants, wasps, and bees of order Hymenoptera, as well as termites). Gynes are those destined to become queens, whereas female workers are typically barren and cannot become queens. Having a queen is what makes a "queenright" hive, nest, or colony of eusociality, eusocial insects. A colony with multiple queens is said to be a polygyne form, whereas one with only one is a monogyne form. The ancient Greek origin of ''gyne'' meant a woman who had given birth to at least one child. In species lacking morphological castes (i.e., where "workers" may not be sterile), the term "gyne" is usually reserved for those females whose entire life is spent as a reproductive or potential reproductive, as opposed to those who start life as a worker and subsequently attain reproductive status (often called a "replacement queen" or a "laying worker"). These can be seen in ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apis Mellifera Scutellata 1355021
Apis or APIS may refer to: * Apis (deity), an ancient Egyptian god * Apis (Greek mythology), several different figures in Greek mythology * Apis (city), an ancient seaport town on the northern coast of Africa * ''Apis'' (genus), the genus of the honey bee *Apis, a fictional character from One Piece anime-only Warship Island arc * Apis (constellation), an obsolete name for Musca * Dragutin Dimitrijević (1876–1917), known as "Apis", Serbian colonel and coup organiser, leader of the Black Hand group * Albastar Apis, a Slovenian motor glider * Wezel Apis 2, a German motor glider * Advance Passenger Information System, an electronic data interchange system *Aircraft Positioning and Information System, an airport stand guidance system See also * API (other) for "APIs" **Application programming interface An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a type of software Interface (computing), interface, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
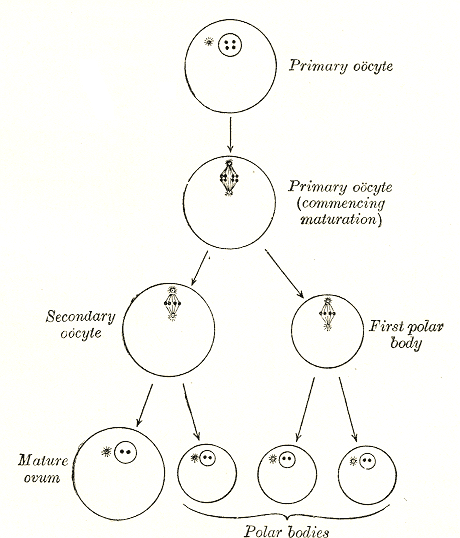
Oocyte
An oocyte (, oöcyte, or ovocyte) is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female germ cells produce a primordial germ cell (PGC), which then undergoes mitosis, forming oogonia. During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation. Formation The formation of an oocyte is called oocytogenesis, which is a part of oogenesis. Oogenesis results in the formation of both primary oocytes during fetal period, and of secondary oocytes after it as part of ovulation. Characteristics Cytoplasm Oocytes are rich in cytoplasm, which contains yolk granules to nourish the cell early in development. Nucleus During the primary oocyte stage of oogenesis, the nucleus is called a germinal vesicle. The only normal human type of secondary oocyte has the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insect Ecology
Insect ecology is the interaction of insects, individually or as a community, with the surrounding Natural environment, environment or ecosystem. This interaction is mostly mediated by the secretion and detection of chemicals (semiochemical) in the environment by insects. Semiochemicals are secreted by the organisms (including insects) in the environment and they are detected by other organism such as insects. Semiochemicals used by organisms, including (insects) to interact with other organism either of the same species or different species can generally grouped into four. These are pheromone, synomones, allomone and kairomone. Pheromones are semiochemicals that facilitates interaction between organisms of same species. Synomones benefit both the producer and receiver, allomone is advantageous to only the producer whiles kairomones is beneficial to the receiver. Insect interact with other species within their community and these interaction include Mutualism (biology), mutua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is an academic publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University. It is a member of the Association of University Presses. Its director since 2017 is George Andreou. The press maintains offices in Cambridge, Massachusetts, near Harvard Square, and in London, England. The press co-founded the distributor TriLiteral LLC with MIT Press and Yale University Press. TriLiteral was sold to LSC Communications in 2018. Notable authors published by HUP include Eudora Welty, Walter Benjamin, E. O. Wilson, John Rawls, Emily Dickinson, Stephen Jay Gould, Helen Vendler, Carol Gilligan, Amartya Sen, David Blight, Martha Nussbaum, and Thomas Piketty. The Display Room in Harvard Square, dedicated to selling HUP publications, closed on June 17, 2009. Related publishers, imprints, and series HUP owns the Belknap Press imprint (trade name), imprint, which it inaugurated in May 1954 with the publication of the ''Harvard Guide to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elsevier
Elsevier ( ) is a Dutch academic publishing company specializing in scientific, technical, and medical content. Its products include journals such as ''The Lancet'', ''Cell (journal), Cell'', the ScienceDirect collection of electronic journals, ''Trends (journals), Trends'', the ''Current Opinion (Elsevier), Current Opinion'' series, the online citation database Scopus, the SciVal tool for measuring research performance, the ClinicalKey search engine for clinicians, and the ClinicalPath evidence-based cancer care service. Elsevier's products and services include digital tools for Data management platform, data management, instruction, research analytics, and assessment. Elsevier is part of the RELX Group, known until 2015 as Reed Elsevier, a publicly traded company. According to RELX reports, in 2022 Elsevier published more than 600,000 articles annually in over 2,800 journals. As of 2018, its archives contained over 17 million documents and 40,000 Ebook, e-books, with over one b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merriam-Webster
Merriam-Webster, Incorporated is an list of companies of the United States by state, American company that publishes reference work, reference books and is mostly known for Webster's Dictionary, its dictionaries. It is the oldest dictionary publisher in the United States. In 1831, George Merriam, George and Charles Merriam founded the company as G & C Merriam Co. in Springfield, Massachusetts. In 1843, after Noah Webster died, the company bought the rights to ''Webster's Dictionary#Noah Webster's American Dictionary of the English Language, An American Dictionary of the English Language'' from Webster's estate. All Merriam-Webster dictionaries trace their lineage to this source. In 1964, Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., acquired Merriam-Webster, Inc., as a subsidiary. The company adopted its current name, Merriam-Webster, Incorporated, in 1982. History 19th century In 1806, Webster published his first dictionary, s:A Compendious Dictionary of the English Language, ''A Compen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
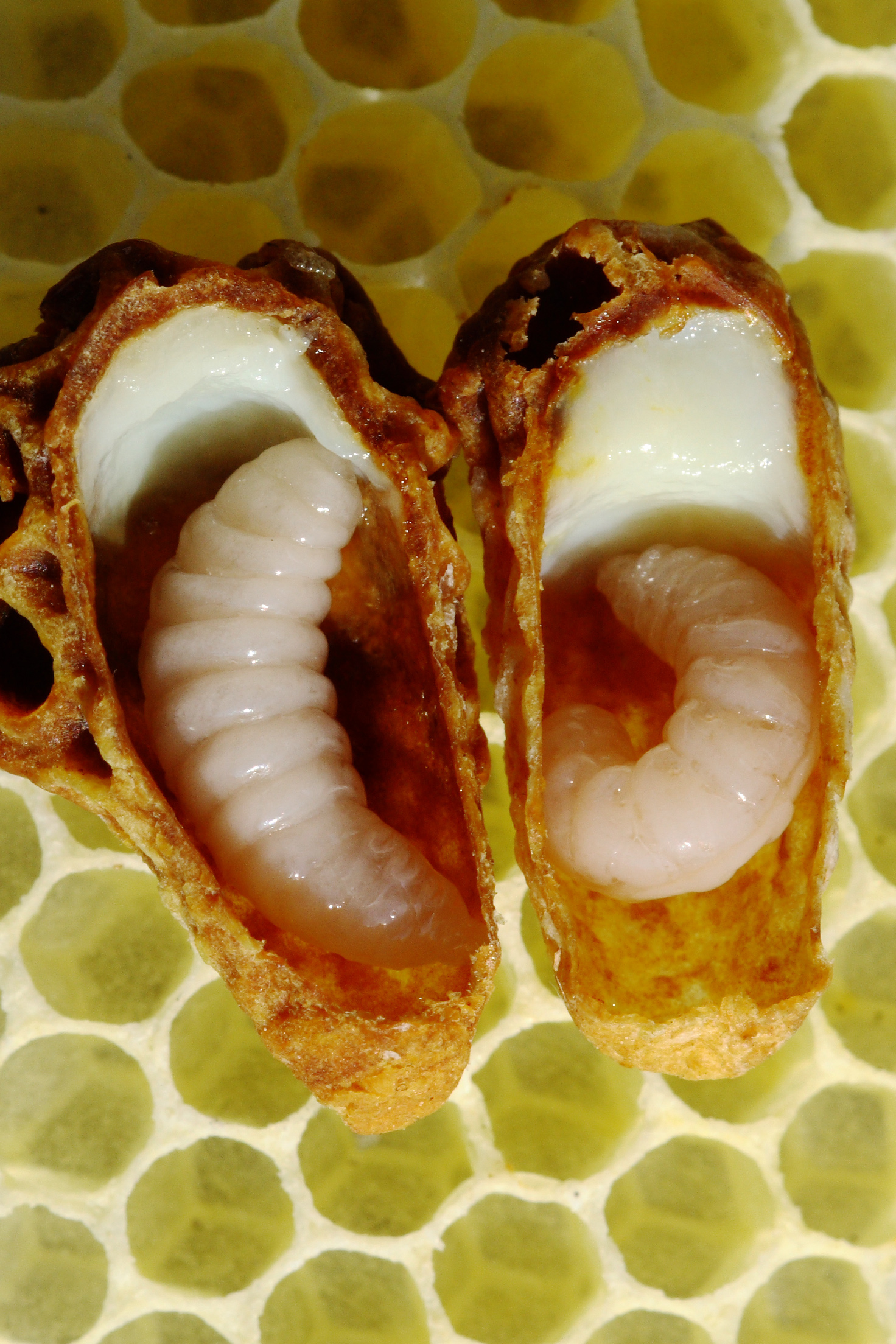
Queen Bee
A queen bee is typically an adult, mated female ( gyne) that lives in a colony or hive of honey bees. With fully developed reproductive organs, the queen is usually the mother of most, if not all, of the bees in the beehive. Queens are developed from larvae selected by worker bees and specially fed in order to become sexually mature. There is normally only one adult, mated queen in a hive, in which case the bees will usually follow and fiercely protect her. The term "queen bee" can be more generally applied to any dominant reproductive female in a colony of a eusocial bee species other than honey bees. However, as in the Brazilian stingless bee ('' Schwarziana quadripunctata''), a single nest may have multiple queens or even dwarf queens, ready to replace a dominant queen in case of a sudden death. Development During the warm parts of the year, female "worker" bees leave the hive every day to collect nectar and pollen. While male bees serve no architectural or pollinating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Ant
A queen ant (also known as a gyne) is an adult, reproducing female ant in an ant colony; she is usually the mother of all the other ants in that colony. Some female ants, such as the '' Cataglyphis'', do not need to mate to produce offspring, reproducing through asexual parthenogenesis or cloning, and all of those offspring will be female. Others, like those in the genus ''Crematogaster'', mate in a nuptial flight. Queen offspring ants among most species develop from larvae specially fed in order to become sexually mature. Depending on the species, there can be either a single mother queen, or potentially hundreds of fertile queens. Not every colony of ants has a queen. Some colonies have multiple queens. Queen ants are the only members of a colony to lay eggs. After mating, they can produce thousands, sometimes millions, of eggs during their lifetime. A queen of '' Lasius niger'' was held in captivity by German entomologist Hermann Appel for 28 years; also a ''Pogonomyrmex ow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eusociality
Eusociality ( Greek 'good' and social) is the highest level of organization of sociality. It is defined by the following characteristics: cooperative brood care (including care of offspring from other individuals), overlapping generations within a colony of adults, and a division of labor into reproductive and non-reproductive groups. The division of labor creates specialized behavioral groups within an animal society, sometimes called castes. Eusociality is distinguished from all other social systems because individuals of at least one caste usually lose the ability to perform behaviors characteristic of individuals in another caste. Eusocial colonies can be viewed as superorganisms. Eusociality has evolved among the insects, crustaceans, trematoda and mammals. It is most widespread in the Hymenoptera (ants, bees, and wasps) and in Isoptera (termites). A colony has caste differences: queens and reproductive males take the roles of the sole reproducers, while soldiers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ropalidia Plebeiana
''Ropalidia plebeiana'' is a eusocial temperate paper wasp. It is unique, as it is the only temperate wasp in the typically tropical Ropalidia genus. ''R. plebeiana'' is widely distributed in eastern Australia, and recently have been found making huge nest aggregations, with thousands of nests on trunks of trees, in south-eastern New South Wales. Taxonomy and phylogeny ''R. plebeiana'' is in the ''Vespidae'' family along with thousands of other wasp species. The genus, '' Ropalidia'', is typically made up of wasps that live in tropical locations, but ''R. plebeiana'' is the exception. The genus, ''Ropalidia'' is classified as brown paper wasps. Although ''R. plebeiana'' does not yet have a place within the taxonomy of the ''Ropalidia'' family, it has been discovered to be closely related to ''R. proletaria''. Description and identification ''R. plebeiana'' is a white-faced, brown paper wasp. It is a medium-size paper wasp, with a reddish-brown-colored body. There are small, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoica Flavissima
''Apoica flavissima'' is a paper wasp found primarily in South America. The species is distinguishable by its light coloring, unique single comb nests, and nocturnal nature. A notable feature of this species is the size dimorphism between queens and workers. Unlike most Vespidae wasps, ''Apocia flavissima'' queens are smaller than their worker counterparts which results in unique intraspecies relationships. Taxonomy and phylogeny Originally, ''Apoica flavissima'' was thought to be a variety of '' Apoica pallens'' because of similar color and physical characteristics. It was not until 1972 that J. Van Der Vecht identified that three distinct species were mistakenly being categorized as one. Today, ''A. pallens'', ''A. flavissima'', and ''A. gelida'' are identified by differences in male genitalia. In addition, distinction can be made through slight color differences. While ''A. flavissima'' are entirely pale yellow, ''A. pallens'' are mostly yellow but have brown legs. Phylogeneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automictic Parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis (; from the Greek + ) is a natural form of asexual reproduction in which the embryo develops directly from an egg without need for fertilization. In animals, parthenogenesis means the development of an embryo from an unfertilized egg cell. In plants, parthenogenesis is a component process of apomixis. In algae, parthenogenesis can mean the development of an embryo from either an individual sperm or an individual egg. Parthenogenesis occurs naturally in some plants, algae, invertebrate animal species (including nematodes, some tardigrades, water fleas, some scorpions, aphids, some mites, some bees, some Phasmatodea, and parasitic wasps), and a few vertebrates, such as some fish, amphibians, and reptiles. This type of reproduction has been induced artificially in animal species that naturally reproduce through sex, including fish, amphibians, and mice. Normal egg cells form in the process of meiosis and are haploid, with half as many chromosomes as their mother' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |