|
Quadrant (astronomy)
A galactic quadrant, or quadrant of the Galaxy, is one of four circular sectors in the division of the Milky Way Galaxy. Quadrants in the galactic coordinate system In actual astronomical practice, the delineation of the galactic quadrants is based upon the galactic coordinate system, which places the Sun as the polar coordinates, pole of the mapping system. The Sun is used instead of the Galactic Center for practical reasons since all astronomical observations (by humans) to date have been based on Earth or within the Solar System. Delineation Quadrants are described using Ordinal number (linguistics), ordinals—for example, "1st galactic quadrant", "second galactic quadrant", or "third quadrant of the Galaxy".M. Lampton ''et al''An All-Sky Catalog of Faint Extreme Ultraviolet Sources''The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series''. 1997 Viewing from the north galactic pole with 0 degree (angle), degrees (°) as the ray (geometry), ray that runs starting from the Sun and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactic Longitude
The galactic coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system in spherical coordinates, with the Sun as its center, the primary direction aligned with the approximate center of the Milky Way Galaxy, and the fundamental plane (spherical coordinates), fundamental plane parallel to an approximation of the galactic plane but offset to its north. It uses the Right-hand rule, right-handed convention, meaning that coordinates are positive toward the north and toward the east in the fundamental plane (spherical coordinates), fundamental plane. Spherical coordinates Galactic longitude Longitude (symbol ) measures the angle, angular distance of an object eastward along the galactic equator from the Galactic Center. Analogous to terrestrial longitude, galactic longitude is usually measured in degrees (°). Galactic latitude Latitude (symbol ) measures the angle of an object northward of the galactic equator (or midplane) as viewed from Earth. Analogous to terrestrial latitude, gala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactic Quadrants
Galactic is an American funk band from New Orleans, Louisiana. Origins and background Formed in 1994 as an octet (under the name Galactic Prophylactic) and including singer Chris Lane and guitarist Rob Gowen, the group was soon pared down to a sextet of: guitarist Jeff Raines, bassist Robert Mercurio, drummer Stanton Moore, Hammond organist Rich Vogel, Theryl DeClouet on vocals, and later adding saxophonist Ben Ellman. The group was started when Raines and Mercurio, childhood friends from affluent Chevy Chase, Maryland, moved to New Orleans together to attend college at Tulane and Loyola Universities, became enamored of the local funk scene, populated by such legendary acts as The Meters and Dirty Dozen Brass Band and inspired by local legends such as Professor Longhair. There they teamed with noted New Orleans drummer Stanton Moore, saxophonist/harmonica (now producer) Ben Ellman, Rich Vogel, and Theryl de Clouet. In 2004, the band parted ways with vocalist DeClouet, and cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
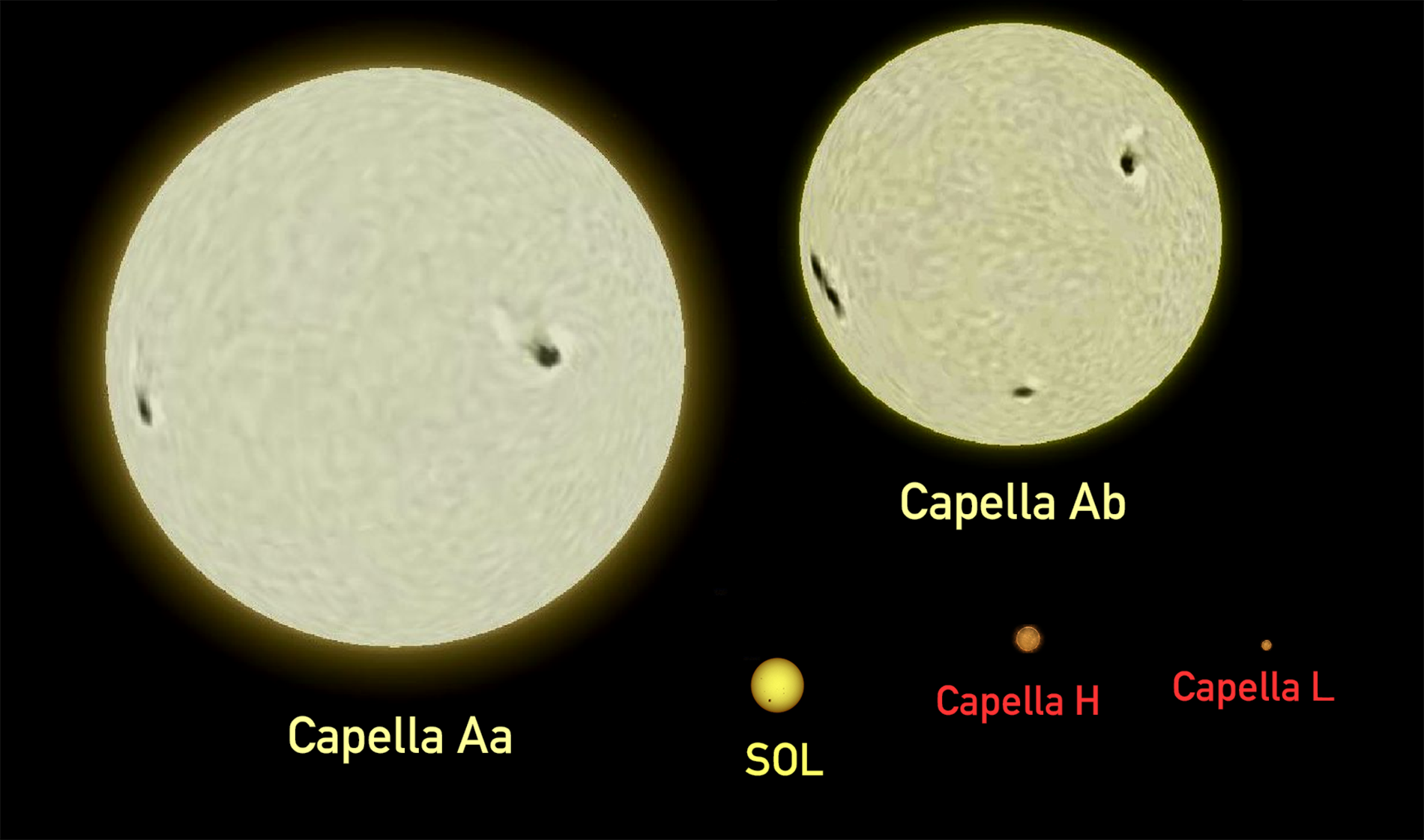
Auriga (constellation)
Auriga is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. It is one of the List of constellations, 88 modern constellations; it was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy. Its name is Latin for '(the) charioteer', associating it with various mythological beings, including Erichthonius of Athens, Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the northern Hemisphere, as are five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism (astronomy), asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far south as −34°; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest, Hydra (constellation), Hydra. Its brightest star, Capella (star), Capella, is an unusual Star system, multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cygnus (constellation)
Cygnus is a northern constellation on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinisation of names, Latinized Greek language, Greek word for swan. Cygnus is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, and it features a prominent asterism (astronomy), asterism known as the Northern Cross (asterism), Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Cygnus contains Deneb (ذنب, translit. ''ḏanab,'' tail)one of the brightest stars in the night sky and the most distant first-magnitude staras its "tail star" and one corner of the Summer Triangle the constellation forming an east pointing Altitude (triangle), altitude of the triangle. It also has some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the List of larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
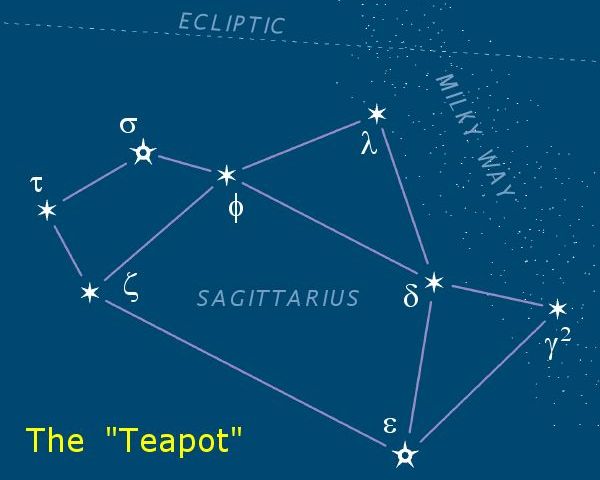
Sagittarius (constellation)
Sagittarius is one of the constellations of the zodiac and is located in the Southern celestial hemisphere. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Its old astronomical symbol is (♐︎). Its name is Latin for "archery, archer". Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur drawing a bow. It lies between Scorpius and Ophiuchus to the west and Capricornus and Microscopium to the east. The center of the Milky Way lies in the westernmost part of Sagittarius (see Sagittarius A). Visualizations As seen from the northern hemisphere, the constellation's brighter stars form an easily recognizable asterism (astronomy), asterism known as "the Teapot". The stars Delta Sagittarii, δ Sgr (Kaus Media), Epsilon Sagittarii, ε Sgr (Kaus Australis), Zeta Sagittarii, ζ Sgr (Ascella), and Phi Sagittarii, φ Sgr form the body of the pot; Lambda Sagittarii, λ Sgr (Kaus Borealis) is the point of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactic Coordinate System
The galactic coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system in spherical coordinates, with the Sun as its center, the primary direction aligned with the approximate center of the Milky Way Galaxy, and the fundamental plane (spherical coordinates), fundamental plane parallel to an approximation of the galactic plane but offset to its north. It uses the Right-hand rule, right-handed convention, meaning that coordinates are positive toward the north and toward the east in the fundamental plane (spherical coordinates), fundamental plane. Spherical coordinates Galactic longitude Longitude (symbol ) measures the angle, angular distance of an object eastward along the galactic equator from the Galactic Center. Analogous to terrestrial longitude, galactic longitude is usually measured in degrees (°). Galactic latitude Latitude (symbol ) measures the angle of an object northward of the galactic equator (or midplane) as viewed from Earth. Analogous to terrestrial latitude, gala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object. The first constellations were likely defined in prehistory. People used them to relate stories of their beliefs, experiences, creation myth, creation, and mythology. Different cultures and countries invented their own constellations, some of which lasted into the early 20th century before today's constellations were internationally recognized. The recognition of constellations has changed significantly over time. Many changed in size or shape. Some became popular, only to drop into obscurity. Some were limited to a single culture or nation. Naming constellations also helped astronomers and navigators identify stars more easily. Twelve (or thirteen) ancient constellations belong to the zodiac (straddling the ecliptic, which the Sun, Moon, and planets all traver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horizon
The horizon is the apparent curve that separates the surface of a celestial body from its sky when viewed from the perspective of an observer on or near the surface of the relevant body. This curve divides all viewing directions based on whether it intersects the relevant body's surface or not. The ''true horizon'' is a theoretical line, which can only be observed to any degree of accuracy when it lies along a relatively smooth surface such as that of Earth's oceans. At many locations, this line is obscured by terrain, and on Earth it can also be obscured by life forms such as trees and/or human constructs such as buildings. The resulting intersection of such obstructions with the sky is called the ''visible horizon''. On Earth, when looking at a sea from a shore, the part of the sea closest to the horizon is called the offing. Pronounced, "Hor-I-zon". The true horizon surrounds the observer and it is typically assumed to be a circle, drawn on the surface of a perfectly sph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrant (astronomy)
A galactic quadrant, or quadrant of the Galaxy, is one of four circular sectors in the division of the Milky Way Galaxy. Quadrants in the galactic coordinate system In actual astronomical practice, the delineation of the galactic quadrants is based upon the galactic coordinate system, which places the Sun as the polar coordinates, pole of the mapping system. The Sun is used instead of the Galactic Center for practical reasons since all astronomical observations (by humans) to date have been based on Earth or within the Solar System. Delineation Quadrants are described using Ordinal number (linguistics), ordinals—for example, "1st galactic quadrant", "second galactic quadrant", or "third quadrant of the Galaxy".M. Lampton ''et al''An All-Sky Catalog of Faint Extreme Ultraviolet Sources''The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series''. 1997 Viewing from the north galactic pole with 0 degree (angle), degrees (°) as the ray (geometry), ray that runs starting from the Sun and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amateur Astronomy
Amateur astronomy is a hobby where participants enjoy observing or imaging celestial objects in the sky using the Naked eye, unaided eye, binoculars, or telescopes. Even though scientific research may not be their primary goal, some amateur astronomers make contributions in doing citizen science, such as by monitoring variable stars, double stars, sunspots, or occultations of stars by the Moon or asteroids, or by discovering transient astronomical events, such as comets, galactic novae or supernovae in other galaxy, galaxies. Amateur astronomers do not use the field of astronomy as their primary source of income or support, and usually have no professional degree in astrophysics or advanced academic training in the subject. Most amateurs are hobbyists, while others have a high degree of experience in astronomy and may often assist and work alongside professional astronomers. Many astronomers have studied the sky throughout history in an amateur framework; however, since the be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined by humans as being in the same celestial sphere, celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar System as Earth's North Pole. Due to Earth's axial tilt of 23.439281°, there is a seasonal variation in the lengths of the day and night. There is also a seasonal variation in temperatures, which lags the variation in day and night. Conventionally, winter in the Northern Hemisphere is taken as the period from the December solstice (typically December 21 UTC) to the March equinox (typically March 20 UTC), while summer is taken as the period from the June solstice through to the September equinox (typically on 23 September UTC). The dates vary each year due to the difference between the calendar year and the Year#Astronomical years, astronomical year. Within the Northern Hemisphere, oceanic currents can change the weather patterns that aff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |