|
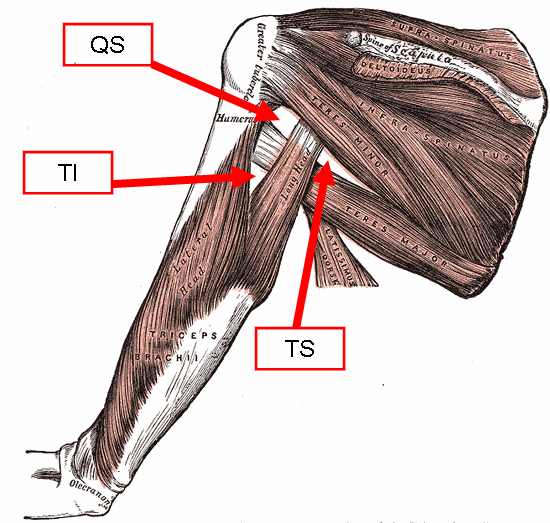
Quadrangular Space
The quadrangular space, also known as the quadrilateral space (of Velpeau) and the foramen humerotricipitale, is one of the three spaces in the axillary space. The other two spaces are: triangular space and triangular interval. Structure The quadrangular space is one of the three spaces in the axillary space. Boundaries The quadrangular space is defined by: - "Scapular Region: Quadrangular Space of Scapular Region" * ''above/superior:'' teres minor muscle. * ''below/inferior:'' teres major muscle. * ''medially:'' long head of the triceps brachii muscle (lateral margin). * ''laterally:'' surgical neck of the humerus. * ''anteriorly:'' subscapularis muscle. Contents The quadrangular space transmits the axillary nerve, the posterior humeral circumflex artery and the posterior circumflex humeral vein. Clinical significance The quadrangular space is a clinically important anatomic space in the arm as it provides the anterior regions of the axilla a passageway to the poste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axillary Space
The axillary spaces are anatomic spaces. through which axillary contents leave the axilla. They consist of the quadrangular space, triangular space, and triangular interval. It is bounded by teres major, teres minor, medial border of the humerus, and long head of triceps brachii. They should not be confused with the true "axillary space" within the borders of the axilla. Structure Axilla The true axilla is a conical space with its apex at the Cervico-axillary Canal, Base at the axillary fascia and skin of the armpit. When viewed in an axillary plane (axillary cut), it is more triangle with: Medial Wall: Serratus Anterior, Anterior Wall: pectoral muscles, Posterior Wall: subscapularis muscle, where the "apex" of the triangle is the humerus Quadrangular space This space is in the posterior wall of the axilla. It is a quadrangular space bounded laterally by surgical neck of the humerus, medially by long head of triceps brachii and inferiorly by teres major. It is bounded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteophytes
Osteophytes are exostoses (bony projections) that form along joint margins. They are distinct from enthesophytes, which are bony projections that form at the attachment of a tendon or ligament. Osteophytes are not always distinguished from exostoses in any definite way, although in many cases there are a number of differences. Osteophytes are typically intra-articular (within the joint capsule). Cause A range of bone-formation processes are associated with aging, degeneration, mechanical instability, and disease (such as diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis). Osteophyte formation has classically been related to sequential and consequential changes in such processes. Often osteophytes form in osteoarthritic joints as a result of damage and wear from inflammation. Calcification and new bone formation can also occur in response to mechanical damage in joints. Pathophysiology Osteophytes form because of the increase in a damaged joint's surface area. This is most common from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangular Space
The triangular space (also known as the medial triangular space, upper triangular space, medial axillary space or foramen omotricipitale) is one of the three spaces found at the axillary space. The other two spaces are the quadrangular space and the triangular interval. Boundaries It has the following boundaries: * Inferior: the superior border of the teres major; * Lateral: the long head of the triceps; * Superior: Teres minor For the superior border, some sources list the teres minor, while others list the subscapularis The subscapularis is a large triangular muscle which fills the subscapular fossa and inserts into the lesser tubercle of the humerus and the front of the capsule of the Glenohumeral joint, shoulder-joint. Structure The subscapularis is covere .... Contents It contains the scapular circumflex vessels. Unlike the quadrangular space or the triangular interval, no major nerve passes through the triangular space. See also * Quadrangular space * Tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
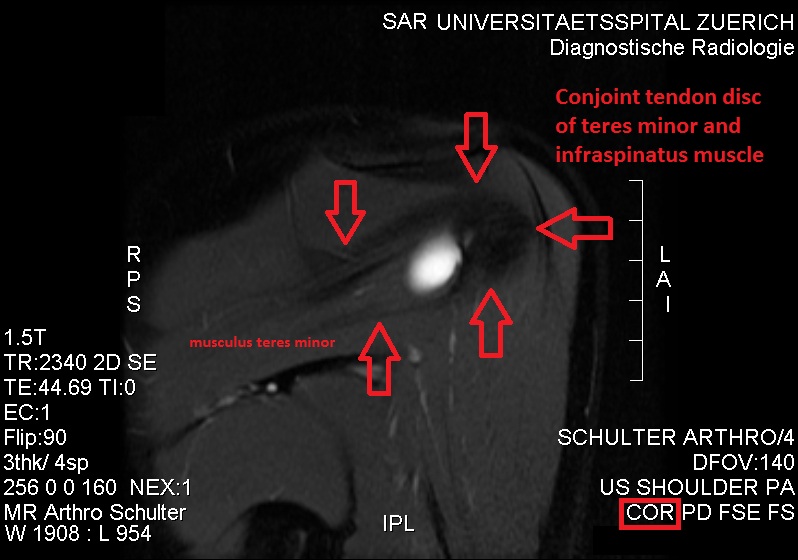
Quadrilateral Space Syndrome
Quadrilateral space syndrome is a rotator cuff denervation syndrome in which the axillary nerve is compressed at the quadrilateral space of the rotator cuff. Cause Diagnosis Diagnosis is usually suspected by clinical history and confirmed by MRI, in which edema of the teres minor is seen, with variable involvement of the deltoid. The circumflex humeral artery may also be compressed. Before the advent of MRI, compression of this vessel on angiography used to be the mechanism of diagnosis, although this is no longer done as it is an invasive procedure. Atrophy can occur in cases of chronic nerve impingement. It can be associated with a glenoid labral cyst, with the cyst also reflecting injury of the glenoid labrum.{{Cite journal, title = Quadrilateral space syndrome caused by glenoid labral cyst, journal = AJR. American Journal of Roentgenology, date = 2000-10-01, issn = 0361-803X, pmid = 11000173, pages = 1103–1105, volume = 175, issue = 4, doi = 10.2214/ajr.175.4.1751103, fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complete Quadrangle
In mathematics, specifically in incidence geometry and especially in projective geometry, a complete quadrangle is a system of geometric objects consisting of any four points in a plane, no three of which are on a common line, and of the six lines connecting the six pairs of points. Dually, a ''complete quadrilateral'' is a system of four lines, no three of which pass through the same point, and the six points of intersection of these lines. The complete quadrangle was called a tetrastigm by , and the complete quadrilateral was called a tetragram; those terms are occasionally still used. The complete quadrilateral has also been called a Pasch configuration, especially in the context of Steiner triple systems. Diagonals The six lines of a complete quadrangle meet in pairs to form three additional points called the ''diagonal points'' of the quadrangle. Similarly, among the six points of a complete quadrilateral there are three pairs of points that are not already connecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Bone
The long bones are those that are longer than they are wide. They are one of five types of bones: long, short, flat, irregular and sesamoid. Long bones, especially the femur and tibia, are subjected to most of the load during daily activities and they are crucial for skeletal mobility. They grow primarily by elongation of the diaphysis, with an epiphysis at each end of the growing bone. The ends of epiphyses are covered with hyaline cartilage ("articular cartilage"). The longitudinal growth of long bones is a result of endochondral ossification at the epiphyseal plate. Bone growth in length is stimulated by the production of growth hormone (GH), a secretion of the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. The long bone category includes the femora, tibiae, and fibulae of the legs; the humeri, radii, and ulnae of the arms; metacarpals and metatarsals of the hands and feet, the phalanges of the fingers and toes, and the clavicles or collar bones. The long bones of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
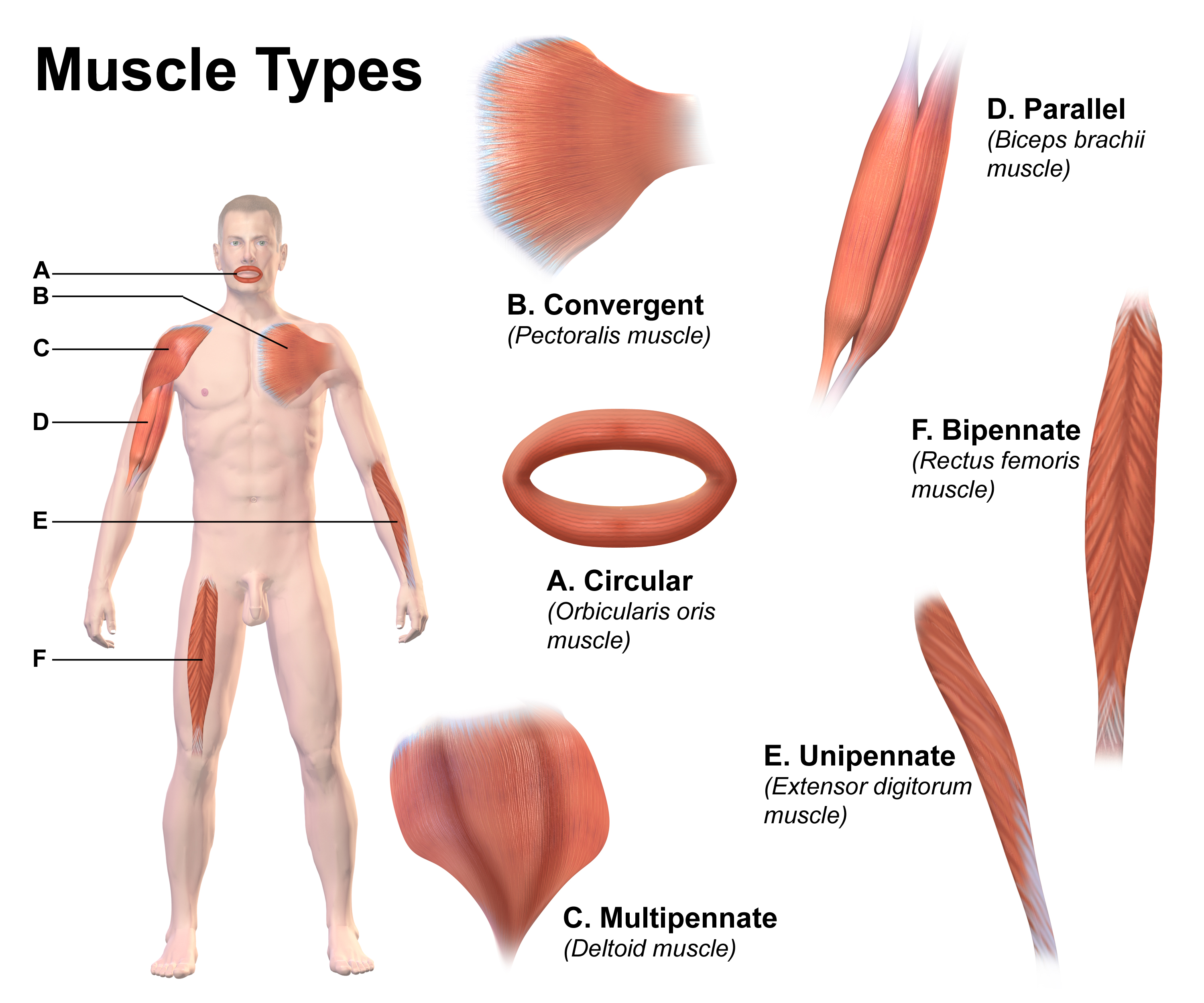
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the somatic nervous system, voluntary muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The skeletal muscle cells are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are also known as ''muscle fibers''. The tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated muscle tissue, striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. A skeletal muscle contains multiple muscle fascicle, fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the cell fusion, fusion of developmental myoblasts in a process known as myogenesis resulting in long multinucleated cells. In these cells, the cell nucleus, nuclei, termed ''myonuclei'', are located along the inside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teres Minor
The teres minor (Latin ''teres'' meaning 'rounded') is a narrow, elongated muscle of the rotator cuff. The muscle originates from the lateral border and adjacent posterior surface of the corresponding right or left scapula and inserts at both the greater tubercle of the humerus and the posterior surface of the joint capsule. The primary function of the teres minor is to modulate the action of the deltoid, preventing the humeral head from sliding upward as the arm is abducted. It also functions to rotate the humerus laterally. The teres minor is innervated by the axillary nerve. Structure It arises from the dorsal surface of the axillary border of the scapula for the upper two-thirds of its extent, and from two aponeurotic laminae, one of which separates it from the infraspinatus muscle, the other from the teres major muscle. Its fibers run obliquely upwards and laterally; the upper ones end in a tendon which is inserted into the lowest of the three impressions on the greater tub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deltoid Muscle
The deltoid muscle is the muscle forming the rounded contour of the shoulder, human shoulder. It is also known as the 'common shoulder muscle', particularly in other animals such as the domestic cat. Anatomically, the deltoid muscle is made up of three distinct sets of muscle fibers, namely the # anterior or clavicular part (pars clavicularis) ( More commonly known as the front delt.) # posterior or scapular part (pars scapularis) ( More commonly known as the rear delt.) # intermediate or acromial part (pars acromialis) ( More commonly known as the side delt) The deltoid's fibres are pennate muscle. However, electromyography suggests that it consists of at least seven groups that can be independently coordinated by the nervous system. It was previously called the deltoideus (plural ''deltoidei'') and the name is still used by some anatomists. It is called so because it is in the shape of the Greek alphabet, Greek capital letter Delta (letter), delta (Δ). Deltoid is also further ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signs And Symptoms
Signs and symptoms are diagnostic indications of an illness, injury, or condition. Signs are objective and externally observable; symptoms are a person's reported subjective experiences. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showing on a medical scan. A symptom is something out of the ordinary that is experienced by an individual such as feeling feverish, a headache or other pains in the body, which occur as the body's immune system fights off an infection. Signs and symptoms Signs A medical sign is an objective observable indication of a disease, injury, or medical condition that may be detected during a physical examination. These signs may be visible, such as a rash or bruise, or otherwise detectable such as by using a stethoscope or taking blood pressure. Medical signs, along with symptoms, help in forming a diagnosis. Some examples of signs are nail clubbing of either the fingernail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of articular cartilage, joint cartilage and underlying bone. A form of arthritis, it is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the world, affecting 1 in 7 adults in the United States alone. The most common symptoms are joint pain and Joint stiffness, stiffness. Usually the symptoms progress slowly over years. Other symptoms may include joint effusion, joint swelling, decreased range of motion, and, when the back is affected, weakness or numbness of the arms and legs. The most commonly involved joints are the two near the ends of the fingers and the joint at the base of the thumbs, the knee and hip joints, and the joints of the neck and lower back. The symptoms can interfere with work and normal daily activities. Unlike some other types of arthritis, only the joints, not internal organs, are affected. Possible causes include previous joint injury, abnormal joint or limb development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axilla
The axilla (: axillae or axillas; also known as the armpit, underarm or oxter) is the area on the human body directly under the shoulder joint. It includes the axillary space, an anatomical space within the shoulder girdle between the arm and the thoracic cage, bounded superiorly by the imaginary plane between the superior borders of the first rib, clavicle and scapula (above which are considered part of the neck), medially by the serratus anterior muscle and thoracolumbar fascia, anteriorly by the pectoral muscles and posteriorly by the subscapularis, teres major and latissimus dorsi muscle. The soft skin covering the lateral axilla contains many hair and sweat glands. In humans, the formation of body odor happens mostly in the axilla. These odorant substances have been suggested by some to serve as pheromones, which play a role related to mate selection, although this is a controversial topic within the scientific community. The underarms seem more importa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |