|
Qirad
The qirad (also known as Muqaradah by Hanafi and Hanbali scholars)Sapuan, Noraina Mazuin. "An evolution of Mudarabah contract: a viewpoint from classical and contemporary Islamic scholars." Procedia economics and finance 35, no. 3 (2016): 349-358. was one of the basic financial instruments of the medieval Islamic world. It was an arrangement between one or more investors and an agent where the investors entrusted capital to an agent who then traded with it in hopes of making profit. Both parties then received a previously settled portion of the profit. The agent was not liable for any losses, provided these did not exceed the capital subscribed. (In later Hanafi jurisprudence, the agent had no authority to incur liabilities in excess of the capital, and so would have to bear any further losses personally.) In modern Islamic finance, the term " Mudarabah" is used for the same instrument. "Mudarabah" is derived from "al-darb al-ard", which is mentioned in the Quran, however "Mudara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Jurisprudence
''Fiqh'' (; ) is the term for Islamic jurisprudence.Fiqh Encyclopædia Britannica ''Fiqh'' is often described as the style of human understanding, research and practices of the ; that is, human understanding of the divine Islamic law as revealed in the and the (the teachings and practices of the Islamic prophet and his companions). Fiqh expands and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
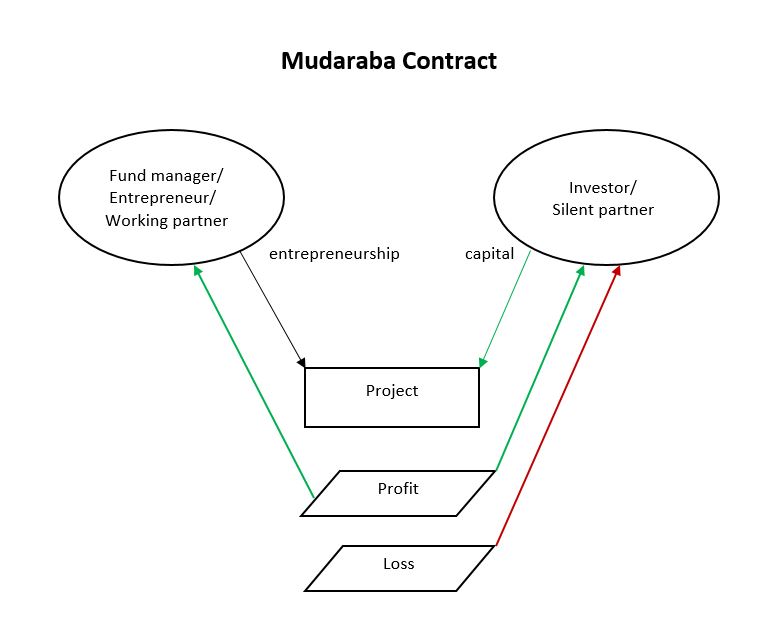
Mudarabah
Profit and Loss Sharing (also called PLS or participatory banking) refers to Sharia-compliant forms of equity financing such as mudarabah and musharakah. These mechanisms comply with the religious prohibition on interest on loans that most Muslims subscribe to. ''Mudarabah'' (مضاربة) refers to "trustee finance" or passive partnership contract, while ''Musharakah'' (مشاركة or مشركة) refers to equity participation contract. Other sources include sukuk (also called "Islamic bonds") and direct equity investment (such as purchase of common shares of stock) as types of PLS. Khan, ''Islamic Banking in Pakistan'', 2015: p.91 The profits and losses shared in PLS are those of a business enterprise or person which/who has obtained capital from the Islamic bank/financial institution (the terms "debt", "borrow", "loan" and "lender" are not used). As financing is repaid, the provider of capital collects some agreed upon percentage of the profits (or deducts if there are losses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanafi
The Hanafi school or Hanafism is the oldest and largest Madhhab, school of Islamic jurisprudence out of the four schools within Sunni Islam. It developed from the teachings of the Faqīh, jurist and theologian Abu Hanifa (), who systemised the use of reasoning (). Hanafi legal theory primarily derives law from the Quran, the sayings and practices of Muhammad (''sunnah''), scholarly consensus () and analogical reasoning (), but also considers juristic discretion () and local customs (). It is distinctive in its greater usage of ''qiyas'' than other schools. The school spread throughout the Muslim world under the patronage of various Islamic empires, including the Abbasids and Seljuk Empire, Seljuks. The Central Asian region of Transoxiana emerged as a centre of classical Hanafi scholarship between the 10th and 12th centuries, which gave rise to the Maturidi school of theology. The Ottoman Empire adopted Hanafism as its official school of law and influenced the legal thought of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanbali
The Hanbali school or Hanbalism is one of the four major schools of Islamic jurisprudence, belonging to the Ahl al-Hadith tradition within Sunni Islam. It is named after and based on the teachings of the 9th-century scholar, jurist and traditionist, Ahmad ibn Hanbal (), and later institutionalized by his students. One who ascribes to the Hanbali school is called a Hanbali (, or ). It adheres to the Athari school of theology and is the smallest out of the four major Sunni schools, the others being the Hanafi, Maliki and Shafi'i schools.Ziauddin Sardar (2014), Mecca: The Sacred City, Bloomsbury, , p. 100 Like the other Sunni schools, it primarily derives sharia from the Quran, hadith and views of Muhammad's companions. In cases where there is no clear answer in the sacred texts of Islam, the Hanbali school does not accept istihsan, juristic discretion or urf, customs of a community as sound bases to derive Islamic law on their own—methods that the Hanafi and Maliki schools ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of scientific, economic, and cultural flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 13th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign of the Abbasid Caliphate, Abbasid caliph Harun al-Rashid (786 to 809) with the inauguration of the House of Wisdom, which saw Ulama, scholars from all over the Muslim world flock to Baghdad, the world's largest city at the time, to translate the known world's classical knowledge into Arabic and Persian language, Persian. The period is traditionally said to have ended with the collapse of the Abbasid caliphate due to Mongol invasions and conquests, Mongol invasions and the Siege of Baghdad (1258), Siege of Baghdad in 1258. There are a few alternative timelines. Some scholars extend the end date of the golden age to around 1350, including the Timurid Renaissance within it, while others place the end of the Islamic Golden Age as late as the en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qur'an
The Quran, also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation directly from God ('' Allāh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which consist of individual verses ('). Besides its religious significance, it is widely regarded as the finest work in Arabic literature, and has significantly influenced the Arabic language. It is the object of a modern field of academic research known as Quranic studies. Muslims believe the Quran was orally revealed by God to the final Islamic prophet Muhammad through the angel Gabriel incrementally over a period of some 23 years, beginning on the Laylat al-Qadr, when Muhammad was 40, and concluding in 632, the year of his death. Muslims regard the Quran as Muhammad's most important miracle, a proof of his prophethood, and the culmination of a series of divine messages starting with those revealed to the first Islamic prophet Adam, including the holy books of the Torah, Psalms, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of Adam in Islam, Adam, Noah in Islam, Noah, Abraham in Islam, Abraham, Moses in Islam, Moses, Jesus in Islam, Jesus, and other Prophets and messengers in Islam, prophets. He is believed to be the Seal of the Prophets in Islam, and along with the Quran, his teachings and Sunnah, normative examples form the basis for Islamic religious belief. Muhammad was born in Mecca to the aristocratic Banu Hashim clan of the Quraysh. He was the son of Abdullah ibn Abd al-Muttalib and Amina bint Wahb. His father, Abdullah, the son of tribal leader Abd al-Muttalib ibn Hashim, died around the time Muhammad was born. His mother Amina died when he was six, leaving Muhammad an orphan. He was raised under the care of his grandfather, Abd al-Muttalib, and paternal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commenda
The commenda was a medieval contract which developed in Italy around the 13th century, and was an early form of limited partnership. The commenda was an agreement between an investing partner and a traveling partner to conduct a commercial enterprise, usually overseas. The terms of the partnership varied, and are usually categorized by modern historians as ''unilateral commenda'' and ''bilateral commenda'', based on the share of contributions and profits between the partners. The bilateral commenda was known in Venice as collegantia or colleganza. The commenda has been described as a foundational innovation in the history of finance and trade. The commenda was a partnership between an investing partner (called the ''commendator'', or ''socius stans'') and a traveling partner (called the ''tractator'' or ''socius procertans''). The investing partner would provide the capital and the traveling partner would execute a commercial enterprise (generally maritime transport), the initial ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinars
The dinar () is the name of the principal currency unit in several countries near the Mediterranean Sea, with a more widespread historical use. The English word "dinar" is the transliteration of the Arabic دينار (''dīnār''), which was borrowed via the Syriac ''dīnarā'' from the Latin ''dēnārius''. The modern gold dinar is a projected bullion gold coin, and is not issued as an official currency by any state. History The modern dinar's historical antecedents are the gold dinar and the silver dirham, the main coin of the medieval Islamic empires, first issued in AH 77 (696–697 AD) (Late Antiquity) by Caliph Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan. The word "dinar" derives from the Latin word " ''dēnārius''," a silver coin of ancient Rome, which was first minted about c. 211 BC. The Kushan Empire introduced a gold coin known as the ''dīnāra'' in India in the 1st century AD; the Gupta Empire and its successors up to the 6th century adopted the coin. The 8th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirhams
The dirham, dirhem or drahm is a unit of currency and of mass. It is the name of the currencies of Morocco, the United Arab Emirates and Armenia, and is the name of a currency subdivision in Jordan, Libya, Qatar and Tajikistan. It was historically a silver coin. Unit of mass The dirham was a unit of mass used across North Africa, the Middle East, Persia and Ifat; later known as Adal, with varying values. The value of Islamic dirham was 14 qirat. 10 dirham equals 7 mithqal (2.975 gm of silver). In the late Ottoman Empire (), the standard dirham was 3.207 g; 400 dirhem equal one oka. The Ottoman dirham was based on the Sasanian drachm (in Middle Persian: 𐭦𐭥𐭦𐭭 ''drahm''), which was itself based on the Greek dram/drachma. In Egypt in 1895, it was equivalent to 47.661 troy grains (3.088 g). There is currently a movement within the Islamic world to revive the dirham as a unit of mass for measuring silver, although the exact value is disputed (either 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Banking
Islamic banking, Islamic finance ( ''masrifiyya 'islamia''), or Sharia-compliant finance is banking or financing activity that complies with Sharia (Islamic law) and its practical application through the development of Islamic economics. Some of the modes of Islamic finance include '' mudarabah'' (profit-sharing and loss-bearing), '' wadiah'' (safekeeping), '' musharaka'' (joint venture), '' murabahah'' (cost-plus), and '' ijarah'' (leasing). Sharia prohibits ''riba'', or usury, generally defined as interest paid on all loans of money (although some Muslims dispute whether there is a consensus that interest is equivalent to ''riba''). Investment in businesses that provide goods or services considered contrary to Islamic principles (e.g. pork or alcohol) is also ''haram'' ("sinful and prohibited"). These prohibitions have been applied historically in varying degrees in Muslim countries/communities to prevent un-Islamic practices. In the late 20th century, as part of the revi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Investment
Investment is traditionally defined as the "commitment of resources into something expected to gain value over time". If an investment involves money, then it can be defined as a "commitment of money to receive more money later". From a broader viewpoint, an investment can be defined as "to tailor the pattern of expenditure and receipt of resources to optimise the desirable patterns of these flows". When expenditures and receipts are defined in terms of money, then the net monetary receipt in a time period is termed cash flow, while money received in a series of several time periods is termed cash flow stream. In finance, the purpose of investing is to generate a Return (finance), return on the invested asset. The return may consist of a capital gain (profit) or loss, realised if the investment is sold, unrealised capital appreciation (or depreciation) if yet unsold. It may also consist of periodic income such as dividends, interest, or rental income. The return may also inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |