|
Psychiatric Genetics
Psychiatric genetics is a subfield of behavioral neurogenetics and Behavioural genetics, behavioral genetics which studies the role of genetics in the development of mental disorders (such as alcoholism, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and autism). The basic principle behind psychiatric genetics is that genetic Polymorphism (biology), polymorphisms (as indicated by linkage to e.g. a single nucleotide polymorphism) are part of the Etiology, causation of Mental illness, psychiatric disorders. Psychiatric genetics is a somewhat new name for the old question, "Are behavioral and psychological conditions and deviations inherited?". The goal of psychiatric genetics is to better understand the Causes of mental disorders, causes of psychiatric disorders, to use that knowledge to improve treatment methods, and possibly also to develop personalized treatments based on genetic profiles (see pharmacogenomics). In other words, the goal is to transform parts of psychiatry into a neuroscience-bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behavioral Neurogenetics
Neurogenetics studies the role of genetics in the development and function of the nervous system. It considers neural characteristics as phenotypes (i.e. manifestations, measurable or not, of the genetic make-up of an individual), and is mainly based on the observation that the nervous systems of individuals, even of those belonging to the same species, may not be identical. As the name implies, it draws aspects from both the studies of neuroscience and genetics, focusing in particular how the genetic code an organism carries affects its expressed Phenotypic trait, traits. Mutations in this genetic sequence can have a wide range of effects on the quality of life of the individual. Neurological diseases, behavior and personality are all studied in the context of neurogenetics. The field of neurogenetics emerged in the mid to late 20th century with advances closely following advancements made in available technology. Currently, neurogenetics is the center of much research utilizing cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adoption Study
Adoption studies typically compare pairs of persons, e.g., adopted child and adoptive mother or adopted child and biological mother, to assess genetic and environmental influences on behavior. These studies are one of the classic research methods of behavioral genetics. The method is used alongside twin studies to identify the roles of genetics and environmental variables that impact intelligence, and behavioral disorders. Adoption studies differ from twin studies in that adoption studies do not necessarily need to use twins; instead, they compare the traits of children to their parents, whether those are the adoptive parents or biological parents. Study designs and methods There are two standard ways in which adoption studies are carried out; the adoptee's study method and the adoptee's family method. The adoptee's study method compares adoptee's similarity to their biological and adoptive parents. Similarity with the biological parent is expected to be due to genetics, while s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major Depressive Disorder
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive depression (mood), low mood, low self-esteem, and anhedonia, loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Introduced by a group of US clinicians in the mid-1970s, the term was adopted by the American Psychiatric Association for this syndrome, symptom cluster under mood disorders in the 1980 version of the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM-III), and has become widely used since. The disorder causes the second-most years lived with disability, after low back pain, lower back pain. The diagnosis of major depressive disorder is based on the person's reported experiences, behavior reported by family or friends, and a mental status examination. There is no laboratory test for the disorder, but testing may be done to rule out physical conditions that can cause similar symptoms. The most common time o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autism
Autism, also known as autism spectrum disorder (ASD), is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by differences or difficulties in social communication and interaction, a preference for predictability and routine, sensory processing differences, focused interests, and repetitive behaviors, which may include stimming. Formal diagnosis requires significant challenges in multiple domains of life, with characteristics that are atypical or more pronounced than expected for one's age and sociocultural context.(World Health Organization: International Classification of Diseases version 11 (ICD-11)): https://icd.who.int/browse/2024-01/mms/en#437815624 Motor coordination difficulties are common but not required for diagnosis. Autism is a spectrum disorder, resulting in wide variations in presentation and support needs, such as that between speaking and non-speaking populations. Increased estimates of autism prevalence since the 1990s are primarily attributed to broader c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anxiety Disorder
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental disorders characterized by significant and uncontrollable feelings of anxiety and fear such that a person's social, occupational, and personal functions are significantly impaired. Anxiety may cause physical and cognitive symptoms, such as restlessness, irritability, easy fatigue, difficulty concentrating, increased heart rate, chest pain, abdominal pain, and a variety of other symptoms that may vary based on the individual. In casual discourse, the words ''anxiety'' and ''fear'' are often used interchangeably. In clinical usage, they have distinct meanings; anxiety is clinically defined as an unpleasant emotional state for which the cause is either not readily identified or perceived to be uncontrollable or unavoidable, whereas fear is clinically defined as an emotional and physiological response to a recognized external threat. The umbrella term 'anxiety disorder' refers to a number of specific disorders that include fears (phobias) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity, and emotional dysregulation that are excessive and pervasive, impairing in multiple contexts, and Developmental psychology, developmentally inappropriate. ADHD symptoms arise from executive dysfunction. Impairments resulting from deficits in self-regulation such as time management, Cognitive inhibition, inhibition, task initiation, and sustained attention can include poor professional performance, relationship difficulties, and numerous health risks, collectively predisposing to a diminished Quality of life (healthcare), quality of life and a reduction in life expectancy. As a consequence, the disorder costs society hundreds of billions of US dollars each year, worldwide. It is associated with other mental disorders as well as non-psychiatric disorders, which can cause additional impairment. While ADHD involves a lack of su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endophenotype
In genetic epidemiology, endophenotype (or intermediate phenotype) is a term used to separate behavioral symptoms into more stable phenotypes with a clear genetic connection. By seeing the EP notion as a special case of a larger collection of multivariate genetic models, which may be fitted using currently accessible methodology, it is possible to maximize its valuable potential lessons for etiological study in psychiatric disorders. The concept was coined by Bernard John and Kenneth R. Lewis in a 1966 paper attempting to explain the geographic distribution of grasshoppers. They claimed that the particular geographic distribution could not be explained by the obvious and external " exophenotype" of the grasshoppers, but instead must be explained by their microscopic and internal "endophenotype". The endophenotype idea represents the influence of two important conceptual currents in biology and psychology research. An adequate technology would be required to perceive the endoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ming Tsuang
Ming Tso Tsuang (; born November 16, 1931) is an American psychiatrist and Distinguished Professor of Psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego. He is considered a pioneering researcher in the genetic epidemiology of schizophrenia and other severe mental disorders. Tsuang has authored and co-authored more than 600 publications and serves as founding and senior editor of the '' American Journal of Medical Genetics'' Part B. Education Tsuang received his medical degree from National Taiwan University in 1957. He received a Ph.D. in psychiatric genetics in 1965 and a D.Sc. in psychiatric genetics and epidemiology in 1981 from the University of London. Career Tsuang holds positions at the University of California, San Diego, as a Distinguished University Professor of Psychiatry and director of the Center for Behavioral Genomics. At Harvard University, Tsuang directs the Harvard Institute of Psychiatric Epidemiology and Genetics, which he created. Tsuang's former positi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homogeneity And Heterogeneity
Homogeneity and heterogeneity are concepts relating to the uniformity of a substance, process or image. A homogeneous feature is uniform in composition or character (i.e., color, shape, size, weight, height, distribution, texture, language, income, disease, temperature, radioactivity, architectural design, etc.); one that is heterogeneous is distinctly nonuniform in at least one of these qualities. Etymology and spelling The words ''homogeneous'' and ''heterogeneous'' come from Medieval Latin ''homogeneus'' and ''heterogeneus'', from Ancient Greek ὁμογενής (''homogenēs'') and ἑτερογενής (''heterogenēs''), from ὁμός (''homos'', "same") and ἕτερος (''heteros'', "other, another, different") respectively, followed by γένος (''genos'', "kind"); -ous is an adjectival suffix. Alternate spellings omitting the last ''-e-'' (and the associated pronunciations) are common, but mistaken: ''homogenous'' is strictly a biological/pathological term whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk Factor
In epidemiology, a risk factor or determinant is a variable associated with an increased risk of disease or infection. Due to a lack of harmonization across disciplines, determinant, in its more widely accepted scientific meaning, is often used as a synonym. The main difference lies in the realm of practice: medicine (clinical practice) versus public health. As an example from clinical practice, low ingestion of dietary sources of vitamin C is a known risk factor for developing scurvy. Specific to public health policy, a determinant is a health risk that is general, abstract, related to inequalities, and difficult for an individual to control. For example, poverty is known to be a determinant of an individual's standard of health. Risk factors may be used to identify high-risk people. Correlation vs causation Risk factors or determinants are correlational and not necessarily causal, because correlation does not prove causation. For example, being young cannot be said to caus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
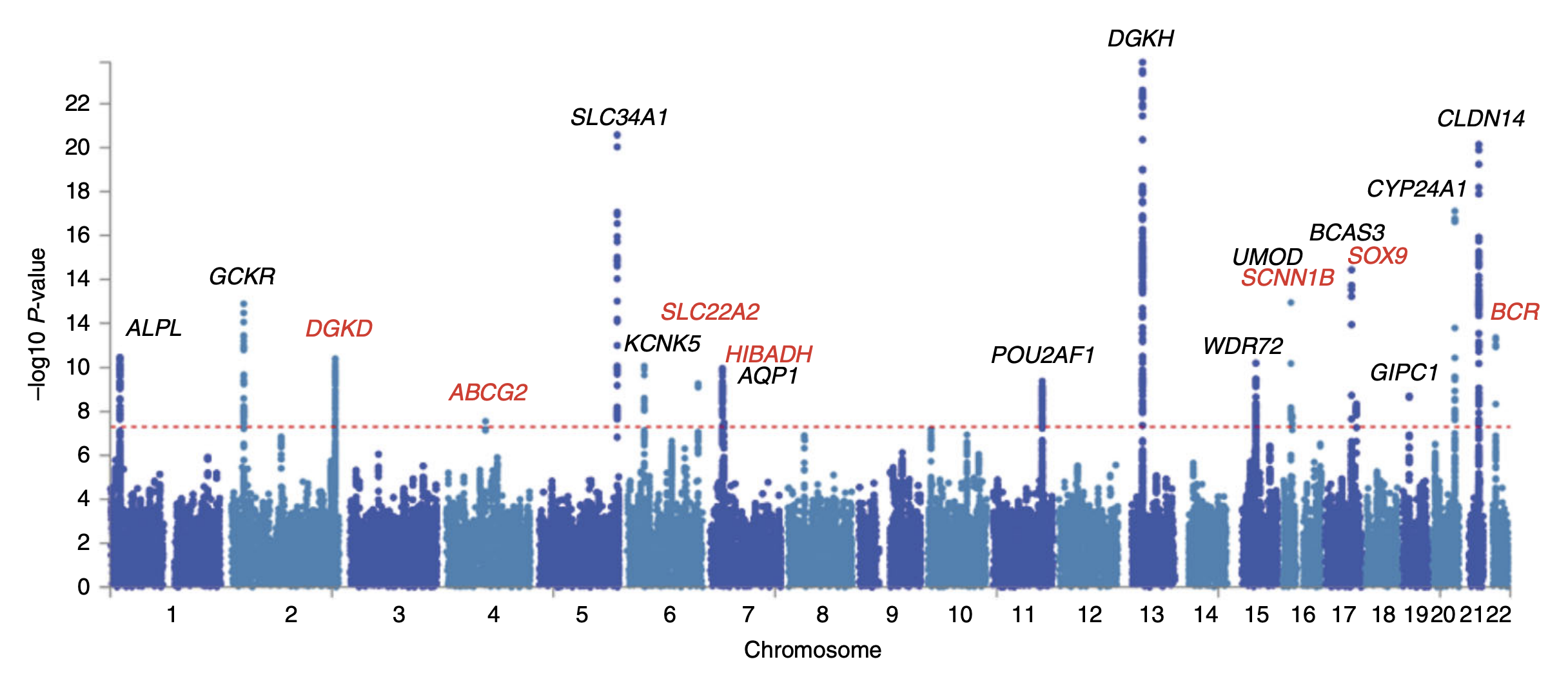
Genome-wide Association Study
In genomics, a genome-wide association study (GWA study, or GWAS), is an observational study of a genome-wide set of Single-nucleotide polymorphism, genetic variants in different individuals to see if any variant is associated with a trait. GWA studies typically focus on associations between single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and traits like major human diseases, but can equally be applied to any other genetic variants and any other organisms. When applied to human data, GWA studies compare the DNA of participants having varying phenotypes for a particular trait or disease. These participants may be people with a disease (cases) and similar people without the disease (controls), or they may be people with different phenotypes for a particular trait, for example blood pressure. This approach is known as phenotype-first, in which the participants are classified first by their clinical manifestation(s), as opposed to Genotype-first approach, genotype-first. Each person gives a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Linkage
Genetic linkage is the tendency of Nucleic acid sequence, DNA sequences that are close together on a chromosome to be inherited together during the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction. Two Genetic marker, genetic markers that are physically near to each other are unlikely to be separated onto different Chromatid, chromatids during chromosomal crossover, and are therefore said to be more ''linked'' than markers that are far apart. In other words, the nearer two Gene, genes are on a chromosome, the lower the chance of Genetic recombination, recombination between them, and the more likely they are to be inherited together. Markers on different chromosomes are perfectly ''unlinked'', although the penetrance of potentially deleterious alleles may be influenced by the presence of other alleles, and these other alleles may be located on other chromosomes than that on which a particular potentially deleterious allele is located. Genetic linkage is the most prominent exception to Gregor M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |