|
Pseudosuchia
Pseudosuchia is one of two major divisions of Archosauria, including living crocodilians and all archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds. Pseudosuchians are also informally known as "crocodilian-line archosaurs". Prior to 2011, the clade Pseudosuchia was often called Crurotarsi in reference to the crurotarsal ankle found in almost all members of the group, which traditionally included phytosaurs, ornithosuchids, and suchians. However, a major 2011 study of Triassic archosaur relations proposed that phytosaurs were not closely related to other traditional "crurotarsans", at least compared to "bird-line archosaurs" (Avemetatarsalians) such as pterosaurs and dinosaurs. As a result, the possession of a crurotarsal ankle was considered a plesiomorphic ("primitive") feature retained by pseudosuchians. Crurotarsi now refers to a broader group of reptiles including Pseudosuchia, Phytosauria, and Avemetatarsalia. Despite Pseudosuchia meaning "false crocodiles", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetosaur
Aetosaurs () are heavily armored reptiles belonging to the extinct order Aetosauria (; from Greek, (aetos, "eagle") and (, "lizard")). They were medium- to large-sized omnivorous or herbivorous pseudosuchians, part of the branch of archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds and other dinosaurs. All known aetosaurs are restricted to the Late Triassic, and in some strata from this time they are among the most abundant fossil vertebrates. They have small heads, upturned snouts, erect limbs, and a body ornamented with four rows of plate-like osteoderms (bony scutes). Aetosaur fossil remains are known from Europe, North and South America, parts of Africa, and India. Since their armoured plates are often preserved and are abundant in certain localities, aetosaurs serve as important Late Triassic tetrapod index fossils. Many aetosaurs had wide geographic ranges, but their stratigraphic ranges were relatively short. Therefore, the presence of particular aetosaurs can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetosauria
Aetosaurs () are heavily armored reptiles belonging to the extinct order Aetosauria (; from Greek, (aetos, "eagle") and (, "lizard")). They were medium- to large-sized omnivorous or herbivorous pseudosuchians, part of the branch of archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds and other dinosaurs. All known aetosaurs are restricted to the Late Triassic, and in some strata from this time they are among the most abundant fossil vertebrates. They have small heads, upturned snouts, erect limbs, and a body ornamented with four rows of plate-like osteoderms (bony scutes). Aetosaur fossil remains are known from Europe, North and South America, parts of Africa, and India. Since their armoured plates are often preserved and are abundant in certain localities, aetosaurs serve as important Late Triassic tetrapod index fossils. Many aetosaurs had wide geographic ranges, but their stratigraphic ranges were relatively short. Therefore, the presence of particular aetosaurs can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crurotarsi
Crurotarsi is a clade of archosauriform reptiles that includes crocodilians and stem-crocodilians and possibly bird-line archosaurs too if the extinct, crocodile-like phytosaurs are more distantly related to crocodiles than traditionally thought. Prior to 2011, the group had invariably included only archosaurs closer to crocodilians than to birds and other dinosaurs. An equivalent term for the crocodilian side of the archosaur family tree is Pseudosuchia. This traditional definition of Crurotarsi assumed that phytosaurs were crown-group archosaurs and more closely related to crocodilians than to birds. However, a 2011 study argued that the phytosaur lineage evolved prior to the split between birds and crocodilians. This would mean that phytosaurs were not true archosaurs, and therefore could not be considered representatives of croc-line archosaurs. The name Crurotarsi is derived from the Latin word ''crus'' (lower leg) and the Greek word ''tarsos'' (ankle). It refers to the spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytosaur
Phytosaurs (Φυτόσαυροι in greek) are an extinct group of large, mostly semiaquatic Late Triassic archosauriform reptiles. Phytosaurs belong to the order Phytosauria. Phytosauria and Phytosauridae are often considered to be equivalent groupings containing the same species, but some studies have identified non-phytosaurid phytosaurians. Phytosaurs were long-snouted and heavily armoured, bearing a remarkable resemblance to modern crocodilians in size, appearance, and lifestyle, as an example of convergence or parallel evolution. The name "phytosaur" means "plant reptile", as the first fossils of phytosaurs were mistakenly thought to belong to plant eaters. The name is misleading because the sharp teeth in phytosaur jaws clearly show that they were predators. For many years, phytosaurs were considered to be the most basal group of Pseudosuchia (crocodile-line archosaurs), meaning that they were thought to be more closely related to the crocodilians than to birds (the other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytosauria
Phytosaurs (Φυτόσαυροι in greek) are an extinct group of large, mostly semiaquatic Late Triassic archosauriform reptiles. Phytosaurs belong to the order Phytosauria. Phytosauria and Phytosauridae are often considered to be equivalent groupings containing the same species, but some studies have identified non-phytosaurid phytosaurians. Phytosaurs were long-snouted and heavily armoured, bearing a remarkable resemblance to modern crocodilians in size, appearance, and lifestyle, as an example of convergence or parallel evolution. The name "phytosaur" means "plant reptile", as the first fossils of phytosaurs were mistakenly thought to belong to plant eaters. The name is misleading because the sharp teeth in phytosaur jaws clearly show that they were predators. For many years, phytosaurs were considered to be the most basal group of Pseudosuchia (crocodile-line archosaurs), meaning that they were thought to be more closely related to the crocodilians than to birds (the oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erpetosuchid
Erpetosuchidae is an extinct family of pseudosuchian archosaurs. Erpetosuchidae was named by D. M. S. Watson in 1917 to include ''Erpetosuchus''. It includes the type species '' Erpetosuchus granti'' from the Late Triassic of Scotland, ''Erpetosuchus'' sp. from the Late Triassic of eastern United States and '' Parringtonia gracilis'' from the middle Middle Triassic of Tanzania Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...; the group might also include ''Dyoplax, Dyoplax arenaceus'' from the Late Triassic of Germany, ''Archeopelta arborensis'' and ''Pagosvenator, Pagosvenator candelariensis'' from Brazil and ''Tarjadia ruthae'' from Argentina. Description General features Erpetosuchids were lithe but well-armored carnivorous pseudosuchians. Two rows of overlapping armored p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prestosuchus
''Prestosuchus'' (meaning "Prestes crocodile") is an extinct genus of pseudosuchian in the group Loricata, which also includes ''Saurosuchus'' and ''Postosuchus''. It has historically been referred to as a "rauisuchian", and was the defining member of the family Prestosuchidae, though the validity of both of these groups is questionable: Rauisuchia is now considered paraphyletic and Prestosuchidae is polyphyletic in its widest form. History of study ''Prestosuchus chiniquensis'' was first discovered in the Santa Maria Formation at the Paleontological Site Chiniquá, near the city of São Pedro do Sul in 1928 or 1929, by the German paleontologist Friedrich von Huene on a trip to Brazil. Von Huene named the genus in 1938 in honor of Vicentino Prestes de Almeida. This site is located in the geopark of Paleorrota. Munich specimens The first two specimens of ''Prestosuchus'' to be described were found at the Weg Sanga site near the town of Sao Pedro do Sul in Rio Grande do S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suchia
Suchia is a clade of archosaurs containing the majority of pseudosuchians (crocodilians and their extinct relatives). It was defined as the least inclusive clade containing ''Aetosaurus ferratus'', '' Rauisuchus tiradentes'', '' Prestosuchus chiniquensis'', and ''Crocodylus niloticus'' (the living Nile crocodile) by Nesbitt (2011). Generally the only pseudosuchian group which is omitted from Suchia is the family Ornithosuchidae, although at least one analysis classifies ornithosuchids as close relatives of erpetosuchids (which are usually considered suchians) and aetosaurs (which are suchians by definition of the group). Phytosaurs are also excluded from Suchia, although it is not certain whether they qualify as pseudosuchians in the first place. There is some controversy over which traits, if any, can be used to distinguish suchians from non-suchian archosaurs. Anatomical features which evolve at the base of a group, and can thus be used to characterize the group, are known a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crocodilian
Crocodilia (or Crocodylia, both ) is an order of mostly large, predatory, semiaquatic reptiles, known as crocodilians. They first appeared 95 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous period ( Cenomanian stage) and are the closest living relatives of birds, as the two groups are the only known survivors of the Archosauria. Members of the order's total group, the clade Pseudosuchia, appeared about 250 million years ago in the Early Triassic period, and diversified during the Mesozoic era. The order Crocodilia includes the true crocodiles (family Crocodylidae), the alligators and caimans (family Alligatoridae), and the gharial and false gharial (family Gavialidae). Although the term 'crocodiles' is sometimes used to refer to all of these, crocodilians is a less ambiguous vernacular term for members of this group. Large, solidly built, lizard-like reptiles, crocodilians have long flattened snouts, laterally compressed tails, and eyes, ears, and nostrils at the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
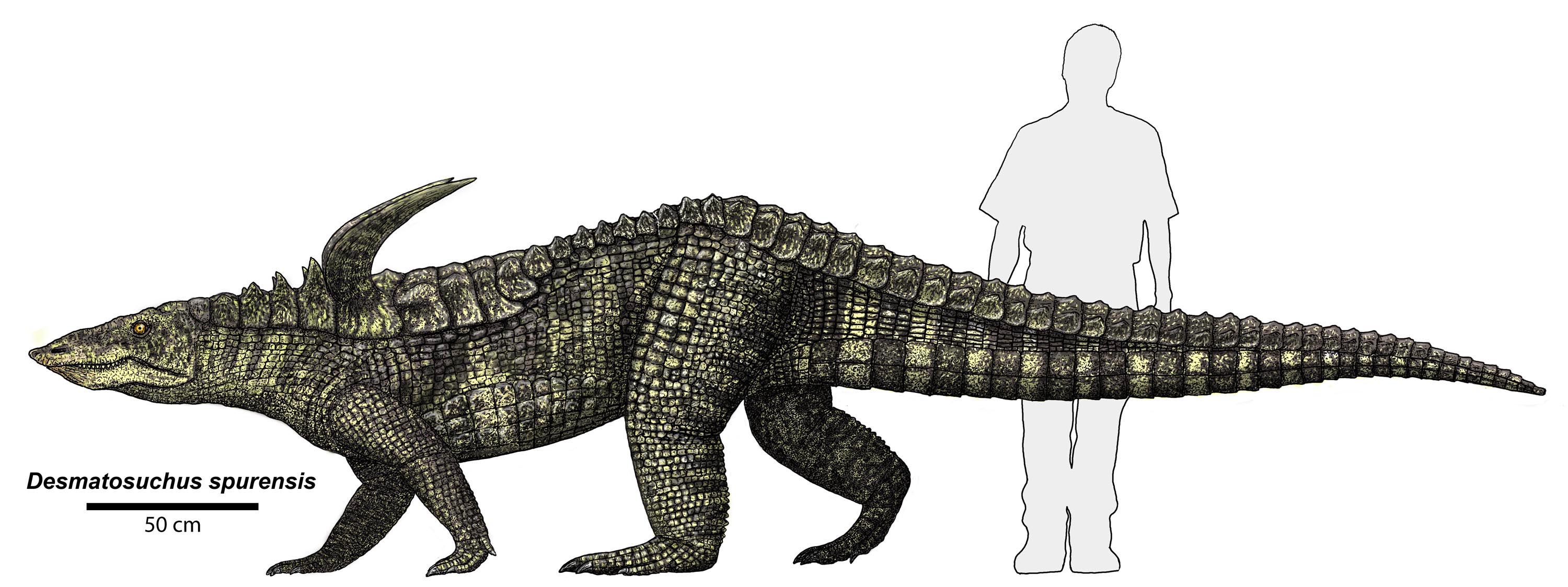
Desmatosuchus
''Desmatosuchus'' (, from Greek δεσμός ''desmos'' 'link' + σοῦχος ''soûkhos'' 'crocodile') is an extinct genus of archosaur belonging to the Order Aetosauria. It lived during the Late Triassic. Description ''Desmatosuchus'' was a large quadrupedal reptile upwards of to in lengthvon Baczko, M. B., Desojo, J. B., Gower, D. J., Ridgely, R., Bona, P., & Witmer, L. M. (2021)New digital braincase endocasts of two species of Desmatosuchus and neurocranial diversity within Aetosauria (Archosauria: Pseudosuchia) The Anatomical Record, 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.24798 and in weight. Its vertebral column had amphicoelus centra and 3 sacral vertebrae. This archosaur's most distinguishing anatomical characteristics were its scapulae which possessed large acromion processes commonly referred to as "shoulder spikes". The forelimbs were much shorter than the hindlimbs, with humeri less than two-thirds the length of the femurs. The pelvic girdle consisted of a long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fasolasuchus
''Fasolasuchus'' is an extinct genus of loricatan. Fossils have been found in the Los Colorados Formation of the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin in northwestern Argentina that date back to the Norian stage of the Late Triassic, making it one of the last rauisuchians to have existed before the order became extinct at the end of the Triassic. Description It is quite possibly the largest known member of Rauisuchia, with an estimated length of to , even bigger than the prestosuchid '' Saurosuchus'' at in length. This would make ''Fasolasuchus'' the largest terrestrial predator to have ever existed save for large theropods. Like ''Saurosuchus'', it had only a single row of caudal osteoderms, unusual among rauisuchians. It also had a hyposphene-hypantrum articulation that gave the vertebral column extra rigidity. This feature is also seen in several other rauisuchians such as '' Postosuchus'' as well as saurischian dinosaurs. Phylogeny Cladogram after the analysis of Nes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |