|
Pseudobulbar Palsy
Pseudobulbar palsy is a medical condition characterized by the inability to control facial movements (such as chewing and speaking) and caused by a variety of neurological disorders. Patients experience difficulty chewing and swallowing, have increased reflexes and spasticity in tongue and the bulbar region, and demonstrate slurred speech (which is often the initial presentation of the disorder), sometimes also demonstrating uncontrolled emotional outbursts. The condition is usually caused by the bilateral damage to corticobulbar pathways, which are upper motor neuron pathways that course from the cerebral cortex to nuclei of cranial nerves in the brain stem. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms of pseudobulbar palsy include: * Slow and indistinct speech * Dysphagia (difficulty in swallowing) * Small, stiff and spastic tongue * Brisk jaw jerk * Dysarthria * Labile affect * Gag reflex may be normal, exaggerated or absent * Examination may reveal upper motor neuron lesion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Neurology
Neurology (from , "string, nerve" and the suffix wikt:-logia, -logia, "study of") is the branch of specialty (medicine) , medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the nervous system, which comprises the Human brain, brain, the spinal cord and the peripheral nervous system , peripheral nerves. Neurological practice relies heavily on the field of neuroscience, the scientific study of the nervous system, using various techniques of neurotherapy. IEEE Brain (2019). "Neurotherapy: Treating Disorders by Retraining the Brain". ''The Future Neural Therapeutics White Paper''. Retrieved 23.01.2025 from: https://brain.ieee.org/topics/neurotherapy-treating-disorders-by-retraining-the-brain/#:~:text=Neurotherapy%20trains%20a%20patient's%20brain,wave%20activity%20through%20positive%20reinforcement International Neuromodulation Society, Retrieved 23 January 2025 from: https://www.neuromodulation.com/ Val Danilov I (2023). "The O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gag Reflex
The pharyngeal reflex or gag reflex is a reflex muscular contraction of the back of the throat, evoked by touching the roof of the mouth, back of the tongue, area around the tonsils, uvula, and back of the throat. It, along with other aerodigestive reflexes such as reflexive pharyngeal swallowing, prevents objects in the oral cavity from entering the throat except as part of normal swallowing and helps prevent choking, and is a form of coughing. The pharyngeal reflex is different from the laryngeal spasm, which is a reflex muscular contraction of the vocal cords. Reflex arc In a reflex arc, a series of physiological steps occur very rapidly to produce a reflex. Generally, a sensory receptor receives an environmental stimulus, in this case from objects reaching nerves in the back of the throat, and sends a message via an afferent nerve to the central nervous system (CNS). The CNS receives this message and sends an appropriate response via an efferent nerve (also known as a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
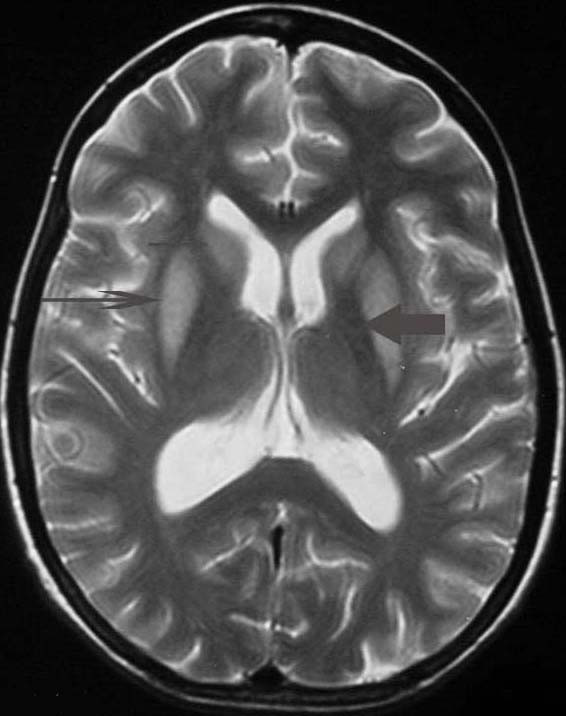
Osmotic Demyelination Syndrome
Central pontine myelinolysis (CPM) is a neurological condition involving severe damage to the myelin sheath of nerve cells in the ''pons'' (an area of the brainstem). It is predominately iatrogenic (treatment-induced), and is characterized by acute paralysis, dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), dysarthria (difficulty speaking), and other neurological symptoms. Central pontine myelinolysis was first described as a disorder in 1959. The original paper described four cases with fatal outcomes, and the findings on autopsy. The disease was described as a disease of alcoholics and malnutrition. 'Central pontine' indicated the site of the lesion and 'myelinolysis' was used to emphasise that myelin was affected. The authors intentionally avoided the term 'demyelination' to describe the condition, in order to differentiate this condition from multiple sclerosis and other neuroinflammatory disorders. Since this original description, demyelination in other areas of the central nervous syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cerebrovascular Disease
Cerebrovascular disease includes a variety of medical conditions that affect the blood vessels of the brain and the cerebral circulation. Arteries supplying oxygen and nutrients to the brain are often damaged or deformed in these disorders. The most common presentation of cerebrovascular disease is an ischemic stroke or mini-stroke and sometimes a hemorrhagic stroke. Hypertension (high blood pressure) is the most important contributing risk factor for stroke and cerebrovascular diseases as it can change the structure of blood vessels and result in atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis narrows blood vessels in the brain, resulting in decreased cerebral perfusion. Other risk factors that contribute to stroke include smoking and diabetes. Narrowed cerebral arteries can lead to ischemic stroke, but continually elevated blood pressure can also cause tearing of vessels, leading to a hemorrhagic stroke. A stroke usually presents with an abrupt onset of a neurologic deficit – such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', ''dolor'', ''rubor'', ''tumor'', and ''functio laesa''). Inflammation is a generic response, and therefore is considered a mechanism of innate immunity, whereas adaptive immunity is specific to each pathogen. Inflammation is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out damaged cells and tissues, and initiate tissue repair. Too little inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus (e.g. bacteria) and compromise the survival of the organism. However inflammation can also have negative effects. Too much inflammation, in the form of chronic inflammation, is associated with variou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit signals, resulting in a range of signs and symptoms, including physical, cognitive disability, mental, and sometimes psychiatric problems. Symptoms include double vision, vision loss, eye pain, muscle weakness, and loss of Sensation (psychology), sensation or coordination. MS takes several forms, with new symptoms either occurring in isolated attacks (relapsing forms) or building up over time (progressive forms). In relapsing forms of MS, symptoms may disappear completely between attacks, although some permanent neurological problems often remain, especially as the disease advances. In progressive forms of MS, bodily function slowly deteriorates once symptoms manifest and will steadily worsen if left untreated. While its cause is unclear, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Demyelination
A demyelinating disease refers to any disease affecting the nervous system where the myelin sheath surrounding neurons is damaged. This damage disrupts the transmission of signals through the affected nerves, resulting in a decrease in their conduction ability. Consequently, this reduction in conduction can lead to deficiencies in sensation, movement, cognition, or other functions depending on the nerves affected. Various factors can contribute to the development of demyelinating diseases, including genetic predisposition, infectious agents, autoimmune reactions, and other unknown factors. Proposed causes of demyelination include genetic predisposition, environmental factors such as viral infections or exposure to certain chemicals. Additionally, exposure to commercial insecticides like sheep dip, weed killers, and flea treatment preparations for pets, which contain organophosphates, can also lead to nerve demyelination. Chronic exposure to neuroleptic medications may also ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
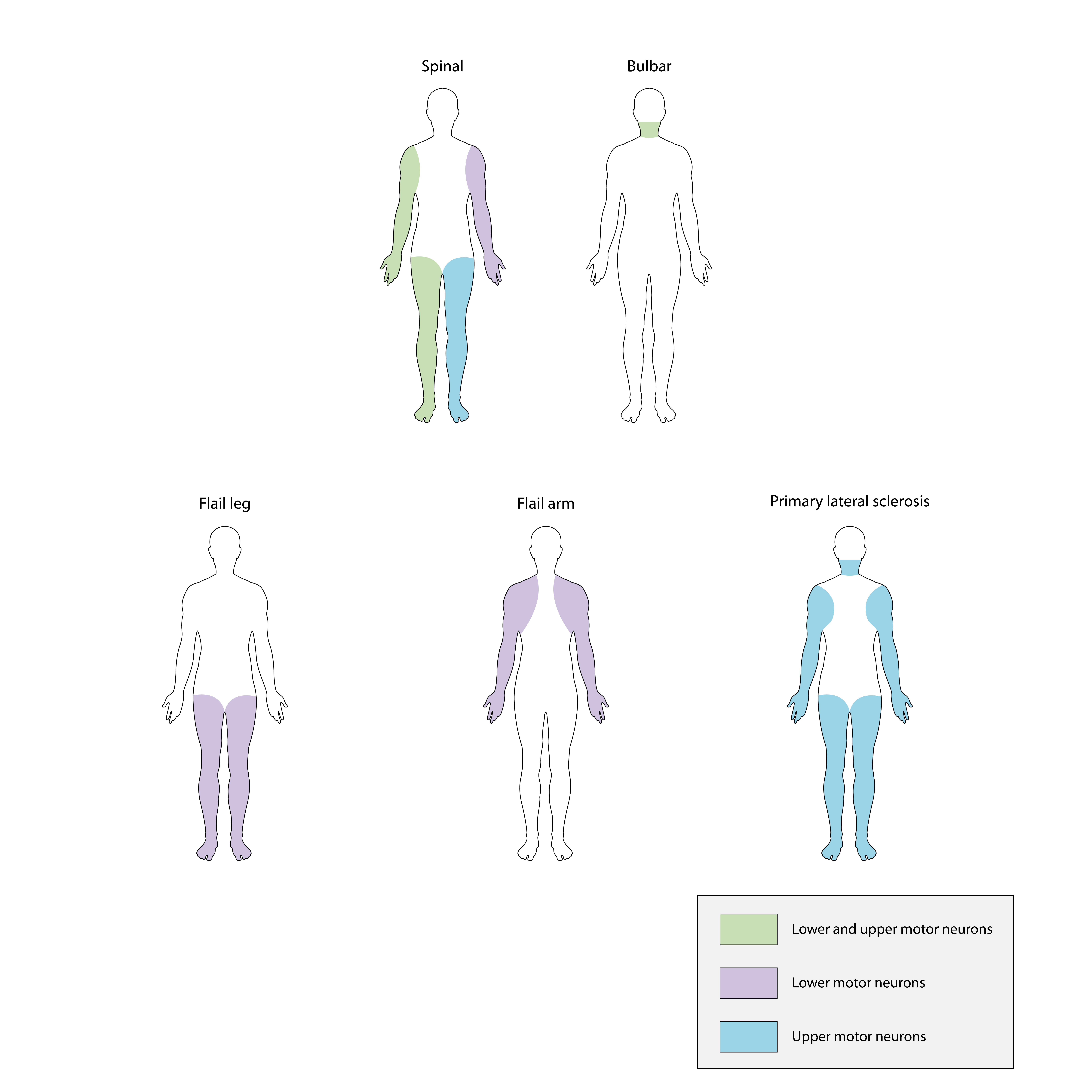
Motor Neuron Disease
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or—in the United States—Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD), is a rare, terminal neurodegenerative disorder that results in the progressive loss of both upper and lower motor neurons that normally control voluntary muscle contraction. ALS is the most common form of the motor neuron diseases. ALS often presents in its early stages with gradual muscle stiffness, twitches, weakness, and wasting. Motor neuron loss typically continues until the abilities to eat, speak, move, and, lastly, breathe are all lost. While only 15% of people with ALS also fully develop frontotemporal dementia, an estimated 50% face at least some minor difficulties with thinking and behavior. Depending on which of the aforementioned symptoms develops first, ALS is classified as ''limb-onset'' (begins with weakness in the arms or legs) or ''bulbar-onset'' (begins with difficulty in speaking or swallowing). Most cases of ALS (ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Multiple System Atrophy
Multiple system atrophy (MSA) is a rare neurodegenerative disorder characterized by tremors, slow movement, muscle rigidity, postural instability (collectively known as parkinsonism), autonomic dysfunction and ataxia. This is caused by progressive degeneration of neurons in several parts of the brain including the basal ganglia, inferior olivary nucleus, and cerebellum. MSA was first described in 1960 by Milton Shy and Glen Drager and was then known as Shy–Drager syndrome. Many people affected by MSA experience dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system, which commonly manifests as orthostatic hypotension, impotence, loss of sweating, dry mouth and urinary retention and incontinence. Palsy of the vocal cords is an important and sometimes initial clinical manifestation of the disorder. A prion of the alpha-synuclein protein within affected neurons may cause MSA. About 55% of MSA cases occur in men, with those affected first showing symptoms at the age of 50–60 ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become more prevalent as the disease progresses. The motor symptoms are collectively called parkinsonism and include tremors, bradykinesia, spasticity, rigidity as well as postural instability (i.e., difficulty maintaining balance). Non-motor symptoms develop later in the disease and include behavior change (individual), behavioral changes or mental disorder, neuropsychiatric problems such as sleep abnormalities, psychosis, anosmia, and mood swings. Most Parkinson's disease cases are idiopathic disease, idiopathic, though contributing factors have been identified. Pathophysiology involves progressive nerve cell death, degeneration of nerve cells in the substantia nigra, a midbrain region that provides dopamine to the basal ganglia, a system invo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or—in the United States—Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD), is a rare, Terminal illness, terminal neurodegenerative disease, neurodegenerative disorder that results in the progressive loss of both upper and lower motor neurons that normally control Skeletal muscle, voluntary muscle contraction. ALS is the most common form of the motor neuron diseases. ALS often presents in its early stages with gradual muscle Spasticity, stiffness, Fasciculation, twitches, Muscle weakness, weakness, and Muscle atrophy, wasting. Motor neuron loss typically continues until the abilities to eat, speak, move, and, lastly, breathe are all lost. While only 15% of people with ALS also fully develop frontotemporal dementia, an estimated 50% face at least some minor difficulties with cognitive disorder, thinking and behavior. Depending on which of the aforementioned symptoms develops first, ALS is classified as ''limb-onset'' (b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy
Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) is a late-onset neurodegenerative disease involving the gradual deterioration and death of specific volumes of the brain, linked to 4-repeat tau pathology. The condition leads to symptoms including Balance disorder, loss of balance, Hypokinesia, slowing of movement, Ophthalmoparesis, difficulty moving the eyes, and cognitive impairment. PSP may be mistaken for other types of neurodegeneration such as Parkinson's disease, frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer's disease. It is the second most common tauopathy behind Alzheimer's disease. The cause of the condition is uncertain, but involves the accumulation of tau protein within the brain. Medications such as L-DOPA, levodopa and amantadine may be useful in some cases. PSP was first officially described by Richardson, Steele, and Olszewski in 1963 as a form of progressive parkinsonism. However, the earliest known case presenting clinical features consistent with PSP, along with pathological co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |