|
Province Of Lecce
The province of Lecce (; Salentino: ) is a province in the Apulia region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Lecce. The province is called the "Heel of Italy". Located on the Salento peninsula, it is the second most-populous province in Apulia and the 21st most-populous province in Italy. The province occupies an area of and has a total population of 802,807 (2016). There are 97 ''comuni'' (: ''comune'') in the province. It is surrounded by the provinces Taranto and Brindisi in the northwest, the Ionian Sea in the west, and the Adriatic Sea in the east. This location has established it as a popular tourist destination. It has been ruled by the Romans, Byzantine Greeks, Carolingians, Lombards, and Normans. The important towns are Lecce, Gallipoli, Nardò, Maglie, and Otranto. Its important agricultural products are wheat and corn. Lecce stone extracted from the province has been used to decorate several historical monuments and is widely used for interior decoration. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salentino Dialect
Salentino () is a dialect of the Extreme Southern Italian ( in Italian) spoken in the Salento peninsula, which is the southern part of the region of Apulia at the southern "heel" of the Italian peninsula. Overview Salentino is a dialect of the Extreme Southern Italian language group (). It is thus closer to the Southern Calabrian dialect and the dialects of Sicily than to the geographically less distant dialects of central and northern Apulia (like Tarantino, Barese and Foggiano). The traditional areas where Salentino is spoken are the province of Lecce, much of the southern part of the province of Brindisi, and the southern part of the province of Taranto. History The Salentino dialect is a product of the different powers and/or populations that have had a presence in the peninsula over the centuries: indigenous Messapian, Ancient Greek, Roman, Byzantine Greek, Lombard, French and Spanish influences are all, to differing levels, present in the modern dialect, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Brindisi
The province of Brindisi () is a province in the Apulia region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Brindisi. It has an area of and a total population of 401,652 (2013). Geography The Province of Brindisi is situated in southeastern Italy, extending for , the second smallest province in the region after the Province of Barletta-Andria-Trani. It was established in 1927 from the ancient Terra d'Otranto. With the Adriatic Sea to the east, it is bordered to the north by the Province of Bari, on the west by the Province of Taranto and to the south-east by the Province of Lecce. The northern, central and western parts are hilly with much woodland, with the Murgia hills of particular note, while to the north-west, bordering on the provinces of Taranto and Bari, it is lower-lying, with the Itria Valley (Valle d'Itria). The maximum height reached within the province is above sea level, near Selva di Fasano. The other peaks are slightly lower and are all located in the north-central ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Bari
The province of Bari (; ; ) was a province in the Apulia region of Italy. Its capital was the city of Bari. It has an area of , and a total population of 1,594,109 (2005). On 1 January 2015 it was replaced by the Metropolitan City of Bari. List of ''comuni'' * Acquaviva delle Fonti * Adelfia * Alberobello * Altamura * Bari * Binetto * Bitetto * Bitonto * Bitritto * Capurso * Casamassima * Cassano delle Murge * Castellana Grotte * Cellamare * Conversano * Corato * Gioia del Colle * Giovinazzo * Gravina in Puglia * Grumo Appula * Locorotondo * Modugno * Mola di Bari * Molfetta * Monopoli * Noci * Noicattaro * Palo del Colle * Poggiorsini * Polignano a Mare * Putignano * Rutigliano * Ruvo di Puglia * Sammichele di Bari * Sannicandro di Bari * Santeramo in Colle * Terlizzi * Toritto * Triggiano * Turi * Valenzano * Andria (to Barletta-Andria-Trani in 2009) * Barletta (to Barletta-Andria-Trani in 2009) * Bisceglie (to Barletta-Andria-Trani in 2009) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cisternino
Cisternino is a ''comune'' in the province of Brindisi in Apulia, on the coast of south-eastern Italy, approximately north-west of the city of Brindisi. It is one of I Borghi più belli d'Italia ("The most beautiful villages of Italy"). Its main economic activities are tourism, the growing of olives and grapes, and dairy farming. Cisternino sits in a historic zone of Itria Valley (in Italian: '' Valle d'Itria''), known for its prehistoric conical, dry stone houses called trulli, which are preserved under UNESCO safeguards due to their cultural significance, dry stone walls (''muretti a secco''), and its fertile soil which makes it the home of the Salento wine region. In 2014, Cisternino was declared the Cittaslow City of the Year. Main sights The architecture is typical of the region with an old Centro Storico (Historical Centre) containing white-washed, stone buildings with cool, shaded, cave-like interiors, narrow streets and churches. The town also features several communi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fasano
Fasano (; Bari dialect, Barese: ) is a town and ''comune'' in the Province of Brindisi, Apulia, southern Italy. It is the second most populated town in the province after Brindisi, with a population in 2021 of 39,026. History According to a folk etymology, the name Fasano derives from the "Faso", a large wild columbus dove (also represented on the civic coat of arms) which drank from the ''fogge'', which was a type of swamp or pool in the open air formed from the water that flowed down from the surrounding hills. This area where the pool once was is now a communal garden. Appian Way, Via Appia, the road from Brindisi to Rome during ancient times, runs along Fasano's ''costal frazioni'', including Savelletri and is visible today. Geography Fasano marks the border between the Salento and the Metropolitan City of Bari. It is about from all three of the provincial capitals in Apulia, namely Bari, Taranto and Brindisi. The municipality borders Alberobello (Metropolitan City of Bari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brindisi
Brindisi ( ; ) is a city in the region of Apulia in southern Italy, the capital of the province of Brindisi, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. Historically, the city has played an essential role in trade and culture due to its strategic position on the Italian Peninsula and its natural port on the Adriatic Sea. The city remains a major port for trade with the Balkan Peninsula, Greece and the Middle East. Its industries include agriculture, chemical works, and the generation of electricity. From September 1943 to February 1944, Brindisi was the provisional government seat of the Kingdom of Italy, meaning that the city has been one of the 5 capitals in the history of Italy. Etymology The name comes from the Latin , through the Greek , is a corruption of the Messapic language, Messapian , meaning "head of the deer", and probably referring to the shape of the natural harbour. It is related to Albanian language, Albanian bri, brî - pl. Brini zi (black horn) brirë, brinë ("horn"; " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taranto
Taranto (; ; previously called Tarent in English) is a coastal city in Apulia, Southern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Taranto, serving as an important commercial port as well as the main Italian naval base. Founded by Spartans in the 8th century BC during the period of Greek colonisation, Taranto was among the most important '' poleis'' in Magna Graecia, becoming a cultural, economic and military power that gave birth to philosophers, strategists, writers and athletes such as Archytas, Aristoxenus, Livius Andronicus, Heracleides, Iccus, Cleinias, Leonidas, Lysis and Sosibius. By 500 BC, the city was among the largest in the world, with a population estimated up to 300,000 people. The seven-year rule of Archytas marked the apex of its development and recognition of its hegemony over other Greek colonies of southern Italy. During the Norman period, it became the capital of the Principality of Taranto, which covered almost all of the heel of Apulia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terra D'Otranto
The Terra di Otranto, or Terra d'Otranto (in English, Land of Otranto), is an historical and geographical region of Apulia, largely corresponding to the Salento peninsula, anciently part of the Kingdom of Sicily and later of the Kingdom of Naples, which became a province of the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies. After the unification of Italy in the 1860s, most of the area was renamed as the province of Lecce. History Since the eleventh century, have formed an integral part of the Terra d'Otranto the territories of today's provinces of Lecce, Taranto and Brindisi (with the exception of Fasano, Cisternino) and, until 1663, there had also included the territory of Matera. Constituted executioner, the territory remained the administrative organization in the Kingdom of Sicily Kingdom of Naples and the next. Its capital was, at first, Otranto, but, during the Norman period (twelfth century), the city's canal was replaced by Lecce. Geography The Otranto was bounded on the north wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
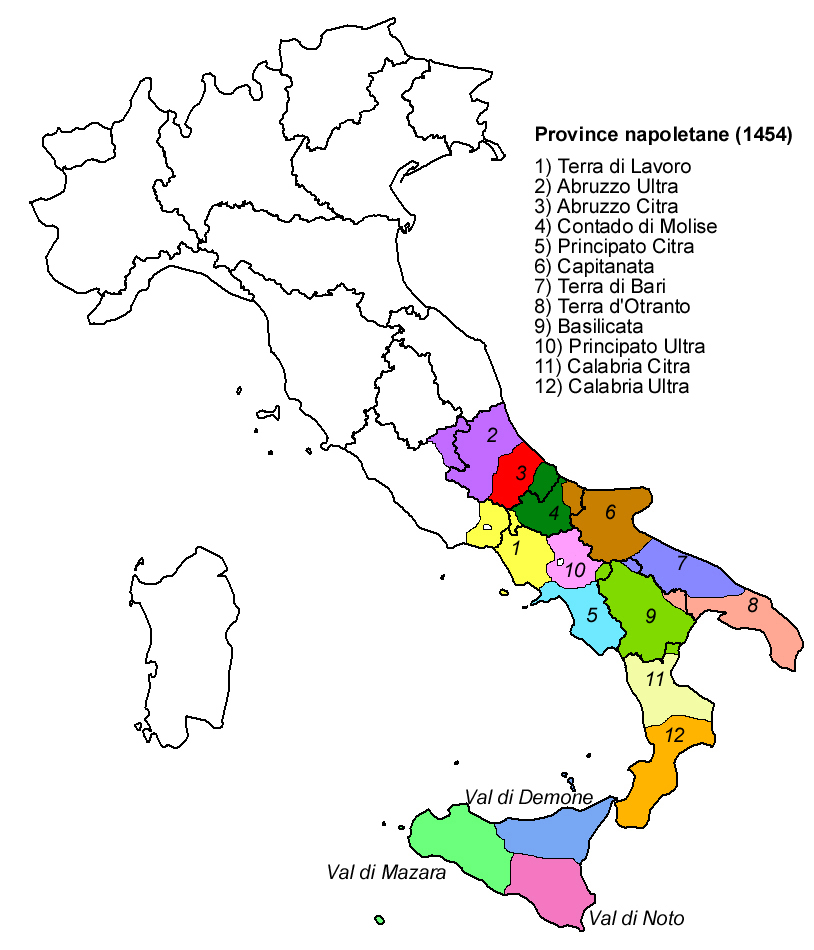
Giustizierato
A justiciarate or justiciarship ( , plural ''giustizierati''; alternatively known as ''circoscrizione'') was a type of administrative subdivision that was used by several Italian states in the medieval period. The Kingdom of Sicily under Frederick II used ''giustizierati'' to divide his realms in the 1230s: Abruzzo, Basilicata, Calabria, Capitanata, Principato e Terra Beneventana, Terra di Bari, Terra di Lavoro (including the modern Frosinone and Latina provinces of today's Lazio region), Terra d'Otranto and Valle di Crati e Terra Giordana. Under Carlo I of Anjou in the 1270s, the subdivision of Abruzzo was considered too large an area to defend and manage efficiently, especially since it was the most northern part of the kingdom. It was decided to follow the border created by the river of Pescara, creating two separate giustizierati of Abruzzo Ulteriore and Abruzzo Citeriore. The era of ''giustizierati'' ended in the time when the Spanish power of Aragon came to power in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otranto
Otranto (, , ; ; ; ; ) is a coastal town, port and ''comune'' in the province of Lecce (Apulia, Italy), in a fertile region once famous for its breed of horses. It is one of I Borghi più belli d'Italia ("The most beautiful villages of Italy"). It is located on the east coast of the Salento peninsula. The Strait of Otranto, to which the city gives its name, connects the Adriatic Sea with the Ionian Sea and separates Italy from Albania. The harbour is small and has little trade. The lighthouse ''Faro della Palascìa'', at approximately southeast of Otranto, marks the most easterly point of the Italian mainland. About south lies the promontory of Santa Maria di Leuca (so called since ancient times from its white cliffs, ''leukos'' being Greek for white), the southeastern extremity of Italy, the ancient ''Promontorium Iapygium'' or ''Sallentinum''. The district between this promontory and Otranto is thickly populated and very fertile. The area that lies between Otranto and Sant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maglie
Maglie (Salentino: ; Griko: , translit. ; ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Lecce in the Apulia region of southeast Italy. History The Maglie area was settled as early as the Bronze Age and the early Iron Age, and before, as testified by the presence of archaic dolmens and menhirs, and by the Cattìe site, discovered in 1980, and featuring 12,000 tools and 800 bone remains. Maglie, initially a countryside ''casale'', developed around the castle built in the 13th century, probably under the Angevine kings of Naples and later renewed by Andriolo Lubello, the local baron under king Alfonso I of Aragon. Main sights *''Duomo'' (Cathedral, also called ''Chiesa Collegiata''). It was built in the late 18th century on the site of two previous buildings tracing back to 14th and 16th century. Its bell tower (1686–90), standing at about , is the tallest in the province. The four upper storeys are attributed to Giuseppe Zimbalo. *Church of ''Madonna delle Grazie'', in Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nardò
Nardò ( or ; ) is a town and ''comune'' in the southern Italian region of Apulia, in the Province of Lecce. Lies on a lowland area placed at south-west of its Province, its border includes part of the Ionian coast of Salento. For centuries, it had been one of the central cities of the Byzantine Empire. In 1497 the ducal House of Acquaviva acquired it under their domain. During those years it became the main cultural hotspot of Salento, seat of many Universities, Academies, literary and philosophical studies: it was given the name of ''Nuoua Atene litterarum''. With almost 32,000 inhabitants and 190 squared kilometres of land, it is the second largest and most populated city among those in the Province, right after Lecce, and also one of the most culturally active towns of Salento. The Old Town is particularly rich with palaces, churches, chapels and other architectural details shaped accordingly to the principles of Lecce's Baroque style. Indeed, the city is a significant exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |