|
Protective Equipment
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is protective clothing, helmets, goggles, or other garments or equipment designed to protect the wearer's body from injury or infection. The hazards addressed by protective equipment include physical, electrical, heat, chemical, biohazards, and airborne particulate matter. Protective equipment may be worn for job-related occupational safety and health purposes, as well as for sports and other recreational activities. ''Protective clothing'' is applied to traditional categories of clothing, and ''protective gear'' applies to items such as pads, guards, shields, or masks, and others. PPE suits can be similar in appearance to a cleanroom suit. The purpose of personal protective equipment is to reduce employee exposure to hazards when engineering controls and administrative controls are not feasible or effective to reduce these risks to acceptable levels. PPE is needed when there are hazards present. PPE has the serious limitation that it do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hazmat DEA
Hazmat, HazMat or HAZMAT may refer to: * Dangerous goods, hazardous materials and items * Hazmat suit * Hazmat diving * Hazmat (comics) is a Marvel Comics character * HazMat (film), ''HazMat'' (film), a 2013 horror film See also * Hazmat Modine, a blues/indie folk/world fusion musical group from Dubai {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hazard Substitution
Hazard substitution is a hazard control strategy in which a material or process is replaced with another that is less hazardous. Substitution is the second most effective of the five members of the hierarchy of hazard controls in protecting workers, after Hazard elimination, elimination. Substitution and elimination are most effective early in the design process, when they may be inexpensive and simple to implement, while for an existing process they may require major changes in equipment and procedures. The concept of prevention through design emphasizes integrating the more effective control methods such as elimination and substitution early in the design phase. Hazard substitutions can involve not only changing one chemical for another, but also using the same chemical in a less hazardous form. Substitutions can also be made to processes and equipment. In making a substitution, the hazards of the new material should be considered and monitored, so that a new hazard is not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
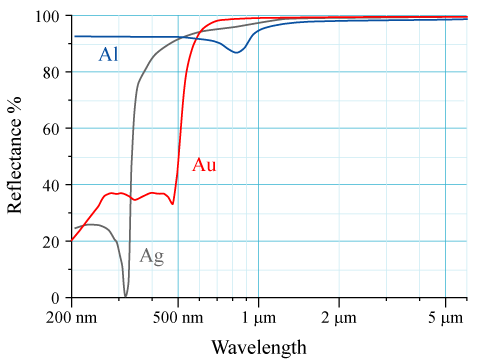
Reflectance
The reflectance of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in reflecting radiant energy. It is the fraction of incident electromagnetic power that is reflected at the boundary. Reflectance is a component of the response of the electronic structure of the material to the electromagnetic field of light, and is in general a function of the frequency, or wavelength, of the light, its polarization, and the angle of incidence. The dependence of reflectance on the wavelength is called a ''reflectance spectrum'' or ''spectral reflectance curve''. Mathematical definitions Hemispherical reflectance The ''hemispherical reflectance'' of a surface, denoted , is defined as R = \frac, where is the radiant flux ''reflected'' by that surface and is the radiant flux ''received'' by that surface. Spectral hemispherical reflectance The ''spectral hemispherical reflectance in frequency'' and ''spectral hemispherical reflectance in wavelength'' of a surface, denoted and respectively, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchurian Plague
The Manchurian plague was a pneumonic plague that occurred mainly in Manchuria in 1910–1911. It killed 60,000 people, stimulating a multinational medical response and the wearing of the first personal protective equipment (PPE). The plague is thought to have originated from a tarbagan marmot which was infected with bacterial pneumonia. The disease was spread when marmot fur hunters gathered together during the winter months, and then infected migrant workers during the Chinese New Year. The University of Cambridge, Cambridge-trained doctor Wu Lien-teh led Chinese efforts to end the plague, and promoted quarantine and the wearing of cloth face masks as safety measures. The hardest hit cities included Changchun, Harbin, and Mukden. Although the disease was largely confined to Manchuria, a number of plague cases were reported in cities such as Beijing and Tianjin. The Manchurian plague highlighted the importance of a multinational medical response, setting precedents for organizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu Lien-teh
Wu Lien-teh ( zh, t=伍連德, p=Wǔ Liándé, poj=Gó͘ Liân-tek, j=Ng5 Lin4 Dak1; Goh Lean Tuck and Ng Leen Tuck in Minnan and Cantonese transliteration respectively; 10 March 1879 – 21 January 1960) was a Malayan physician renowned for his work in public health, particularly the Manchurian plague of 1910–11. He is the inventor of the Wu mask, which is the forerunner of today's N95 respirator. Wu was the first medical student of Chinese descent to study at the University of Cambridge. He was also the first Malayan nominated for the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, in 1935. Life and education Wu was born in Penang, one of the three towns of the Straits Settlements (the others being Malacca and Singapore), currently as one of the states of Malaysia. The Straits Settlements formed part of the colonies of the United Kingdom. His father was a recent immigrant from Taishan, China, and worked as a goldsmith. Wu's mother's was of Hakka heritage and was a second-gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloth Facemask
A cloth face mask is a mask made of common textiles, usually cotton, worn over the mouth and nose. When more effective masks are not available, cloth face masks are recommended by public health agencies for disease source control in epidemic situations to protect others from virus-laden aerosols emitted by infected mask wearers' as they breathe, talk, cough, or sneeze. Cloth masks are also used to reduce the risk of transmission to the wearer. Because they are less effective than N95 masks in protecting the wearer against viruses and other airborne particles, they are not considered to be personal protective equipment by public health agencies. Cloth face masks were routinely used by healthcare workers starting from the late 19th century. They fell out of use in the developed world in favor of disposable surgical masks, and respirators with an electret (electrically charged) filter material, but cloth masks persisted in developing countries. During the COVID-19 pandemic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prescientific
In the philosophy of science, protoscience is a research field that has the characteristics of an undeveloped science that may ultimately develop into an established science. Philosophers use protoscience to understand the history of science and distinguish protoscience from science and pseudoscience. The word "protoscience" is a hybrid Greek-Latin compound of the roots '' proto-'' + '' scientia'', meaning a first or primeval rational knowledge. Examples of protoscience include alchemy, Wegener's original theory of continental drift and political economy (the predecessor to the modern economic sciences). History Protoscience as a research field with the characteristics of an undeveloped science appeared in the early 20th century. In 1910, Jones described the field of political economy as it began the transition to the modern field of economics: : I confess to a personal predilection for some term such as proto-science, pre-science, or nas-science, to give expression to what I c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miasma Theory
The miasma theory (also called the miasmic theory) is an abandoned medical theory that held that diseases—such as cholera, chlamydia, or plague—were caused by a ''miasma'' (, Ancient Greek for 'pollution'), a noxious form of "bad air", also known as night air. The theory held that epidemics were caused by miasma, emanating from rotting organic matter. Though miasma theory is typically associated with the spread of contagious diseases, some academics in the early nineteenth century suggested that the theory extended to other conditions as well, e.g. one could become obese by inhaling the odor of food. The miasma theory was advanced by Hippocrates in the fifth century BC and accepted from ancient times in Europe and China. The theory was eventually abandoned by scientists and physicians after 1880, replaced by the germ theory of disease: specific germs, not miasma, caused specific diseases. However, cultural beliefs about getting rid of odor made the clean-up of waste a h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water-resistant
Waterproofing is the process of making an object, person or structure waterproof or water-resistant so that it remains relatively unaffected by water or resists the ingress of water under specified conditions. Such items may be used in wet environments or underwater to specified depths. ''Water-resistant'' and ''waterproof'' often refer to resistance to penetration of water in its liquid state and possibly under pressure, whereas '' damp proof'' refers to resistance to humidity or dampness. Permeation of water vapour through a material or structure is reported as a moisture vapor transmission rate (MVTR). The hulls of boats and ships were once waterproofed by applying tar or pitch. Modern items may be waterproofed by applying water-repellent coatings or by sealing seams with gaskets or o-rings. Waterproofing is used in reference to building structures (such as basements, decks, or wet areas), watercraft, canvas, clothing ( raincoats or waders), electronic devices and pape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plague (disease)
Plague is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium '' Yersinia pestis''. Symptoms include fever, weakness and headache. Usually this begins one to seven days after exposure. There are three forms of plague, each affecting a different part of the body and causing associated symptoms. Pneumonic plague infects the lungs, causing shortness of breath, coughing and chest pain; bubonic plague affects the lymph nodes, making them swell; and septicemic plague infects the blood and can cause tissues to turn black and die. The bubonic and septicemic forms are generally spread by flea bites or handling an infected animal, whereas pneumonic plague is generally spread between people through the air via infectious droplets. Diagnosis is typically by finding the bacterium in fluid from a lymph node, blood or sputum. Those at high risk may be vaccinated. Those exposed to a case of pneumonic plague may be treated with preventive medication. If infected, treatment is with antibiotics a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plague Doctor Costume
The clothing worn by plague doctors was intended to protect them from airborne diseases during outbreaks of bubonic plague in Europe. * Pommerville (Body Systems), p. 15 * Bauer, p. 145 * Byfield, p. 26 * Glaser, pp. 33-34 It is often seen as a symbol of death and disease. Contrary to popular belief, no evidence suggests that the beak mask costume was worn during the Black Death or the Middle Ages. The costume started to appear in the 17th century when physicians studied and treated plague patients. Description The costume consists of a leather hat, mask with glass eyes and a beak, stick to remove clothes of a plague victim, gloves, waxed linen robe, and boots. The typical mask had glass openings for the eyes and a curved beak shaped like a bird's beak with straps that held the beak in front of the doctor's nose.Ellis, p. 202 The mask had two small nose holes and was a type of respirator that contained aromatic items. The beak could hold dried flowers (commonly roses and carnati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plague Doctor
A plague doctor was a physician who treated victims of bubonic plague during epidemics in 17th-century Europe. These physicians were hired by cities to treat infected patients regardless of income, especially the poor, who could not afford to pay. Plague doctors had a mixed reputation, with some citizens seeing their presence as a warning to leave the area or that death was near. Some plague doctors were said to charge patients and their families additional fees for special treatments or false cures. In many cases, these doctors were not experienced or trained physicians or surgeons, instead being volunteers, second-rate doctors, or young doctors just starting a career. Plague doctors rarely cured patients, instead serving to record death tolls and the number of infected people for demographic purposes. In France and the Netherlands, plague doctors often lacked medical training and were referred to as " empirics". Plague doctors were known as municipal or "community plague doctors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |