|
Propeller
A propeller (often called a screw if on a ship or an airscrew if on an aircraft) is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon a working fluid such as water or air. Propellers are used to pump fluid through a pipe or duct, or to create thrust to propel a boat through water or an aircraft through air. The blades are shaped so that their rotational motion through the fluid causes a pressure difference between the two surfaces of the blade by Bernoulli's principle which exerts force on the fluid. Most marine propellers are screw propellers with helical blades rotating on a propeller shaft (ship), propeller shaft with an approximately horizontal axis. History Early developments The principle employed in using a screw propeller is derived from stern sculling. In sculling, a single blade is moved through an arc, from side to side taking care to keep presenting the blade to the wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
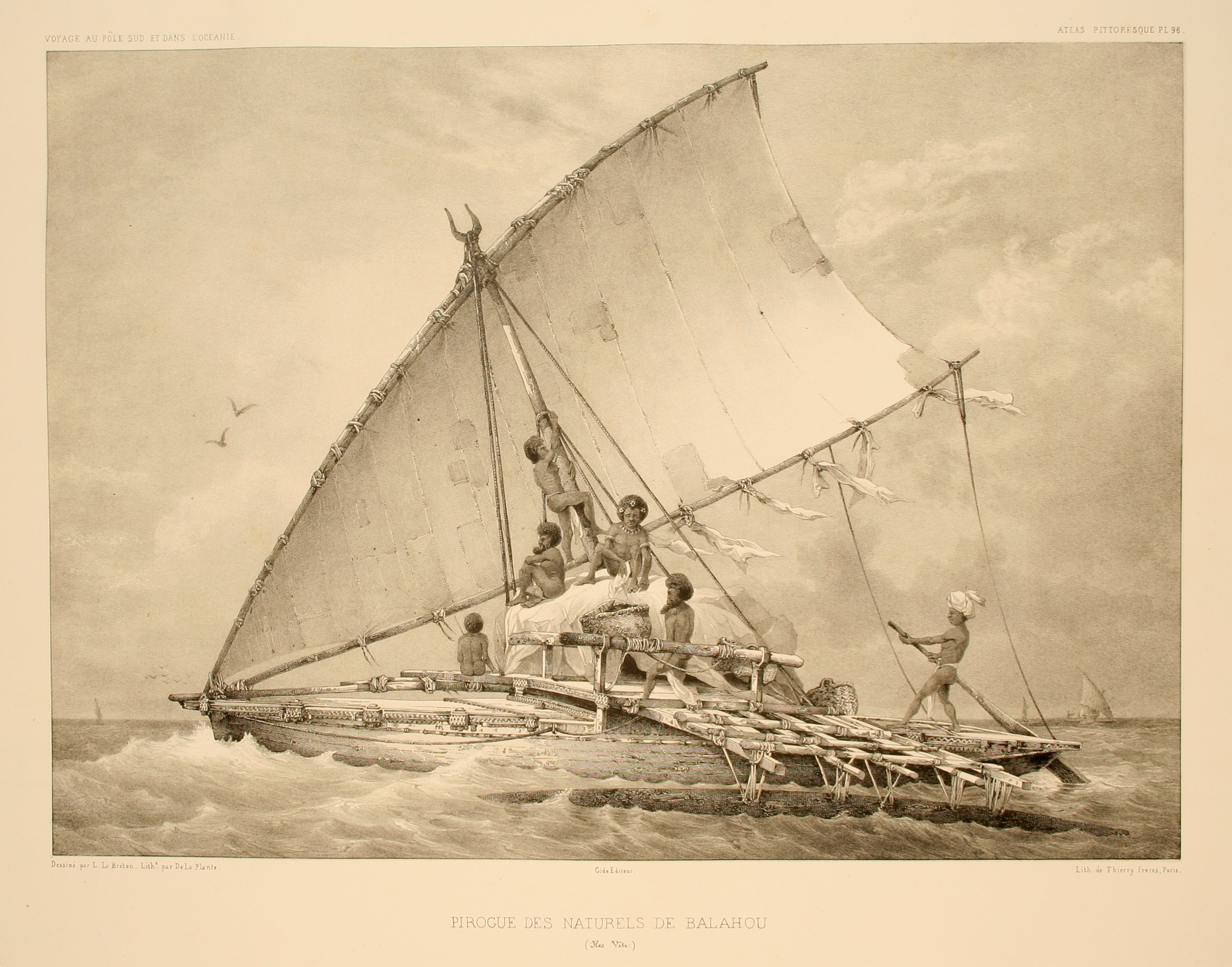
Ship
A ship is a large watercraft, vessel that travels the world's oceans and other Waterway, navigable waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished from boats, based on size, shape, load capacity and purpose. Ships have supported Geographic exploration, exploration, Global trade, trade, Naval warfare, warfare, Human migration, migration, colonization, and science. Ship transport is responsible for the largest portion of world commerce. The word ''ship'' has meant, depending on the era and the context, either just a large vessel or specifically a Full-rigged ship, ship-rigged sailing ship with three or more masts, each of which is Square rig, square-rigged. The earliest historical evidence of boats is found in Egypt during the 4th millennium BCE. In 2024, ships had a global cargo capacity of 2.4 billion tons, with the three largest classes being ships carrying dry bulk (43%), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Propeller Shaft (ship)
A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, tailshaft (Australian English), propeller shaft (prop shaft), or Cardan shaft (after Girolamo Cardano) is a component for transmitting mechanical power, torque, and rotation, usually used to connect other components of a drivetrain that cannot be connected directly because of distance or the need to allow for relative movement between them. As torque carriers, drive shafts are subject to torsion and shear stress, equivalent to the difference between the input torque and the load. They must therefore be strong enough to bear the stress, while avoiding too much additional weight as that would in turn increase their inertia. To allow for variations in the alignment and distance between the driving and driven components, drive shafts frequently incorporate one or more universal joints, jaw couplings, or rag joints, and sometimes a splined joint or prismatic joint. History The term ''driveshaft'' first appeared during the mid-19th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Single-blade Propeller
A single-blade propeller may be used on aircraft to generate thrust. Normally propellers are multi-blades but the simplicity of a single-blade propeller fits well on motorized gliders, because it permits the design of a smaller aperture of the glider fuselage for retraction of the power plant. The counterbalanced teetering mono-blade propeller generates fewer vibrations than conventional multi-blade configurations. Often, single blade propeller configurations are touted as having a much greater efficiency than multi-blade propellers, but this is a falsehood outside the inertial losses in spinning a heavier propeller, and the minimal additional drag from added blades. Single bladed propellers are principally used to fulfill engineering requirements that fall outside the scope of efficiency. Patents US Patent 2742095 Mechanism for balancing single blade aircraft rotorUS Patent 6619585 Helicopter single-blade rotorUS Patent 5971322- Propeller propulsion unit for aircraft in gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Thrust
Thrust is a reaction force described quantitatively by Newton's third law. When a system expels or accelerates mass in one direction, the accelerated mass will cause a force of equal magnitude but opposite direction to be applied to that system. The force applied on a surface in a direction perpendicular or normal to the surface is also called thrust. Force, and thus thrust, is measured using the International System of Units (SI) in newtons (symbol: N), and represents the amount needed to accelerate 1 kilogram of mass at the rate of 1 meter per second per second. In mechanical engineering, force orthogonal to the main load (such as in parallel helical gears) is referred to as static thrust. Examples A fixed-wing aircraft propulsion system generates forward thrust when air is pushed in the direction opposite to flight. This can be done by different means such as the spinning blades of a propeller, the propelling jet of a jet engine, or by ejecting hot gases f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Aircraft
An aircraft ( aircraft) is a vehicle that is able to flight, fly by gaining support from the Atmosphere of Earth, air. It counters the force of gravity by using either Buoyancy, static lift or the Lift (force), dynamic lift of an airfoil, or, in a few cases, direct Powered lift, downward thrust from its engines. Common examples of aircraft include airplanes, rotorcraft (including helicopters), airships (including blimps), Glider (aircraft), gliders, Powered paragliding, paramotors, and hot air balloons. Part 1 (Definitions and Abbreviations) of Subchapter A of Chapter I of Title 14 of the U. S. Code of Federal Regulations states that aircraft "means a device that is used or intended to be used for flight in the air." The human activity that surrounds aircraft is called ''aviation''. The science of aviation, including designing and building aircraft, is called ''aeronautics.'' Aircrew, Crewed aircraft are flown by an onboard Aircraft pilot, pilot, whereas unmanned aerial vehicles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bamboo-copter
The bamboo-copter, also known as the bamboo dragonfly or Chinese top ( Chinese ''zhuqingting'' (竹蜻蜓), Japanese ''taketonbo'' ), is a toy helicopter rotor that flies up when its shaft is rapidly spun. This helicopter-like top originated in Jin dynasty China around 320 AD, and was the object of early experiments by English engineer George Cayley, the inventor of modern aeronautics.Leishman, J. Gordon (2006)''Principles of Helicopter Aerodynamics'' Cambridge University Press. pp. 7–9. In China, the earliest known flying toys consisted of feathers at the end of a stick, which was rapidly spun between the hands and released into flight. "While the Chinese top was no more than a toy, it is perhaps the first tangible device of what we may understand as a helicopter." The Jin dynasty Daoist philosopher Ge Hong's (c. 317) book '' Baopuzi'' (抱樸子 "Master Who Embraces Simplicity") mentioned a flying vehicle in what Joseph Needham calls "truly an astonishing passage".J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
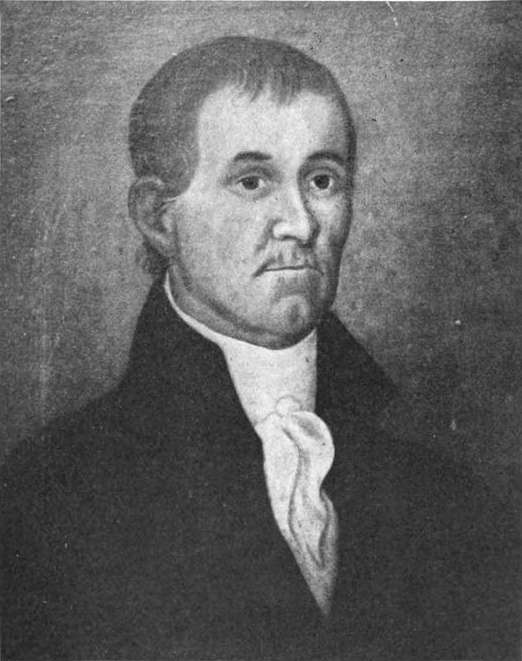
Isaac Doolittle
Isaac Doolittle (August 3, 1721 – February 13, 1800) was an early American clockmaker, inventor, engineer, manufacturer, militia officer, entrepreneur, printer, politician, and brass, iron, and silver artisan. Doolittle was a watchmaker and clockmaker, known for making and selling at his shop in New Haven, Connecticut, one of the first brass wheel Grandfather clock, hall clocks in America, where he also crafted and sold scientific instruments, and is regarded as "the first native practitioner" of silversmithing in the Connecticut Colony. He was also an engraver and Printer (publishing), printer of both legal forms and currency, and became the first American to design, manufacture, and sell a printing press in 1769. Somewhat late in life, he became a successful self-educated Bellfounding, bell-foundryman, learning the difficult craft of casting large metal bells. Doolittle was an important figure in the religious life of Connecticut as an Episcopal Church (United States), Episcop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Archimedes' Screw
The Archimedes' screw, also known as the Archimedean screw, hydrodynamic screw, water screw or Egyptian screw, is one of the earliest documented hydraulic machines. It was so-named after the Greek mathematician Archimedes who first described it around 234 BC, although the device had been developed in Egypt earlier in the century. It is a reversible hydraulic machine that can be operated both as a pump or a power generator. As a machine used for lifting water from a low-lying body of water into irrigation ditches, water is lifted by turning a screw-shaped surface inside a pipe. In the modern world, Archimedes screw pumps are widely used in wastewater treatment plants and for dewatering low-lying regions. Run in reverse, Archimedes screw turbines act as a new form of small hydroelectric powerplant that can be applied even in low head sites. Such generators operate in a wide range of flows (0.01 m^3/s to 14.5 m^3/s) and heads (0.1 m to 10 m), including low heads and moderate flow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Archimedes Screw
The Archimedes' screw, also known as the Archimedean screw, hydrodynamic screw, water screw or Egyptian screw, is one of the earliest documented hydraulic machines. It was so-named after the Greek mathematician Archimedes who first described it around 234 BC, although the device had been developed in Egypt earlier in the century. It is a reversible hydraulic machine that can be operated both as a pump or a power generator. As a machine used for lifting water from a low-lying body of water into irrigation ditches, water is lifted by turning a screw-shaped surface inside a pipe. In the modern world, Archimedes screw pumps are widely used in wastewater treatment plants and for dewatering low-lying regions. Run in reverse, Archimedes screw turbines act as a new form of small hydroelectric powerplant that can be applied even in low head sites. Such generators operate in a wide range of flows (0.01 m^3/s to 14.5 m^3/s) and heads (0.1 m to 10 m), including low heads and moderate flow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
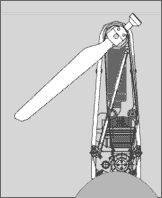
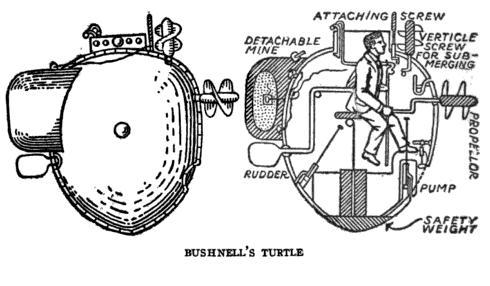
Ezra Lee
Ezra Lee (August 1749 – October 29, 1821) was an American colonial soldier, best known for commanding and operating the one-man ''Turtle'' submarine. Early life and career Lee was born in Lyme, Connecticut. On January 1, 1776, he enlisted in the 10th Continental Regiment, which was raised in Connecticut, as a sergeant. In August 1776 he was selected by brother-in-law Brigadier General Samuel Holden Parsons, also of Lyme, as one of several volunteers to learn to operate the ''Turtle'', an early submarine invented by Saybrook, Connecticut, native David Bushnell. When General George Washington authorized an attack on British Admiral Richard Howe's flagship , then lying in New York harbor, Lee was chosen to operate the "infernal machine". Governors Island attack Sergeant Lee piloted the ''Turtle'' up to the ''Eagle'', which was moored off what is today called Governors Island, due south of Manhattan. A common misconception was that Lee failed because he could not manage to bor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
David Bushnell (inventor)
David Bushnell (August 30, 1740 – 1824) was an American inventor, Patriot (American Revolution), patriot, teacher, and a medical doctor. Bushnell invented the first submarine to be used in battle, ''Turtle (submersible), Turtle'', as well as a floating mine triggered by contact. He was a veteran of the American Revolutionary War, Revolutionary War. Early life David Bushnell was born in a secluded part of Saybrook, Connecticut on 30 August 1740 and baptized in 1753 into a farming family in what is now Westbrook, Connecticut where his parents Nehemiah Bushnell and Sarah (Susan) Ingham Bushnell owned a farm. He was the first of five children born. Following the death of his father circa 1769, he sold his half interest in the family Westbrook farm to his brother Ezra and entered Yale University, Yale College in 1771 at the relatively old age of 31. The ''Turtle'' submarine Bushnell is credited with creating the first submarine ever used in combat, while studying at Yale in 177 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse ( ; ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Greek mathematics, mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and Invention, inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse, Sicily, Syracuse in History of Greek and Hellenistic Sicily, Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, based on his surviving work, he is considered one of the leading scientists in classical antiquity, and one of the greatest mathematicians of all time. Archimedes anticipated modern calculus and mathematical analysis, analysis by applying the concept of the Cavalieri's principle, infinitesimals and the method of exhaustion to derive and rigorously prove many geometry, geometrical theorem, theorems, including the area of a circle, the surface area and volume of a sphere, the area of an ellipse, the area under a parabola, the volume of a segment of a paraboloid of revolution, the volume of a segment of a hyperboloid of revolution, and the area of a spiral. Archimedes' other math ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |