|
Promiscuous Mode
In computer networking, promiscuous mode is a mode for a wired network interface controller (NIC) or wireless network interface controller (WNIC) that causes the controller to pass all traffic it receives to the central processing unit (CPU) rather than passing only the frames that the controller is specifically programmed to receive. This mode is normally used for packet sniffing that takes place on a router or on a computer connected to a wired network or one being part of a wireless LAN. Interfaces are placed into promiscuous mode by Network bridge, software bridges often used with hardware virtualization. In IEEE 802 networks such as Ethernet or IEEE 802.11, each frame includes a destination MAC address. In non-promiscuous mode, when a NIC receives a frame, it drops it unless the frame is addressed to that NIC's MAC address or is a Broadcasting (networking), broadcast or multicast addressed frame. In promiscuous mode, however, the NIC allows all frames through, thus allowin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Networking
A computer network is a collection of communicating computers and other devices, such as printers and smart phones. In order to communicate, the computers and devices must be connected by wired media like copper cables, optical fibers, or by wireless communication. The devices may be connected in a variety of network topologies. In order to communicate over the network, computers use agreed-on rules, called communication protocols, over whatever medium is used. The computer network can include personal computers, Server (computing), servers, networking hardware, or other specialized or general-purpose Host (network), hosts. They are identified by network addresses and may have hostnames. Hostnames serve as memorable labels for the nodes and are rarely changed after initial assignment. Network addresses serve for locating and identifying the nodes by communication protocols such as the Internet Protocol. Computer networks may be classified by many criteria, including the tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Token Ring
Token Ring is a Physical layer, physical and data link layer computer networking technology used to build local area networks. It was introduced by IBM in 1984, and standardized in 1989 as IEEE Standards Association, IEEE 802.5. It uses a special three-byte frame (networking), frame called a ''token'' that is passed around a logical ''ring'' of workstations or server (computing), servers. This token passing is a channel access method providing fair access for all stations, and eliminating the collision (telecommunications), collisions of contention (telecommunications), contention-based access methods. Following its introduction, Token Ring technology became widely adopted, particularly in corporate environments, but was gradually eclipsed by newer iterations of Ethernet. The last formalized Token Ring standard that was completed was Gigabit Token Ring (IEEE 802.5z), published on May 4, 2001. History A wide range of different local area network technologies were developed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ntop
ntop is computer software that probes a computer network to show network use in a way similar to what the program top does for processes. Not to be confused with the CAD/ CAE software nTop (formerly nTopology). Software In interactive mode, it displays the network status on the user's terminal. In Web mode, it acts as a web server, creating a HTML dump of the network status. It supports a NetFlow- sFlow emitter-collector, a Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) based client interface for creating ntop-centric monitoring applications, and RRDtool (RRD) for persistently storing traffic statistics. ntop is available for both Unix and Win32-based platforms. It has been developed by Luca Deri, an Italian research scientist and network manager at University of Pisa. Common usage on a Linux system is to start the ntop daemon (), then one can use the web interface to ntop via visiting provided the loopback device has been started () and the listening port for ntop is 3000 (look out for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capsa (software)
Capsa is the name for a family of packet analyzers developed by Colasoft for network administrators to monitor, troubleshoot and analyze wired & wireless networks. The company provides a free edition for individuals, but paid licenses are available for businesses and enterprises. The software includes Ethernet packet analysis, diagnostics and a security monitoring system. References {{smalldiv, *{{cite web , url=https://www.techrepublic.com/article/test-drive-colasoft-capsa-network-analyzer/ , website=TechRepublic , date=July 19, 2009 , title=Test-drive: Colasoft Capsa network analyzer , first=Rick , last=Vanove , access-date=February 28, 2022 *{{cite web, url=https://techcrunch.com/2009/08/03/review-colasoft-capsa-network-analyzer/, website=TechCrunch, date=August 3, 2009, title=Review: Colasoft Capsa Network Analyzer, first=Scott, last=Merrill, access-date=February 28, 2022 *{{cite magazine, url=https://www.pcworld.com/article/520665/capsa.html, magazine=PC World, date=Dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OmniPeek
Omnipeek is a packet analyzer software tool from Savvius, a LiveAction company, for network troubleshooting and protocol analysis. It supports an application programming interface (API) for plugins. History Savvius (formerly WildPackets) was founded in 1990 as The AG Group by Mahboud Zabetian and Tim McCreery. In 2000 the company changed its name to WildPackets to address the popular market it had developed for its products. The first product by the company was written for the Macintosh and was called EtherPeek. It was the first affordable software-only protocol analyzer for Ethernet networks. It was later ported to Microsoft Windows, which was released in 1997. Earlier, LocalPeek and TokenPeek were developed for LocalTalk and Token Ring networks respectively. In 2001, AiroPeek was released, which added support for wireless IEEE 802.11 (marketed with the Wi-Fi brand) networks. In 2003, the OmniEngine Distributed Capture Engine was released as software, and as a hardware network ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tcpdump
tcpdump is a data-network packet analyzer computer program that runs under a command line interface. It allows the user to display TCP/IP and other packets being transmitted or received over a network to which the computer is attached. Distributed under the BSD license, tcpdump is free software. Tcpdump works on most Unix-like operating systems: Linux, Solaris, FreeBSD, DragonFly BSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, OpenWrt, macOS, HP-UX 11i, and AIX. In those systems, tcpdump uses the libpcap library to capture packets. The port of tcpdump for Windows is called WinDump; it uses WinPcap, the Windows version of libpcap. History tcpdump was originally written in 1988 by Van Jacobson, Sally Floyd, Vern Paxson and Steven McCanne who were, at the time, working in the Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory Network Research Group. By the late 1990s there were numerous versions of tcpdump distributed as part of various operating systems, and numerous patches that were not well coordinat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wireshark
Wireshark is a Free and open-source software, free and open-source packet analyzer. It is used for computer network, network troubleshooting, analysis, software and communications protocol development, and education. Originally named Ethereal, the project was renamed Wireshark in May 2006 due to trademark issues. Wireshark is cross-platform, using the Qt (software), Qt widget toolkit in current releases to implement its user interface, and using pcap to capture packets; it runs on Linux, macOS, BSD, Solaris (operating system), Solaris, some other Unix-like operating systems, and Microsoft Windows. There is also a terminal-based (non-GUI) version called TShark. Wireshark, and the other programs distributed with it such as TShark, are free software, released under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 or any later version. Functionality Wireshark is very similar to tcpdump, but has a Graphical user interface, graphical front-end and back-end, front-end and integ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NetScout
NetScout Systems, Inc. (stylized as NETSCOUT) is a provider of application performance management and network performance management products located in Westford, Massachusetts. In July 2015, NetScout acquired the communications business of Danaher Corporation, including Arbor Networks, Fluke Networks, Tektronix Communications and VSS Monitoring. NetScout has subsidiaries in the Cayman Islands, a tax haven. History NetScout Systems was founded by Anil Singhal and Narendra Popat as Frontier Software in 1984. NetScout created the first RMON-based Ethernet Probe in 1992. In November 2007, NetScout acquired the Sniffer, Infinistream, and Network Intelligence product lines of Network General. NetScout merged both product lines to allow their Performance Manager product to use both probes and Infinistream technologies. In April 2011, NetScout acquired voice and video management company, Psytechnics, from Ipswich U.K. It then acquired Fox Replay, a privately held Dutch company in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
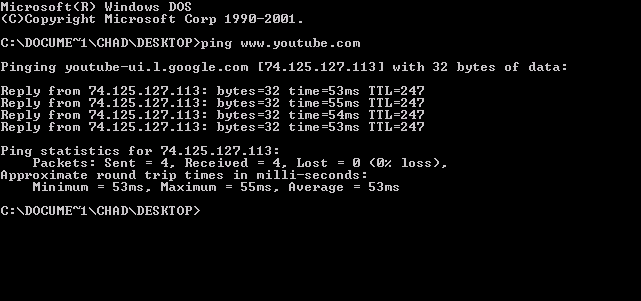
ICMP Echo Request
ping is a computer network administration software utility used to test the reachability of a host on an Internet Protocol (IP) network. It is available in a wide range of operating systems including most embedded network administration software. Ping measures the round-trip time for messages sent from the originating host to a destination computer that are echoed back to the source. The name comes from active sonar terminology that sends a pulse of sound and listens for the echo to detect objects under water. Ping operates by means of Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) packets. ''Pinging'' involves sending an ICMP echo request to the target host and waiting for an ICMP echo reply. The program reports errors, packet loss, and a statistical summary of the results, typically including the minimum, maximum, the mean round-trip times, and standard deviation of the mean. Command-line options and terminal output vary by implementation. Options may include the size ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Security
Computer security (also cybersecurity, digital security, or information technology (IT) security) is a subdiscipline within the field of information security. It consists of the protection of computer software, systems and computer network, networks from Threat (security), threats that can lead to unauthorized information disclosure, theft or damage to computer hardware, hardware, software, or Data (computing), data, as well as from the disruption or misdirection of the Service (economics), services they provide. The significance of the field stems from the expanded reliance on computer systems, the Internet, and wireless network standards. Its importance is further amplified by the growth of smart devices, including smartphones, televisions, and the various devices that constitute the Internet of things (IoT). Cybersecurity has emerged as one of the most significant new challenges facing the contemporary world, due to both the complexity of information systems and the societi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data In Transit
Data in transit, also referred to as data in motion and data in flight, is data en route between source and destination, typically on a computer network. Data in transit can be separated into two categories: information that flows over the public or untrusted network such as the Internet and data that flows in the confines of a private network such as a corporate or enterprise local area network (LAN). Data in transit is used as a complement to the terms '' data in use'', and '' data at rest'' which together define the three states of digital data. See also * Bandwidth-delay product *End-to-end encryption End-to-end encryption (E2EE) is a method of implementing a secure communication system where only communicating users can participate. No one else, including the system provider, telecom providers, Internet providers or malicious actors, can ... (data encryption in transit) References {{network-stub Computer networks engineering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telnet
Telnet (sometimes stylized TELNET) is a client-server application protocol that provides access to virtual terminals of remote systems on local area networks or the Internet. It is a protocol for bidirectional 8-bit communications. Its main goal was to connect terminal devices and terminal-oriented processes. The name "Telnet" refers to two things: a protocol itself specifying how two parties are to communicate and a software application that implements the protocol as a service. User data is interspersed in-band with Telnet control information in an 8-bit byte oriented data connection over the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). Telnet transmits all information including usernames and passwords in plaintext so it is not recommended for security-sensitive applications such as remote management of routers. Telnet's use for this purpose has waned significantly in favor of SSH. Some extensions to Telnet which would provide encryption have been proposed. Description The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |