|
Projected Set
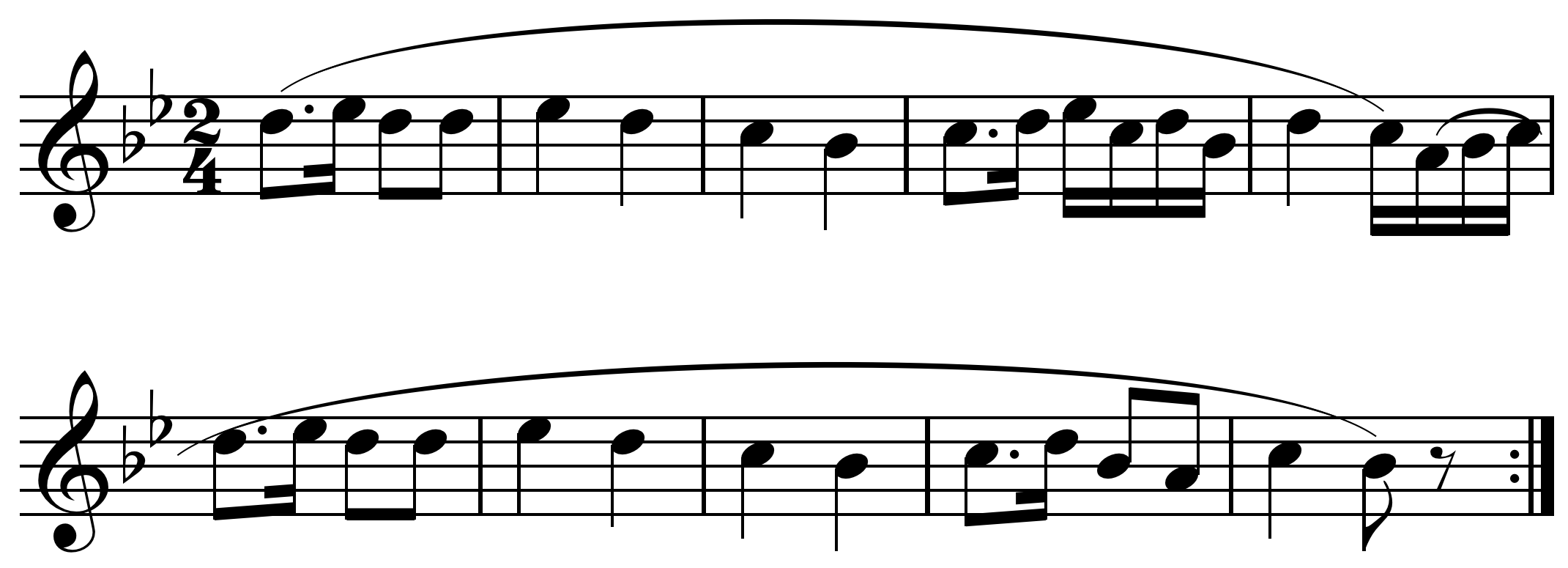
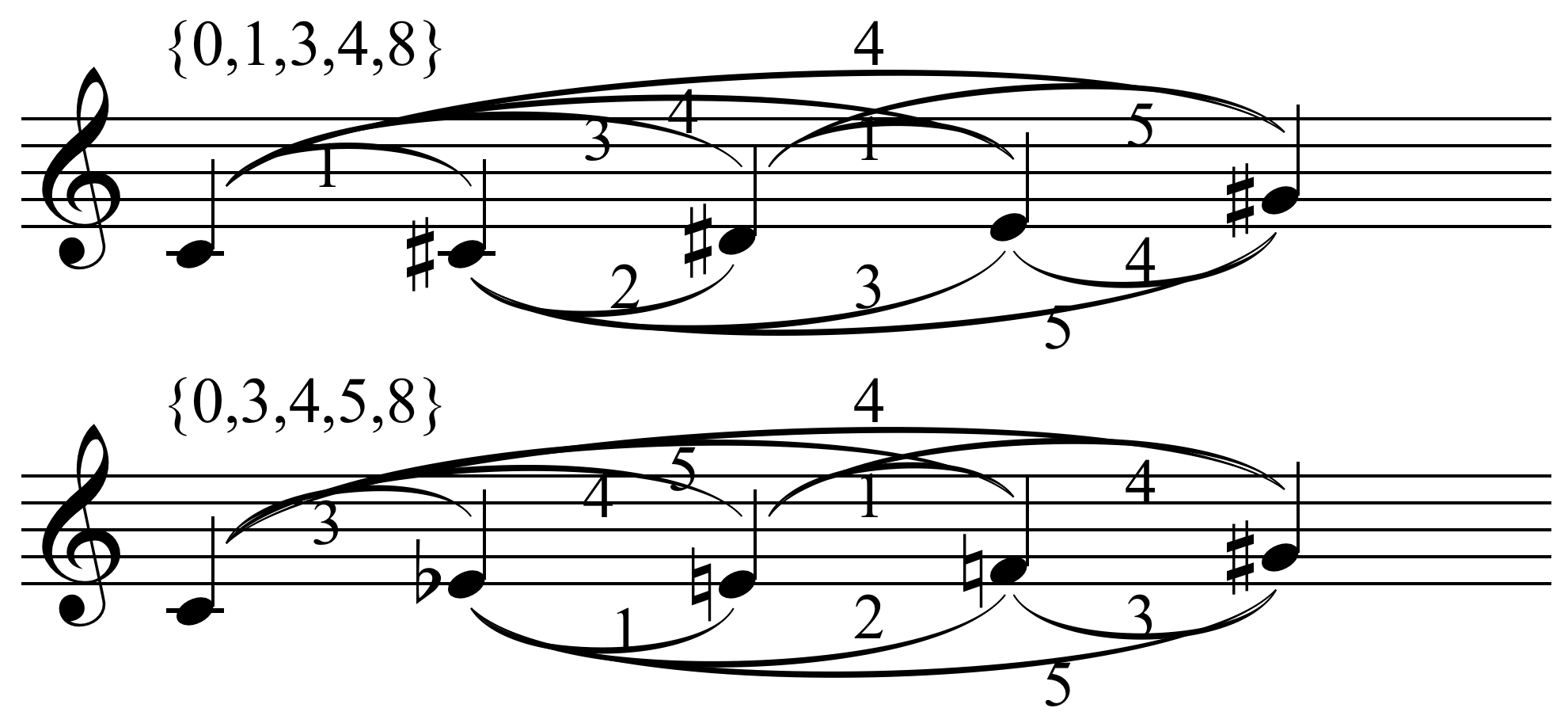
In music, a projected set is a technique where a collection of pitches or pitch classes is extended in a texture through the emphasized simultaneous statement of a set followed or preceded by a successive emphasized statement of each of its members. For example, a set may be stated as a simultaneity and then a series of phrases may end on notes which are the members of the set, as in the downbeat of m. 19 through measures 46 of Béla Bartók Béla Viktor János Bartók (; ; 25 March 1881 – 26 September 1945) was a Hungarian composer, pianist and ethnomusicologist. He is considered one of the most important composers of the 20th century; he and Franz Liszt are regarded as Hunga ...'s Second String Quartet. (Wilson 1992, p. 23) Pattern completion is "the use of a projected set to organize a work over a long span of time" (ibid, p. 210n5). Sources *Wilson, Paul (1992). ''The Music of Béla Bartók''. . Musical set theory {{Music-theory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music
Music is the arrangement of sound to create some combination of Musical form, form, harmony, melody, rhythm, or otherwise Musical expression, expressive content. Music is generally agreed to be a cultural universal that is present in all human societies. Definitions of music vary widely in substance and approach. While scholars agree that music is defined by a small number of elements of music, specific elements, there is no consensus as to what these necessary elements are. Music is often characterized as a highly versatile medium for expressing human creativity. Diverse activities are involved in the creation of music, and are often divided into categories of musical composition, composition, musical improvisation, improvisation, and performance. Music may be performed using a wide variety of musical instruments, including the human voice. It can also be composed, sequenced, or otherwise produced to be indirectly played mechanically or electronically, such as via a music box ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitch (music)
Pitch is a perception, perceptual property that allows sounds to be ordered on a frequency-related scale (music), scale, or more commonly, pitch is the quality that makes it possible to judge sounds as "higher" and "lower" in the sense associated with musical melody, melodies. Pitch is a major auditory system, auditory attribute of musical tones, along with duration (music), duration, loudness, and timbre. Pitch may be quantified as a frequency, but pitch is not a purely objective physical property; it is a subjective Psychoacoustics, psychoacoustical attribute of sound. Historically, the study of pitch and pitch perception has been a central problem in psychoacoustics, and has been instrumental in forming and testing theories of sound representation, processing, and perception in the auditory system. Perception Pitch and frequency Pitch is an auditory sensation in which a listener assigns musical tones to relative positions on a musical scale based primarily on their percep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitch Class
In music, a pitch class (p.c. or pc) is a set of all pitches that are a whole number of octaves apart; for example, the pitch class C consists of the Cs in all octaves. "The pitch class C stands for all possible Cs, in whatever octave position." Important to musical set theory, a pitch class is "all pitches related to each other by octave, enharmonic equivalence, or both." Thus, using scientific pitch notation, the pitch class "C" is the set : = . Although there is no formal upper or lower limit to this sequence, only a few of these pitches are audible to humans. Pitch class is important because human pitch-perception is periodic: pitches belonging to the same pitch class are perceived as having a similar quality or color, a property called " octave equivalence". Psychologists refer to the quality of a pitch as its "chroma". A ''chroma'' is an attribute of pitches (as opposed to ''tone height''), just like hue is an attribute of color. A ''pitch class'' is a set of all p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texture (music)
In music, texture is how the tempo and the melodic and harmonic materials are combined in a musical composition, determining the overall quality of the sound in a piece. The texture is often described in regard to the density, or thickness, and range, or width, between lowest and highest pitches, in relative terms as well as more specifically distinguished according to the number of voices, or parts, and the relationship between these voices (see Common types below). For example, a thick texture contains many 'layers' of instruments. One of these layers could be a string section or another brass. The thickness also is changed by the amount and the richness of the instruments playing the piece. The thickness varies from light to thick. A piece's texture may be changed by the number and character of parts playing at once, the timbre of the instruments or voices playing these parts and the harmony, tempo, and rhythms used. The types categorized by number and relationship of parts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simultaneity (music)
In music, a simultaneity is more than one complete musical texture occurring at the same time, rather than in succession. This first appeared in the music of Charles Ives, and is common in the music of Conlon Nancarrow and others. Types In music theory, a pitch simultaneity is more than one pitch or pitch class all of which occur at the same time, or simultaneously: "A set of notes sounded together." ''Simultaneity'' is a more specific and more general term than chord: many but not all chords or harmonies are simultaneities, though not all but some simultaneities are chords. For example, arpeggios are chords whose tones are not simultaneous. "The practice of harmony typically involves both simultaneity...and linearity."Hijleh, Mark (2012). ''Towards a Global Music Theory: Practical Concepts and Methods for the Analysis of Music Across Human Cultures'', chapter 4, . Ashgate. . A simultaneity succession is a series of different groups of pitches or pitch classes, each of which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Set Theory (music)
Musical set theory provides concepts for categorizing musical objects and describing their relationships. Howard Hanson first elaborated many of the concepts for analyzing tonal music. Other theorists, such as Allen Forte, further developed the theory for analyzing atonal music, drawing on the twelve-tone theory of Milton Babbitt. The concepts of musical set theory are very general and can be applied to tonal and atonal styles in any equal temperament tuning system, and to some extent more generally than that. One branch of musical set theory deals with collections ( sets and permutations) of pitches and pitch classes (pitch-class set theory), which may be ordered or unordered, and can be related by musical operations such as transposition, melodic inversion, and complementation. Some theorists apply the methods of musical set theory to the analysis of rhythm as well. Comparison with mathematical set theory Although musical set theory is often thought to involve the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrase (music)
In music theory, a phrase () is a unit of Meter (music), musical meter that has a complete musical sense of its own, built from figure (music), figures, motif (music), motifs, and Cell (music), cells, and combining to form Melody, melodies, period (music), periods and larger Section (music), sections. Terms such as ''sentence'' and ''verse'' have been adopted into the vocabulary of music from linguistic syntax. Though the analogy between the musical and the phrase, linguistic phrase is often made, still the term "is one of the most ambiguous in music....there is no consistency in applying these terms nor can there be...only with melodies of a very simple type, especially those of some dances, can the terms be used with some consistency." John D. White defines a phrase as "the smallest musical unit that conveys a more or less complete musical thought. Phrases vary in length and are terminated at a point of full or partial repose, which is called a ''cadence''." Edward T. Cone, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beat (music)
In music and music theory, the beat is the basic unit of time, the pulse (regularly repeating event), of the ''mensural level'' (or ''beat level''). The beat is often defined as the rhythm listeners would tap their toes to when listening to a piece of music, or the numbers a musician counts while performing, though in practice this may be technically incorrect (often the first multiple level). In popular use, ''beat'' can refer to a variety of related concepts, including pulse, tempo, meter, specific rhythms, and groove. Rhythm in music is characterized by a repeating sequence of stressed and unstressed beats (often called "strong" and "weak") and divided into bars organized by time signature and tempo indications. Beats are related to and distinguished from pulse, rhythm (grouping), and meter: Metric levels faster than the beat level are division levels, and slower levels are multiple levels. Beat has always been an important part of music. Some music genres such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Béla Bartók
Béla Viktor János Bartók (; ; 25 March 1881 – 26 September 1945) was a Hungarian composer, pianist and ethnomusicologist. He is considered one of the most important composers of the 20th century; he and Franz Liszt are regarded as Hungary's greatest composers. Among his notable works are the opera ''Bluebeard's Castle'', the ballet ''The Miraculous Mandarin'', ''Music for Strings, Percussion and Celesta'', the Concerto for Orchestra (Bartók), Concerto for Orchestra and List of string quartets by Béla Bartók, six string quartets. Through his collection and analytical study of folk music, he was one of the founders of comparative musicology, which later became known as ethnomusicology. Per Anthony Tommasini, Bartók "has empowered generations of subsequent composers to incorporate folk music and classical traditions from whatever culture into their works and was "a formidable modernist who in the face of Schoenberg’s breathtaking formulations showed another way, forgi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pattern Completion
In music pattern completion is "the use of a projected set to organize a work over a long span of time" (Wilson 1992, p. 210n5). The compositional technique has been used by Béla Bartók and Igor Stravinsky Igor Fyodorovich Stravinsky ( – 6 April 1971) was a Russian composer and conductor with French citizenship (from 1934) and American citizenship (from 1945). He is widely considered one of the most important and influential 20th-century c .... Sources *Wilson, Paul (1992). ''The Music of Béla Bartók''. . References *Straus, Joseph (1982). "A Principle of Voice Leading in the Music of Stravinsky", ''Music Theory Spectrum'' 4, p. 106-124. Musical composition {{music-theory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |