|
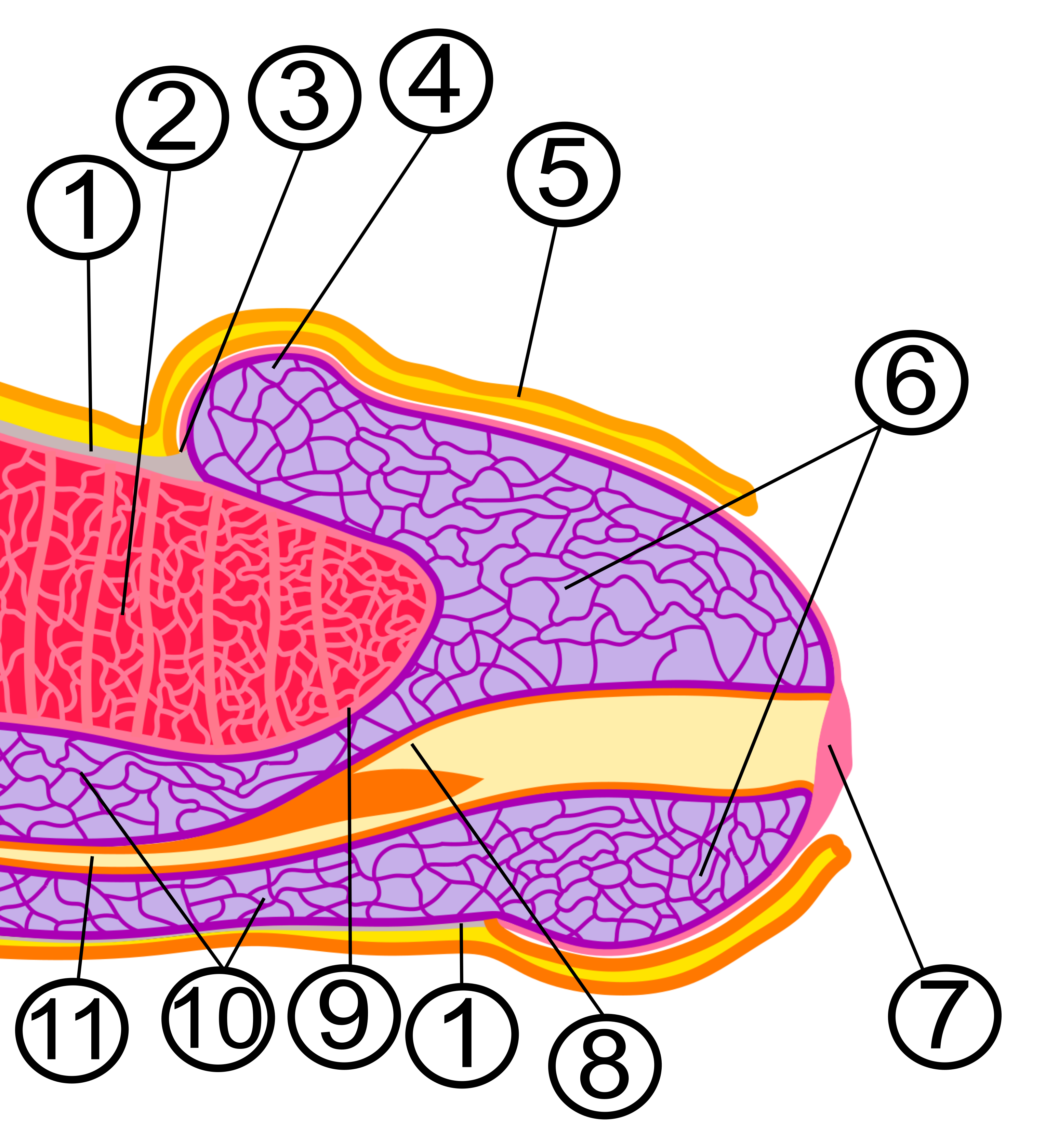
Preputial Orifice
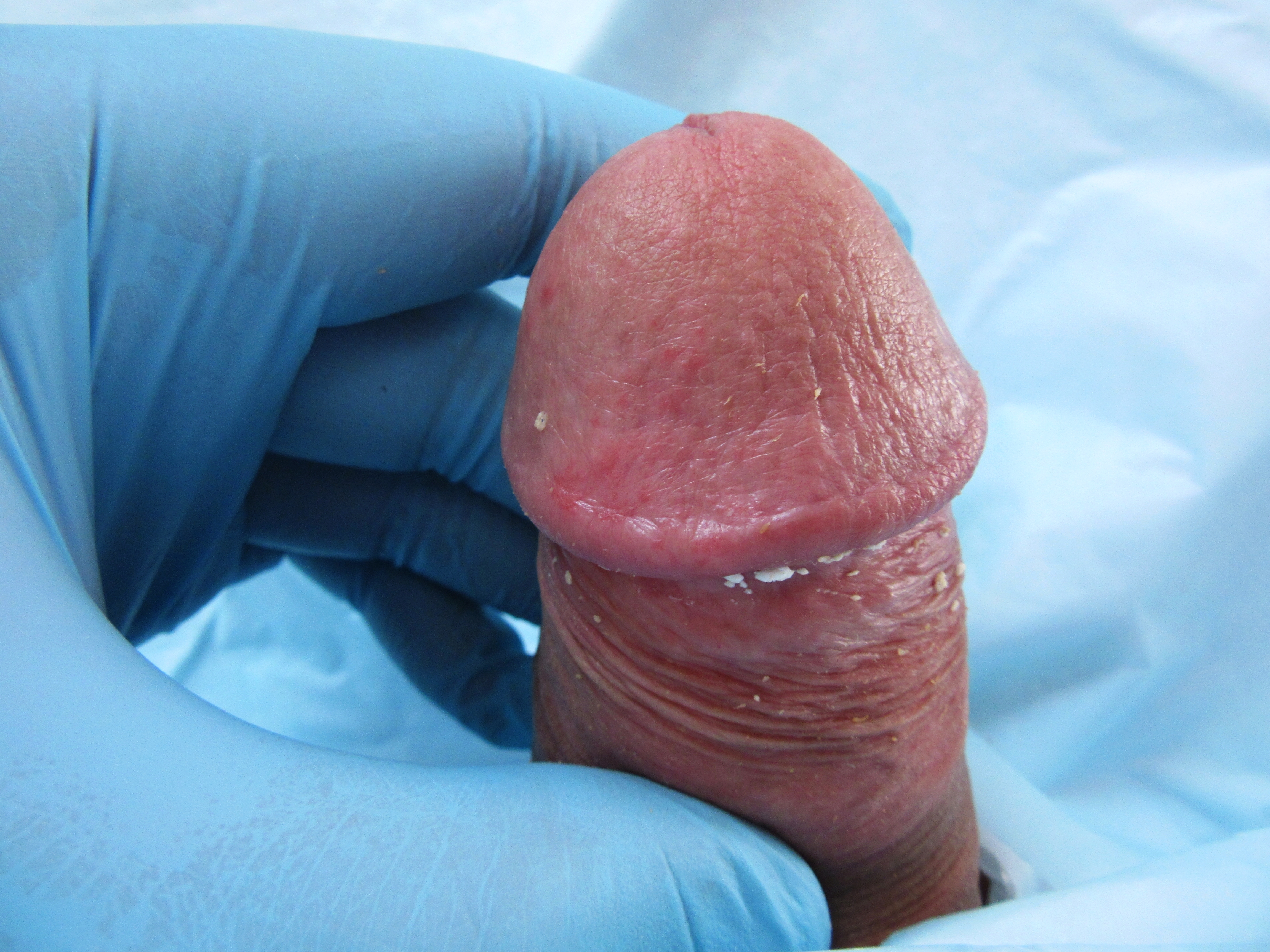
In male human anatomy, the foreskin, also known as the prepuce (), is the double-layered fold of skin, mucosal and muscular tissue at the distal end of the human penis that covers the glans and the urinary meatus. The foreskin is attached to the glans by an elastic band of tissue, known as the frenulum. The outer skin of the foreskin meets with the inner preputial mucosa at the area of the mucocutaneous junction. The foreskin is mobile, fairly stretchable and sustains the glans in a moist environment. Except for humans, a similar structure known as a penile sheath appears in the male sexual organs of all primates and the vast majority of mammals. In humans, foreskin length varies widely and coverage of the glans in a flaccid and erect state can also vary. The foreskin is fused to the glans at birth and is generally not retractable in infancy and early childhood. Inability to retract the foreskin in childhood should not be considered a problem unless there are other symptoms. Ret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glans Penis
In male human anatomy, the glans penis or penile glans, commonly referred to as the glans, (; from Latin ''glans'' meaning "acorn") is the bulbous structure at the Anatomical terms of location#Proximal and distal, distal end of the human penis that is the human male's most sensitive erogenous zone and primary anatomical source of Human sexuality, sexual pleasure. The glans penis is present in the male reproductive system, reproductive organs of humans and most other mammals where it may appear smooth, spiny, elongated or divided. It is externally lined with Mucosa, mucosal tissue, which creates a smooth texture and glossy appearance. In humans, the glans is located over the distal ends of the Corpus cavernosum penis, corpora cavernosa and is a continuation of the Corpus spongiosum (penis), corpus spongiosum of the penis. At the summit appears the urinary meatus and at the base forms the Corona of glans penis, corona glandis. An elastic band of tissue, known as the Penile frenulum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
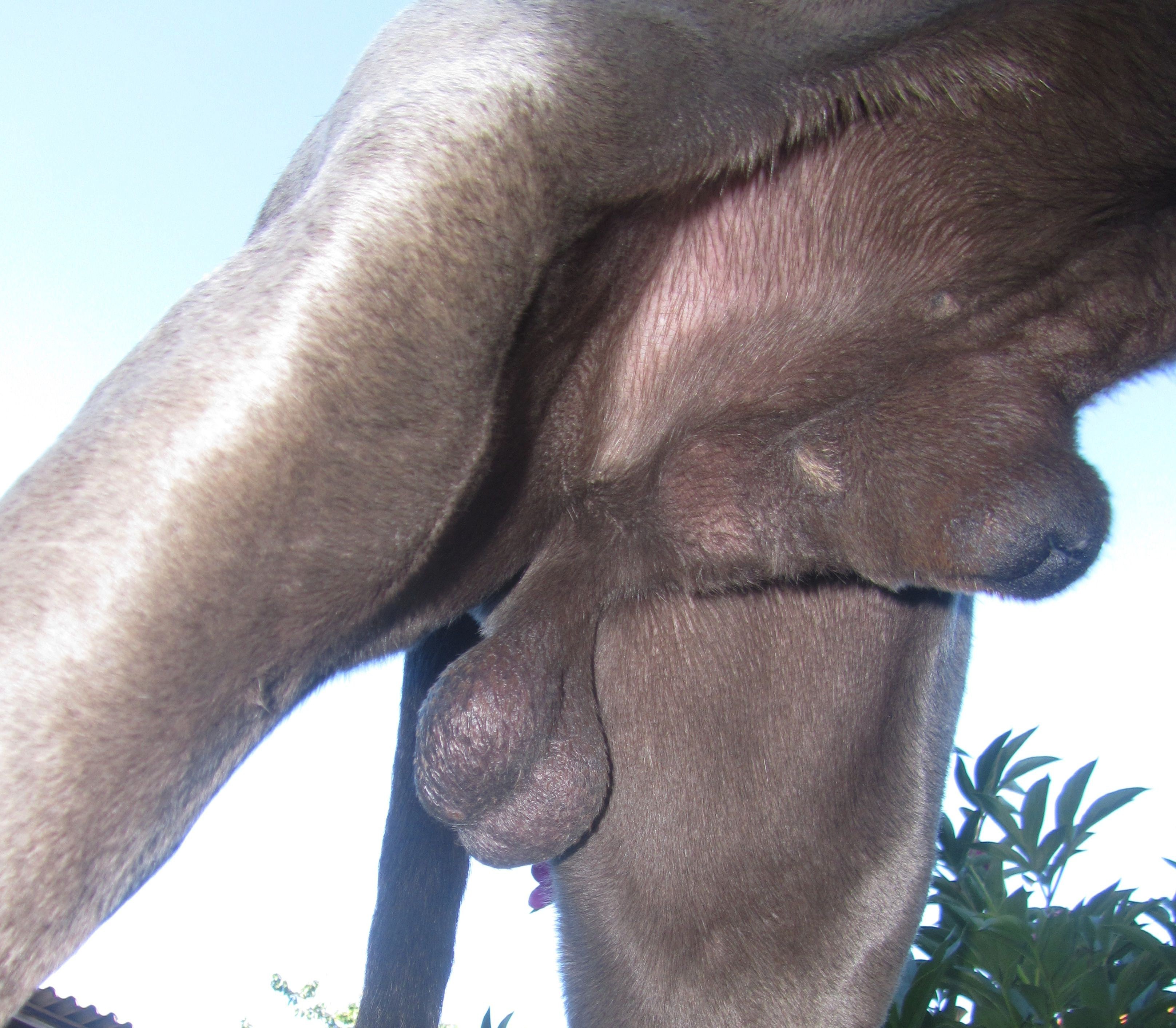
Penile Sheath
Almost all mammal penises have foreskins or prepuces. In non-human mammals, the prepuce is sometimes called the penile sheath or preputial sheath. In koalas, the foreskin contains naturally occurring bacteria that play an important role in fertilization. In some bat species, the prepuce contains an erectile tissue structure called the ''accessory corpus cavernosum''. During musth, a male elephant may urinate with the penis still in the sheath, which causes the urine to spray on the hind legs.Sukumar, pp. 100–08. Male dogs and wild dogs have a large and conspicuous penile sheath. In stallions, the retractor penis muscle contracts to retract the stallion's penis into the sheath and relaxes to allow the penis to extend from the sheath. The penile sheath of a male axis deer is elongated and urine-stained. When rubbing trees with their horns, these stags sometimes move the penis back and forth rapidly inside its sheath. Male bison and fallow deer Fallow deer is the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
A stratified squamous epithelium consists of squamous (flattened) epithelial cells arranged in layers upon a basal membrane. Only one layer is in contact with the basement membrane; the other layers adhere to one another to maintain structural integrity. Although this epithelium is referred to as squamous, many cells within the layers may not be flattened; this is due to the convention of naming epithelia according to the cell type at the surface. In the deeper layers, the cells may be columnar or cuboidal. There are no intercellular spaces. This type of epithelium is well suited to areas in the body subject to constant abrasion, as the thickest layers can be sequentially sloughed off and replaced before the basement membrane is exposed. It forms the outermost layer of the skin and the inner lining of the mouth, esophagus and vagina. In the epidermis of skin in mammals, reptiles, and birds, the layer of keratin in the outer layer of the stratified squamous epithelial surface is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. It is the key structural material making up Scale (anatomy), scales, hair, Nail (anatomy), nails, feathers, horn (anatomy), horns, claws, Hoof, hooves, and the outer layer of skin in vertebrates. Keratin also protects epithelial cells from damage or stress. Keratin is extremely insoluble in water and organic solvents. Keratin monomers assemble into bundles to form intermediate filaments, which are tough and form strong mineralization (biology), unmineralized epidermal appendages found in reptiles, birds, amphibians, and mammals. Excessive keratinization participate in fortification of certain tissues such as in horns of cattle and rhinos, and armadillos' osteoderm. The only other biology, biological matter known to approximate the toughness of keratinized tissue is chitin. Keratin comes in two types: the primitive, softer forms found in all vertebrates and the harder, derived forms fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Of Penis
The body or shaft of the penis is the free portion of the human penis that is located outside of the pelvic cavity. It is the continuation of the internal root, which is embedded in the pelvis and extends to the glans. It is made up of the two corpora cavernosa and the corpus spongiosum on the underside. The corpora cavernosa are intimately bound to one another with a dorsally fenestrated septum, which becomes a complete one before the penile crura. The body of the penis is homologous to the female clitoral body. Structure The body of the penis is suspended from the pubic symphysis. It has two surfaces; the ''dorsal'' and the ventral or ''urethral''. The penile raphe runs on its ventral surface. The body is surrounded by a bi-layered model of tunica albuginea in which a distal ligament buttresses the glans penis and plays an integral role to the penile fibroskeleton, and the structure is called "os analog", a term coined by Geng Long Hsu in the Encyclopedia of Reproduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
22-05-18 Retractability 5 Diagr EN
The symbol , known in Unicode as hyphen-minus, is the form of hyphen most commonly used in digital documents. On most keyboards, it is the only character that resembles a minus sign or a dash, so it is also used for these. The name ''hyphen-minus'' derives from the original ASCII standard, where it was called ''hyphen (minus)''. The character is referred to as a ''hyphen'', a ''minus sign'', or a ''dash'' according to the context where it is being used. Description In early typewriters and character encodings, a single key/code was almost always used for hyphen, minus, various dashes, and strikethrough, since they all have a similar appearance. The current Unicode Standard specifies distinct characters for several different dashes, an unambiguous minus sign (sometimes called the ''Unicode minus'') at code point U+2212, an unambiguous hyphen (sometimes called the ''Unicode hyphen'') at U+2010, the hyphen-minus at U+002D and a variety of other hyphen symbols for various uses. Wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posthitis
Posthitis is the inflammation of the foreskin (prepuce) of the penis. It is characterised by swelling and redness on the skin and it may be accompanied by a malodorous discharge. The term ''posthitis'' comes from the Greek "posthe", meaning foreskin, and "-itis", meaning inflammation. Causes Posthitis can have infectious causes such as bacteria or fungi, or non-infectious causes such as contact dermatitis or psoriasis. The inflammation may be caused by irritants in the environment. Common causative organisms include candida, chlamydia, and gonorrhea. The cause must be properly diagnosed before a treatment can be prescribed. A common risk factor is diabetes. Posthitis can lead to phimosis, the tightening of the foreskin which makes it difficult to retract over the glans. Posthitis can also lead to superficial ulcerations and diseases of the inguinal lymph nodes. Prevention Hygiene, in particular the regular cleaning of the glans, is generally considered sufficient to prevent in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balanitis
Balanitis is inflammation of the glans penis. Balanoposthitis is the proper term when the foreskin is also affected. Balanitis on boys in diapers must be distinguished from redness caused by ammoniacal dermatitis. Etymology The word ''balanitis'' is from the Greek βάλανος'' '', literally meaning 'acorn' because of the similarity in shape to the glans penis. ''-Itis'' is a suffix from the Greek for 'inflammation'. ''Posthe'' is the Greek word meaning 'foreskin'. Signs and symptoms * Small red erosions on the glans (first sign) * Redness of the foreskin * Redness of the penis * Other rashes on the head of the penis * Foul-smelling discharge * Painful foreskin and penis Complications Recurrent bouts of balanitis may cause scarring of the preputial orifice; the reduced elasticity may lead to pathologic phimosis. Further complications may include: * Stricture of urinary meatus * Paraphimosis Causes Inflammation has many possible causes, including irritation by environ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phimosis
Phimosis (from Greek language, Greek φίμωσις ''phimōsis'' 'muzzling') is a condition in which the foreskin of the Human penis, penis cannot stretch to allow it to be pulled back past the Glans penis, glans. A balloon-like swelling under the foreskin may occur with urination. In teenagers and adults, it may result in pain during an erection, but is otherwise not painful. Those affected are at greater risk of inflammation of the glans, known as balanitis, and other complications. In infancy, phimosis is considered physiological (normal). At birth, the foreskin is naturally adhered to the glans, and cannot be retracted. As the child ages, in most cases, the foreskin will naturally detach. In young boys, it is normal not to be able to pull back the foreskin at all. Over 90% of cases resolve by the age of seven, although full retraction is still prevented by balanopreputial adhesions in over half at this age. Occasionally, phimosis may be caused by an underlying condition s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clitoral Hood
In female humans and other mammals, the clitoral hood (also called preputium clitoridis, clitoral prepuce, and clitoral foreskin) is a fold of skin that surrounds and protects the glans of the clitoris; it also covers the external clitoral shaft, develops as part of the labia minora and is homologous with the foreskin (also called the ''prepuce'') in the male reproductive system. The clitoral hood is composed of mucocutaneous tissues; these tissues are between the mucous membrane and the skin, and they may have immunological importance because they may be a point of entry of mucosal vaccines. Development and variation The clitoral hood is formed during the fetal stage by the cellular lamella. The cellular lamella grows down on the dorsal side of the clitoris and is eventually fused with the clitoris. The clitoral hood varies in the size, shape, thickness, and other aesthetic aspects. Some women have large clitoral hoods that completely cover the clitoral glans. Some of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homology (biology)
In biology, homology is similarity in anatomical structures or genes between organisms of different taxa due to shared ancestry, ''regardless'' of current functional differences. Evolutionary biology explains homologous structures as retained heredity from a common descent, common ancestor after having been subjected to adaptation (biology), adaptive modifications for different purposes as the result of natural selection. The term was first applied to biology in a non-evolutionary context by the anatomist Richard Owen in 1843. Homology was later explained by Charles Darwin's theory of evolution in 1859, but had been observed before this from Aristotle's biology onwards, and it was explicitly analysed by Pierre Belon in 1555. A common example of homologous structures is the forelimbs of vertebrates, where the bat wing development, wings of bats and origin of avian flight, birds, the arms of primates, the front flipper (anatomy), flippers of whales, and the forelegs of quadrupedalis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |