|
Prenatal And Perinatal Psychology
Prenatal and perinatal psychology explores the psychological and psychophysiological effects and implications of the earliest experiences of the individual, before birth, prenatal, as well as during and immediately after childbirth, perinatal. Prenatal and perinatal psychology can be seen as a part of developmental psychology, although historically it was developed in the heterogenous field of psychoanalysis. Prenatal and perinatal psychology are often discussed together to group the period during pregnancy, childbirth, and through the early stages of infancy. The role of prenatal and perinatal psychology is to explain the experience and behavior of the individual before birth, postnatal consequences, and the lasting effects on development that occur during this time period. Although there are various perspectives on the topic, a common thread is the importance of prenatal and perinatal experiences in the shaping the future psychological development. There is a debate among scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychological
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feelings, and motivation, motives. Psychology is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between the Natural science, natural and social sciences. Biological psychologists seek an understanding of the Emergence, emergent properties of brains, linking the discipline to neuroscience. As social scientists, psychologists aim to understand the behavior of individuals and groups.Hockenbury & Hockenbury. Psychology. Worth Publishers, 2010. A professional practitioner or researcher involved in the discipline is called a psychologist. Some psychologists can also be classified as Behavioural sciences, behavioral or Cognitive science, cognitive scientists. Some psychologists attempt to understand the role of mental functions in i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nandor Fodor
Nandor Fodor (May 13, 1895 – May 17, 1964) was a British and American Parapsychology, parapsychologist, Psychoanalysis, psychoanalyst, author and journalist of Hungary, Hungarian origin. Biography Fodor was born in Beregszász, Austro-Hungarian Empire (now Berehove in Ukraine), to a Jewish family. He received a doctorate in law from the Royal Hungarian University of Science in Budapest. He moved to New York to work as a journalist and to Britain in 1929 where he worked for a newspaper company.Raymond Buckland, Buckland, Raymond. (2005). ''The Spirit Book: The Encyclopedia of Clairvoyance, Channeling, and Spirit Communication''. Visible Ink Press. p. 144. Fodor was one of the leading authorities on poltergeists, haunting and paranormal phenomena usually associated with mediumship. He was at one time Sigmund Freud's associate and wrote on subjects like prenatal development and dream interpretation, although he is mostly credited for his Masterpiece, magnum opus, ''Encyclopedia o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
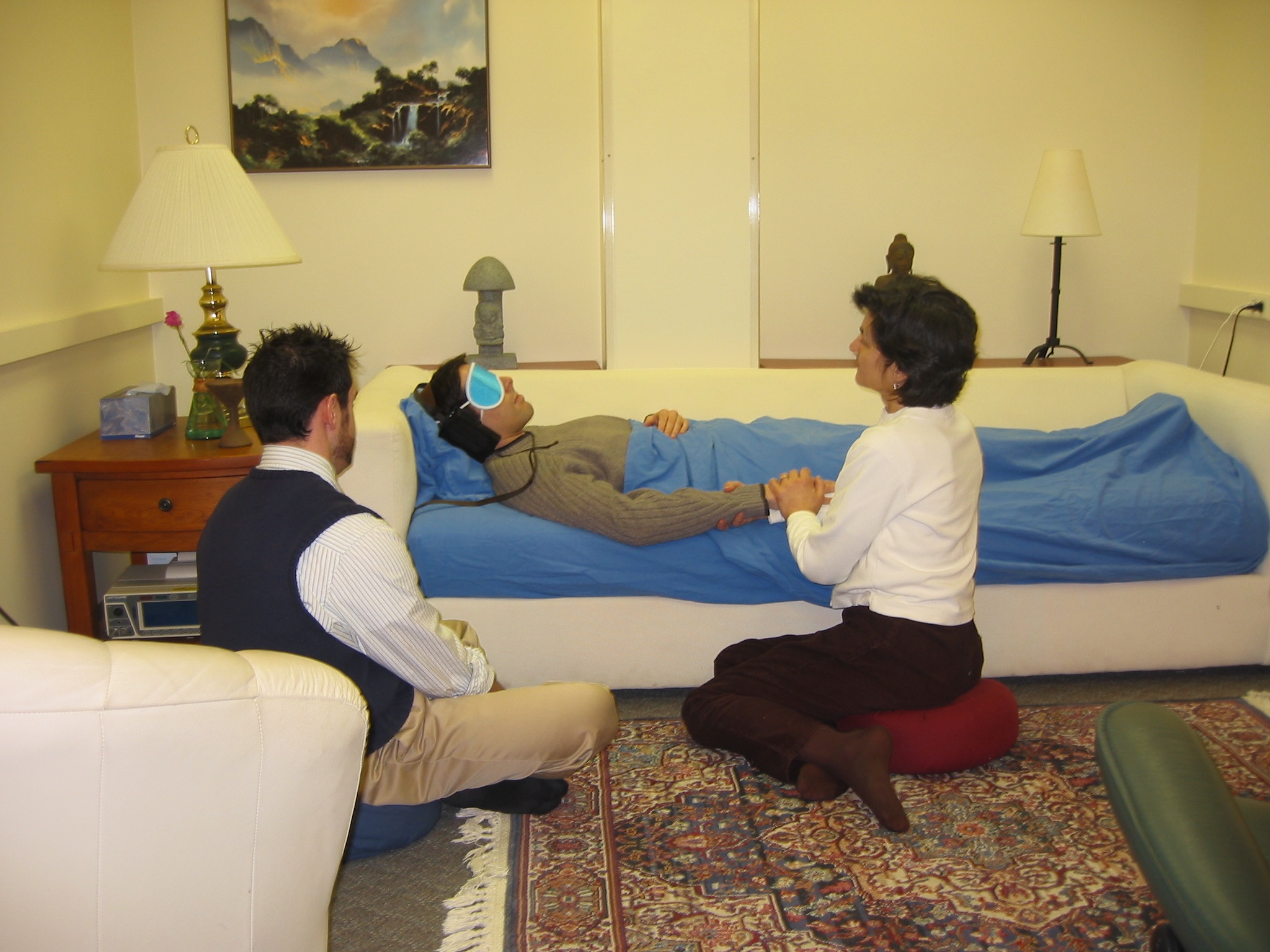
Psychedelic Psychotherapy
Psychedelic therapy (or psychedelic-assisted therapy) refers to the proposed use of psychedelic drugs, such as psilocybin, ayahuasca, LSD, psilocin, mescaline (peyote), DMT, 5-MeO-DMT, Ibogaine, MDMA, to treat mental disorders. As of 2021, psychedelic drugs are controlled substances in most countries and psychedelic therapy is not legally available outside clinical trials, with some exceptions. The procedure for psychedelic therapy differs from that of therapies using conventional psychiatric medications. While conventional medications are usually taken without supervision at least once daily, in contemporary psychedelic therapy the drug is administered in a single session (or sometimes up to three sessions) in a therapeutic context. The therapeutic team prepares the patient for the experience beforehand and helps them integrate insights from the drug experience afterwards. After ingesting the drug, the patient normally wears eyeshades and listens to music to facilitate fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placenta
The placenta (: placentas or placentae) is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between the physically separate maternal and fetal circulations, and is an important endocrine organ, producing hormones that regulate both maternal and fetal physiology during pregnancy. The placenta connects to the fetus via the umbilical cord, and on the opposite aspect to the maternal uterus in a species-dependent manner. In humans, a thin layer of maternal decidual ( endometrial) tissue comes away with the placenta when it is expelled from the uterus following birth (sometimes incorrectly referred to as the 'maternal part' of the placenta). Placentas are a defining characteristic of placental mammals, but are also found in marsupials and some non-mammals with varying levels of development. Mammalian placentas probably first evolved abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroses
Neurosis (: neuroses) is a term mainly used today by followers of Freudian thinking to describe mental disorders caused by past anxiety, often that has been repressed. In recent history, the term has been used to refer to anxiety-related conditions more generally. The term "neurosis" is no longer used in condition names or categories by the World Health Organization's ''International Classification of Diseases'' (ICD) or the American Psychiatric Association's ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM). According to the ''American Heritage Medical Dictionary'' of 2007, the term is "no longer used in psychiatric diagnosis". Neurosis is distinguished from ''psychosis'', which refers to a loss of touch with reality. Its descendant term, ''neuroticism'', refers to a personality trait of being prone to anxiousness and mental collapse. The term "neuroticism" is also no longer used for DSM or ICD conditions; however, it is a common name for one of the Big Five p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Trauma Of Birth
''The Trauma of Birth'' () is a 1924 book by the psychoanalyst Otto Rank. It was first published in English translation in 1929. Especially with its focus on the connection between microcosm and macrocosm, it foreshadows Rank's most popular book, ''Art and Artist,'' published in 1932 and considered a masterpiece by scholars of art history. Sigmund Freud, the founder of psychoanalysis, reacted both favorably and critically to ''The Trauma of Birth'', responding to Rank's ideas in his own work. Summary Rank aims to apply psychoanalysis to "the comprehension of the whole development of mankind, even of the actual fact of becoming human.". The chief purpose of the work, according to Rank, is elaboration of how the form of the womb expresses the protective forms of art, myth, religion, philosophy and culture. Publication history ''The Trauma of Birth'' was first published in 1924. The book was published in English by Kegan Paul, Trench, Trubner and Co., Ltd. in 1929. The book was repu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigmund Freud
Sigmund Freud ( ; ; born Sigismund Schlomo Freud; 6 May 1856 – 23 September 1939) was an Austrian neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis, a clinical method for evaluating and treating psychopathology, pathologies seen as originating from conflicts in the Psyche (psychology), psyche, through dialogue between patient and psychoanalyst, and the distinctive theory of mind and human agency derived from it. Freud was born to Galician Jews, Galician Jewish parents in the Moravian town of Příbor, Freiberg, in the Austrian Empire. He qualified as a doctor of medicine in 1881 at the University of Vienna. Upon completing his habilitation in 1885, he was appointed a docent in neuropathology and became an affiliated professor in 1902. Freud lived and worked in Vienna having set up his clinical practice there in 1886. Following the Anschluss, German annexation of Austria in March 1938, Freud left Austria to escape Nazi persecution. He died in exile in the United Kingdom in 1939. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Françoise Dolto
Françoise Dolto (; November 6, 1908 – August 25, 1988) was a French pediatrician and psychoanalyst. Biography Françoise Dolto was born as Françoise Marette, into an affluent, devoutly Catholic, royalist and Maurrassian family in Paris. Her Alsatian mother, Suzanne Demmler, was the daughter of an engineer, and Henri Marette, her father, was also a '' polytechnicien'' engineer who became an industrialist. She was the fourth child of a family of seven. Her brother Jacques Marette (1922–1984), was French Postmaster (minister of Posts and Telecommunications) from 1962 to 1967. An Irish nurse frequently took care of her when she was a baby and developed a close bond with her, to the point that her parents then had to learn to speak English to get her to smile. Her parents fired the nurse when she was 8 months old, for a grave mistake: in order to finance her addiction to opium, which was popular in '' Belle époque'' Paris, she would prostitute herself at an establishment whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bela Grunberger
Bela may refer to: Places Asia *Bela Pratapgarh, a town in Pratapgarh District, Uttar Pradesh, India *Bela, a small village near Bhandara, Maharashtra, India *Bela, another name for the biblical city Zoara * Bela, Dang, in Nepal * Bela, Janakpur, in Nepal * Bela, Pakistan, a town in Balochistan, Pakistan Europe * Bela, Vidin Province, a village in Bulgaria * Bela, Varaždin County, a village in Croatia *Bělá (other), places in the Czech Republic * River Bela, in Cumbria, England * Bela (Epirus), a medieval fortress and bishopric in Epirus, Greece *Bela, a village administered by Pucioasa town, Dâmboviţa County, Romania *Belá (other), places in Slovakia * Bela, Ajdovščina, Slovenia * Bela, Kamnik, Slovenia People *Béla (given name), Hungarian name * Béla of Hungary (other), any of five kings of Hungary to bear that name * Bela (or Belah), the name of three Biblical figures, including ** Bela ben Beor, king of Edom * Bela of Saint Omer (died ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanie Klein
Melanie Klein (; ; Reizes; 30 March 1882 – 22 September 1960) was an Austrian-British author and psychoanalysis, psychoanalyst known for her work in child analysis. She was the primary figure in the development of object relations theory. Klein's work primarily focused on the role of ambivalence and moral ambiguity in human development. Klein suggested that pre-verbal existentialism, existential anxiety in infancy catalyzed the formation of the unconscious, which resulted in the unconscious splitting of the world into good and bad fantasy (psychology), idealizations. In her theory, how the child resolves that split depends on the constitution of the child and the character of nurturing the child experiences. The quality of resolution can inform the presence, absence, and/or type of distresses a person experiences later in life. Life Melanie Klein was born into a History of the Jews in Austria, Jewish family and spent most of her early life in Vienna, Austria, Vienna. She was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Gustav Jung
Carl Gustav Jung ( ; ; 26 July 1875 – 6 June 1961) was a Swiss psychiatrist, psychotherapist, and psychologist who founded the school of analytical psychology. A prolific author of over 20 books, illustrator, and correspondent, Jung was a complex and convoluted academic, best known for his concept of archetypes. Alongside contemporaries Freud and Adler, Jung became one of the most influential psychologists of the early 20th century and has fostered not only scholarship, but also popular interest. Jung's work has been influential in the fields of psychiatry, anthropology, archaeology, literature, philosophy, psychology, and religious studies. He worked as a research scientist at the Burghölzli psychiatric hospital in Zurich, under Eugen Bleuler. Jung established himself as an influential mind, developing a friendship with Sigmund Freud, founder of psychoanalysis, conducting a lengthy correspondence paramount to their joint vision of human psychology. Jung is widely re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |