|
Precycling
Precycling is the practice of reducing waste by attempting to avoid buying items which will generate waste into home or business. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also cites that precycling is the preferred method of integrated solid waste management because it cuts waste at its source and therefore trash is eliminated before it is created. According to the EPA, precycling is also characterized as a decision-making process on the behalf of the consumer because it involves making informed judgments regarding a product's waste implications. The implications that are taken into consideration by the consumer include: whether a product is reusable, durable, or repairable; made from renewable or non-renewable resources; over-packaged; and whether or not the container is reusable. About Precycling has the ability to build industrial, social, environmental, and economic circumstances that allow for old products to be converted into new resources *Industrial: increasing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zero Waste
Zero waste, or ''waste minimization'', is a set of principles focused on waste prevention that encourages redesigning resource life cycles so that all products are repurposed (i.e. "up-cycled") and/or reused. The goal of the movement is to avoid sending trash to landfills, incinerators, oceans, or any other part of the environment. Currently 9% of global plastic is recycled. In a zero waste system, all materials are reused until the optimum level of consumption is reached. Zero waste refers to waste prevention as opposed to end-of-pipe waste management. It is a "whole systems" approach that aims for a massive change in the way materials flow through society, resulting in no waste. Zero waste encompasses more than eliminating waste through reducing, reusing, and recycling. It focuses on restructuring distribution and production systems to reduce waste. Zero waste provides guidelines for continually working towards eliminating waste. According to the ''Zero Waste International ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waste Reduction
Waste minimisation is a set of processes and practices intended to reduce the amount of waste produced. By reducing or eliminating the generation of harmful and persistent wastes, waste minimisation supports efforts to promote a more sustainable society.. Waste minimisation involves redesigning products and processes and/or changing societal patterns of consumption and production. The most environmentally resourceful, economically efficient, and cost effective way to manage waste often is to not have to address the problem in the first place. Managers see waste minimisation as a primary focus for most waste management strategies. Proper waste treatment and disposal can require a significant amount of time and resources; therefore, the benefits of waste minimisation can be considerable if carried out in an effective, safe and sustainable manner. Traditional waste management focuses on processing waste after it is created, concentrating on re-use, recycling, and waste-to-en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resource Depletion
Resource depletion occurs when a natural resource is consumed faster than it can be replenished. The value of a resource depends on its availability in nature and the cost of extracting it. By the law of supply and demand, the Scarcity, scarcer the resource the more valuable it becomes. There are several types of resource depletion, including but not limited to: wetland and ecosystem degradation, soil erosion, aquifer depletion, and overfishing. The depletion of wildlife populations is called ''defaunation''. It is a matter of research and debate how humanity will be impacted and what the future will look like if resource consumption continues at the current rate, and when specific resources will be completely exhausted. History of resource depletion The depletion of resources has been an issue since the beginning of the 19th century amidst the Industrial Revolution, First Industrial Revolution. The extraction of both renewable and non-renewable resources increased drasticall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastic-coated Carton
Coated paper (also known as enamel paper, gloss paper, and thin paper) is paper that has been coated with a mixture of materials or a polymer to impart certain qualities to the paper, including weight, surface gloss, smoothness, or reduced ink absorbency. Various materials, including kaolinite, calcium carbonate, bentonite, and talc, can be used to coat paper for high-quality printing, such as that used in the packaging industry and in magazines. The chalk or china clay is bound to the paper with synthetic s, such as styrene-butadiene latexes and natural organic binders such as starch. The coating formulation may also contain chemical additives as dispersants, resins, or polyethylene to give water resistance and wet strength to the paper, or to protect against ultraviolet radiation. Coated papers have been traditionally used for printing magazines. Varieties Machine-finished coated paper ''Machine-finished coated paper'' (MFC) has a basis weight of 48–80 g/m2. They ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
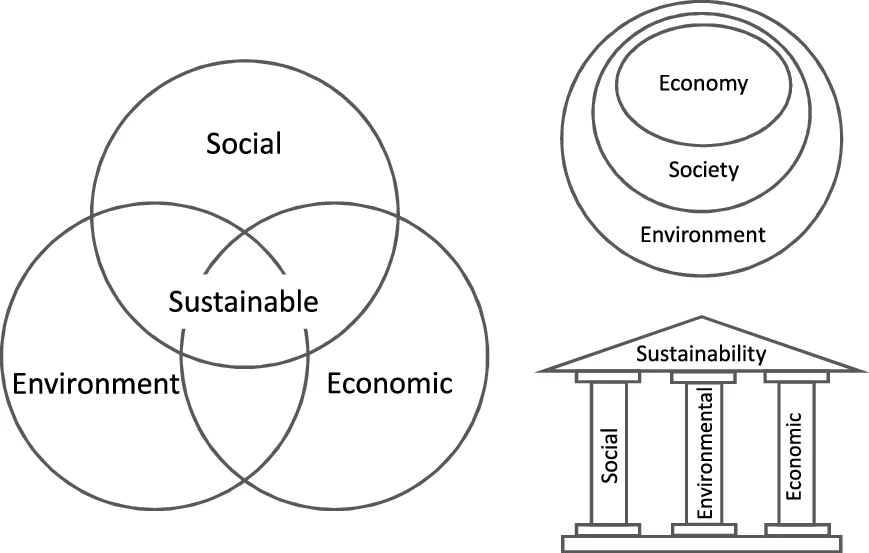
Sustainable Production
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long period of time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Sustainability usually has three dimensions (or pillars): environmental, economic, and social. Many definitions emphasize the environmental dimension. This can include addressing key environmental problems, including climate change and biodiversity loss. The idea of sustainability can guide decisions at the global, national, organizational, and individual levels. A related concept is that of sustainable development, and the terms are often used to mean the same thing. UNESCO distinguishes the two like this: "''Sustainability'' is often thought of as a long-term goal (i.e. a more sustainable world), while ''sustainable development'' refers to the many processes and pathways to achieve it." Details around the economic dimension of sustainability are controversial. Scholars have discussed this under t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Awareness
In public relations and communication science, publics are groups of individual people, and the public (a.k.a. the general public) is the totality of such groupings. This is a different concept to the sociological concept of the ''Öffentlichkeit'' or public sphere. The concept of a public has also been defined in political science, psychology, marketing, and advertising. In public relations and communication science, it is one of the more ambiguous concepts in the field. Although it has definitions in the theory of the field that have been formulated from the early 20th century onwards, and suffered more recent years from being blurred, as a result of conflation of the idea of a public with the notions of audience, market segment, community, constituency, and stakeholder. Etymology and definitions The name "public" originates with the Latin '' publicus'' (also '' poplicus''), from ''populus'', to the English word ' populace', and in general denotes some mass population ("the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biodegradability
Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. It is generally assumed to be a natural process, which differentiates it from composting. Composting is a human-driven process in which biodegradation occurs under a specific set of circumstances. The process of biodegradation is threefold: first an object undergoes biodeterioration, which is the mechanical weakening of its structure; then follows biofragmentation, which is the breakdown of materials by microorganisms; and finally assimilation, which is the incorporation of the old material into new cells. In practice, almost all chemical compounds and materials are subject to biodegradation, the key element being time. Things like vegetables may degrade within days, while glass and some plastics take many millennia to decompose. A standard for biodegradability used by the European Union is that greater than 90% of the original material must be converted into , water and minerals b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Growth
In economics, economic growth is an increase in the quantity and quality of the economic goods and Service (economics), services that a society Production (economics), produces. It can be measured as the increase in the inflation-adjusted Output (economics), output of an economy in a given year or over a period of time. The rate of growth is typically calculated as List of countries by real GDP growth rate, real gross domestic product (GDP) growth rate, List of countries by real GDP per capita growth, real GDP per capita growth rate or List of countries by GNI per capita growth, GNI per capita growth. The "rate" of economic growth refers to the Exponential growth, geometric annual rate of growth in GDP or GDP per capita between the first and the last year over a period of time. This growth rate represents the trend in the average level of GDP over the period, and ignores any fluctuations in the GDP around this trend. Growth is usually calculated in "real" value, which is real v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embodied Energy
Embodied energy is the sum of all the energy required to produce any goods or services, considered as if that energy were incorporated or 'embodied' in the product itself. The concept can help determine the effectiveness of energy-producing or energy saving devices, or the "real" replacement cost of a building, and, because energy-inputs usually entail greenhouse gas emissions, in deciding whether a product contributes to or mitigates global warming. One fundamental purpose for measuring this quantity is to compare the amount of energy produced or saved by the product in question to the amount of energy consumed in producing it. Embodied energy is an accounting method that aims to find the sum total of the energy necessary for an entire product lifecycle. Determining what constitutes this lifecycle includes assessing the relevance and extent of energy in raw material extraction, transport, manufacture, assembly, installation, disassembly, deconstruction and/or decomposition, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Downcycling
Downcycling, or cascading, is the recycling of waste where the recycled material is of lower quality and functionality than the original material. Often, this is due to the accumulation of tramp elements in secondary metals, which may exclude the latter from high-quality applications. For example, steel scrap metal, scrap from end-of-life vehicles is often contaminated with copper from wires and tin from coating. This contaminated scrap yields a secondary steel that does not meet the specifications for automotive steel and therefore, it is mostly applied in the construction sector. Origin and effect Downcycling can help to keep materials in use, reduce consumption of raw materials, and avoid the energy usage, greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, and water pollution of primary production and resource extraction. The first documented use of the term ''downcycling'' was by Reiner Pilz in an interview by Thornton Kay in SalvoNEWS in 1994. We talked about the impending EU De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recycling
Recycling is the process of converting waste materials into new materials and objects. This concept often includes the recovery of energy from waste materials. The recyclability of a material depends on its ability to reacquire the properties it had in its original state. It is an alternative to "conventional" waste disposal that can save material and help lower greenhouse gas emissions. It can also prevent the waste of potentially useful materials and reduce the consumption of fresh raw materials, reducing energy use, air pollution (from incineration) and water pollution (from landfilling). Recycling is a key component of modern waste reduction and represents the third step in the "Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle" waste hierarchy, contributing to environmental sustainability and resource conservation. It promotes environmental sustainability by removing raw material input and redirecting waste output in the economic system. There are some ISO standards related to recycling, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |